Chapter 2 Economic Systems
advertisement

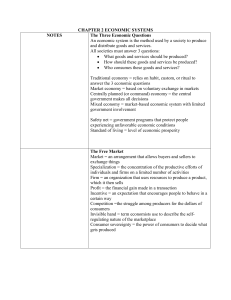
Three Economic Questions What Goods and Services should be produced? How should these goods and services be produced? Who consumes these goods and services? Economic Goals Economic Efficiency Making the most of resources Economic Freedom Freedom of gov. intervention in production and distribution Economic Security and Predictability Assurance that goods and services will be available Economic Equity Fair distribution of wealth Economic Growth and Innovation Leads to a higher standard of living Small Group Discussion Discuss with 2-3 other classmates What economic goals the United States is accomplishing ○ Examples of those goals What goods are produced in the U.S. Four Economic Systems Traditional Economies Market Economies Centrally Planned Economies Mixed Economies Free Market Economy Market-arrangement that allows buyers and sellers to exchange things Why? Specialization Free Market Economy Cont. In a free market system, individuals and privately owned businesses own the factors of production, make what they want, and buy what they want Circular Flow Diagram Household Firm organization using the resources Transforms inputs (factors of production) into outputs (products) Factor Market Purchasing factors of production from households Product Market Purchase the goods and services that firms produce Self-Regulating Nature of Marketplace How do they all cooperate? Self Interest Adam Smith Consumers in pursuit of their selfinterest have the incentive to look for lower prices Competition The struggle among the producers for the dollars of consumers The Invisible Hand Describes the self-regulating nature of the marketplace Advantages of the Free Market Economic Efficiency 2. Economic Freedom 3. Economic Growth 4. Consumer Sovereignty 1. Critical Thinking and Review How does specialization make us more efficient? Why is economic equity difficult to achieve in a free market economy? Explain what Adam Smith meant by “the invisible hand of the marketplace.” Centrally Planned Economy Central Government answers key economic questions Gov. owns both land and capital Socialism and Communism Socialism Social and political philosophy based on the belief that democratic means should be used to evenly distribute wealth throughout society Communism A political system characterized by a centrally planned economy with all economic and political power resting in the hands of the central government The Former USSR Read pages 36 & 37 in your textbook With a partner discuss The role of the centrally planned government in the Soviet Union The affects of the government on the agriculture and industry The impact of Soviet Consumers What is a current day example of a country that is centrally planned? Problem s of Centrally Planned Economies Could be used to jumpstart Economy Poor quality Serious shortages Diminishing production Read pg. 39 in textbook Real Case Study Russia in Crisis Answer Applying Economic Ideas Questions Modern Economies Mixed Economies Laissez Faire Doctrine that states government should not intervene in the marketplace Circular Flow Diagram of Mixed Economy Comparing Mixed Economies