lesson12
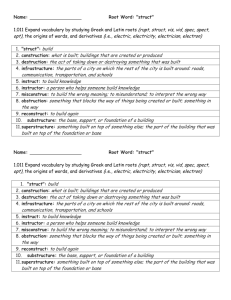
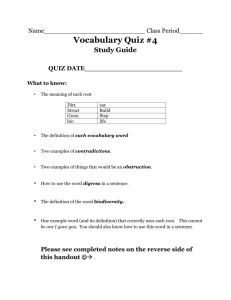
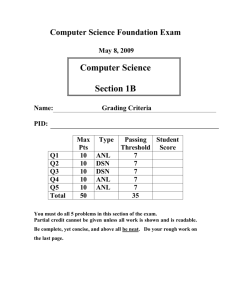
advertisement

Linux Memory Issues
An introduction to some low-level
and some high-level memory
management concepts
Some Architecture History
•
•
•
•
•
•
8080 (late-1970s) 16-bit address (64-KB)
8086 (early-1980s) 20-bit address (1-MB)
80286 (mid-’80s) 24-bit address (16-MB)
80386 (late-’80s) 32-bit address (4-GB)
80686 (late-’90s) 36-bit address (64-GB)
Core2 (mid-2000s) 40-bit address (1-TB)
‘Backward Compatibility’
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Many buyers resist ‘early obsolescence’
New processors need to run old programs
Early design-decisions leave their legacy
8086 could run recompiled 8080 programs
80x86 can still run most 8086 applications
Win95/98 could run most MS-DOS apps
But a few areas of incompatibility existed
Linux must accommodate legacy
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Legacy elements: hardware and firmware
CPU: reset-address and interrupt vectors
ROM-BIOS: data area and boot location
Display Controllers: VRAM & video BIOS
Support chipsets: 15MB ‘Memory Window’
DMA: 24-bit memory-address bus
SMP: combined Local and I/O APICs
Other CPU Architectures
• Besides IA-32, Linux runs on other CPUs
(e.g., PowerPC, MC68000, IBM360, Sparc)
• So must accommodate their differences
– Memory-Mapped I/O
– Wider address-buses
– Non-Uniform Memory Access (NUMA)
Nodes, Zones, and Pages
•
•
•
•
•
Nodes: to accommodate NUMA systems
However 80x86 doesn’t support NUMA
So on 80x86 Linux uses just one ‘node’
Zones: to accommodate distinct regions
Three ‘zones’ on 80x86:
– ZONE_DMA
– ZONE_NORMAL
– ZONE_HIGHMEM
(memory below 16-MB)
(from 16-MB to 896-MB)
(memory above 896-MB)
Zones divided into Pages
•
•
•
•
80x86 supports 4-KB page-frames
Linux uses an array of ‘page descriptors’
Array of page descriptors: ‘mem_map[]’
physical memory is ‘mapped’ by CPU
How 80x86 Addresses RAM
• Two-stages: ‘segmentation’ plus ‘paging’:
– First: logical address linear address
– Then: linear address physical address
• CPU employs special caches:
– Segment-registers contain ‘hidden’ fields
– Paging uses ‘Translation Lookaside Buffer’
Logical to Linear
segment-register
virtual address-space
operand-offset
selector
global descriptor table
descriptor
GDTR
base-address
and segment-limit
memory
segment
Segment Descriptor Format
31
0
Base[ 31..24 ]
Base[ 15..0 ]
Limit
[19..16 ]
Base[ 23..16 ]
Limit[ 15..0 ]
Linear to Physical
linear address
dir-index
table-index
offset
physical address-space
page
table
page
directory
CR3
page frame
CR3 and CR4
• Register CR3 holds the physical address
of the current task’s page-directory table
• Register CR4 was added in the 80486 so
software would have the option of “turning
on” certain advanced new CPU features,
yet older software still could execute (by
just leaving the new features “turned off”)
Example: Page-Size Extensions
• 80586 can map either 4KB or 4MB pages
• With 4MB pages: middle table is omitted
• Entire 4GB address-space is subdivided
into 1024 4MB-pages
Demo-module: ‘cr3.c’ creates a pseudo-file
showing the values in CR3 and in CR4
Linear to Physical
linear address
dir-index
offset
physical address-space
page
directory
page frame
CR3
4-MB page-frames
PageTable Entry Format
31
12 11
Frame Address
0
Frame attributes
Some Frame Attributes:
P : (present=1, not-present=0)
R/W : (writable=1, readonly=0)
U/S : (user=1, supervisor=0)
D : (dirty=1, clean=0)
A : (accessed=1, not-accessed=0)
S : (size 4MB = 1, size 4KB = 0)
Visualizing Memory
• Our ‘pgdir.c’ module creates a pseudo-file
that lets users see a visual depiction of the
CPU’s current ‘map’ of ‘virtual memory’
• Virtual address-space (4-GB)
– subdivided into 4MB pages (1024 pels)
– Text characters: 16 rows by 64 columns
Virtual Memory Visualization
•
•
•
•
•
Shows which addresses are ‘mapped’
Display granularity is 4MB
Data is gotten from task’s page-directory
Page-Directory location is in register CR3
Legend:
‘-’ = frame not mapped
‘3’ = r/w by supervisor
‘7’ = r/w by user
Assigning memory to tasks
• Each Linux process has a ‘process descriptor’
with a pointer inside it named ‘mm’:
struct task_struct {
pid_t
pid;
char
comm[16];
struct mm_struct
*mm;
/* plus many additional fields */
};
struct mm_struct
•
•
•
•
•
•
It describes the task’s ‘memory map’
Where’s the code, the data, the stack?
Where are the ‘shared libraries’?
What are attributes of each memory area?
How many distinct memory areas?
Where is the task’s ‘page directory’?
Demo: ‘mm.c’
• It creates a pseudo-file: ‘/proc/mm’
• Allows users to see values stored in some
of the ‘mm_struct’ object’s important fields
Virtual Memory Areas
• Inside ‘mm_struct’ is a pointer to a list
• Name of this pointer is ‘mmap’
struct mm_struct {
struct vm_area_struct
/* plus many other fields */
*mmap;
};
Linked List of VMAs
• Each ‘vm_area_struct’ points to another
struct vm_area_struct {
unsigned long
vm_start;
unsigned long
vm_end;
unsigned long
vm_flags;
struct vm_area_struct *vm_next;
/* plus some other fields */
};
Structure relationships
The ‘process descriptor’ for a task
Task’s mm structure
task_struct
mm_struct
*mmap
VMA
*mm
VMA
VMA
VMA
VMA
Linked list of ‘vm_area_struct’ structures
Demo ‘vma.c’ module
• It creates a pseudo-file: /proc/vma
• Lets user see the list of VMAs for a task
• Also shows the ‘pgd’ field in ‘mm_struct’
EXERCISE
• Compare our demo to ‘/proc/self/maps’
In-class exercise #2
• Try running our ‘domalloc.cpp’ demo
• It lets you see how a call to the ‘malloc()’
function would affect an application list of
‘vm_area_struct’ objects
• NOTE: You have to install our ‘vma.ko’
kernel-object before running ‘domalloc’