Optimizing Antibiotic Use in 2015
advertisement

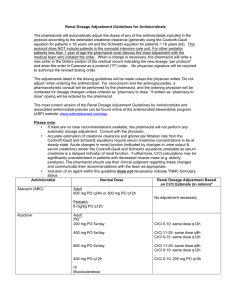
Optimizing Antibiotic Use in 2015 Jamie McCarrell, Pharm.D., BCPS, CGP Assistant Professor, TTUHSC SOP/SOM Objectives • Review new antibiotics approved for use by the FDA for various bacterial infections. • Identify current trends in resistance for common multi-drug resistant bacteria. • Develop strategies for appropriately dosing antibiotics in patients with varying degrees of renal dysfunction. • Outline major points from several landmark guidelines for acute bacterial syndromes. • Given a patient case, optimize antibiotic pharmacotherapy to adequately treat the bacterial infection while minimizing adverse effects. 2014-2015 NEW ANTIBIOTICS Zerbaxa® • Ceftolozane/tazobactam • 5th generation cephalosporin • Indications: Intra-abdominal infections, complicated UTIs • Key features: – ~$100/gram (dosed 1.5 gm Q8h for 4-14 days) – Covers Pseudomonas aeruginosa – Must use with Flagyl for intra-abdominal infections – Crosses placenta, but Category B Orbactiv® • Oritavancin • Lipoglycopeptide (inhibits cross-linking of cell wall membrane) • Indications: ABSSSI due to Gram (+) including MRSA (but not VRE) • Key Features: – Single dose therapy (t1/2 = 245 hours!) – Cost = $3480 for single dose Dalvance® • Dalbavancin • Lipoglycopeptide (inhibits cross-linking of cell wall membrane) • Indications: ABSSSI due to Gram (+) infections including MRSA • Key Features: – One dose with one follow-up dose 7 days later – Cost: Initial dose = $3576, FU dose = $1788 Sivextro® • Tedizolid • Oxazolidinone • Indications: ABSSI due to Gram (+) infections including MRSA • Key features: – Price = $2124 (oral), $2820 (IV) for 6 days – May be useful in linezolid-resistant infections Kerydin® • • • • Tavaborole Oxaborole antifungal (inhibits tRNA synthesis) Indications: onychomycosis Key Features – Duration of therapy: 48 weeks (daily) – Cost/bottle = $589, which lasts 3 weeks – Cost/treatment = $9,424 – Chance of cure = 6.5 – 9.1% Jublia® • Efinaconazole • Azole antifungal, inhibits fungal cell membrane synthesis • Indications: Onychomycosis • Key features: – Duration of therapy: 48 weeks (daily) – Cost/bottle = $539, which lasts 3 weeks – Cost/treatment = $8,624 – Chance of cure = 15 – 17% Xtoro® • • • • Finafloxacin otic solution Fluoroquinolone Indications: Swimmer’s ear Key features – Covers Staph aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa – Approved 12/2014 – Cost info not yet available TRENDS IN RESISTANCE Vancomycin • MIC “Creep” occurring nationally • Occurs in MSSA and MRSA • Higher MICs associated with higher rates of Tx failure and mortality • VRSA – multiple cases on multiple continents The “D-Test” • “Erm” gene • Induced by ERY • Causes clinda resistance http://microblog.me.uk/wp-content/uploads/TheDtest.jpg Carbapenemases • Class A – Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC) • Class B – Metallo-β-Lactamases (MBL) • Class D – OXA – 48 type UNASYN AMIKACIN AMPICILLIN AUGMENTIN AZACTAM ROCEPHIN FORTAZ CLAFORAN ANCEF ZINACEF GENTAMICIN ZOSYN BACTRIM TETRACYCLINE TIMENTIN TOBRAMYCIN 5 40 100 0 20 60 80 80 100 20 60 80 100 100 60 80 80 67 80 Enterobacter aerogenes 7 43 86 0 29 57 71 71 71 14 57 86 86 86 86 86 57 60 86 Enterobacter cloacae 19 37 89 0 11 47 74 68 79 5 26 89 100 84 84 95 74 57 89 Escherichia coli 102 44 99 35 81 79 84 84 86 76 80 83 100 68 94 70 62 90 81 Klebsiella oxytoca 8 62 100 0 75 62 62 75 62 50 75 88 100 88 100 88 88 75 100 Klebsiella pneumoniae 27 93 100 0 100 81 93 93 93 81 89 100 100 100 100 96 89 100 100 Pseudomonas aeruginosa 38 53 24 74 11 Proteus mirabilis 23 Stenotrophomonas maltophilia 5 Serratia marcesens 5 Shigella sonnei 0 Salmonella 1 84 78 100 74 100 100 100 100 100 87 100 20 0 100 100 0 0 100 100 The shaded areas represent a 10% or greater decrease in sensitivity. 100 100 100 100 0 100 100 100 LEVAQUIN # of isolates Citrobacter freundii PRIMAXIN Systemic Gram Negative HOUSEWIDE 76 89 61 84 65 100 61 100 60 0 0 61 0 100 100 100 100 100 100 71 79 100 70 25 40 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 80 UTI- Adult Women • Uncomplicated Cystitis – Nitrofurantoin 100 mg PO BID x 5 days – Bactrim DS, 1 tab PO BID X 3 days – FQN • 3 day regimens • Side effects, resistance issues reserve – Beta-lactams • 3-7 day regimens, only when recommended agents can’t be used • Amoxicillin or ampicillin NOT recommended for empiric therapy UTI – Geriatric Women • Nitrofurantoin issues – Beers criteria – CrCl cutoff (later slide) • Bactrim issues – New study…sudden death risk? – Hyperkalemia – Risk of INR fluctuations UTI – Geriatric Women • Levofloxacin issues – – – – – Renal dose adjustments (later slide) QTc prolongation Mental status changes Tendon rupture Drug interactions • Difficult to make a good choice…must consider all aspects of the patient before deciding on empiric therapy in the elderly! More Isn’t Always Better RENAL ADJUSTMENT OF ANTIBIOTICS Levaquin® Desired Dose CrCl > 50 ml/min CrCl 20 – 49 ml/min CrCl 10 – 19 ml/min 750 mg daily 750 mg daily 750 mg Q48 hrs 750 mg x1, then 500 mg Q48 hrs 500 mg daily 500 mg daily 250 mg daily 250 mg daily 500 mg x1, then 250 500 mg x1, then 250 mg Q24 hrs mg Q48 hrs 250 mg daily CrCl vs MDRD 250 mg Q48 hrs Vancomycin • Loading dose of 25 – 30 mg/kg • Maintenance: 15 – 20 mg/kg/dose every 8-12 hours (adjusted to desired trough) – Note: MIC = 1 mcg/ml requires trough of 15 • Renal dysfunction: – CrCl > 50: No adjustment – CrCl 20 – 49: increase interval to Q24h – CrCl < 20: Pharmacokinetic modeling • Oral administration: No adjustments Nitrofurantoin • CrCl > 60 ml/min is required to get adequate concentration – Debatable… • Pulmonary toxicity if not cleared – Free radical formation = tissue damage – Allergic and eosinophilic response as well Other Antibiotics • Safe to assume adjustments are needed… • Nearly all antibiotics require some adjustment. • Can check drug references or package labeling…or call the pharmacist! • Benefits of proper dosing: – Minimize adverse effects and kidney injury – Minimize patient costs and QOL Pneumonia Guidelines - Review • IDSA – CAP – Previously healthy, no Abx for 3 months • Macrolide • Alternative: Doxycycline – Comorbidities OR inpatient • Respiratory FQN: Levo, Moxi • Beta-lactam + Macrolide (R & Z) – ICU • Beta-lactam + Resp FQN • Alternative: Beta-lactam + Macrolide Group work PATIENT CASE