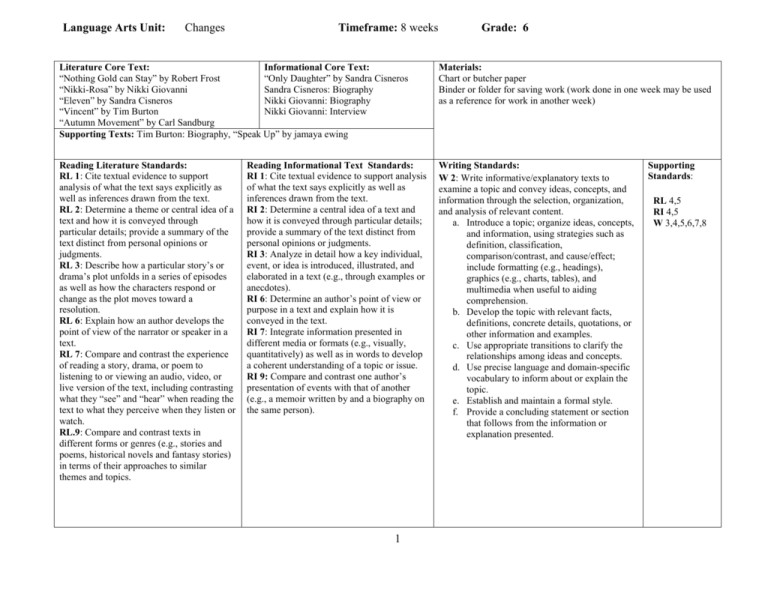
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Literature Core Text:
Informational Core Text:
“Nothing Gold can Stay” by Robert Frost
“Only Daughter” by Sandra Cisneros
“Nikki-Rosa” by Nikki Giovanni
Sandra Cisneros: Biography
“Eleven” by Sandra Cisneros
Nikki Giovanni: Biography
“Vincent” by Tim Burton
Nikki Giovanni: Interview
“Autumn Movement” by Carl Sandburg
Supporting Texts: Tim Burton: Biography, “Speak Up” by jamaya ewing
Materials:
Chart or butcher paper
Binder or folder for saving work (work done in one week may be used
as a reference for work in another week)
Reading Literature Standards:
RL 1: Cite textual evidence to support
analysis of what the text says explicitly as
well as inferences drawn from the text.
RL 2: Determine a theme or central idea of a
text and how it is conveyed through
particular details; provide a summary of the
text distinct from personal opinions or
judgments.
RL 3: Describe how a particular story’s or
drama’s plot unfolds in a series of episodes
as well as how the characters respond or
change as the plot moves toward a
resolution.
RL 6: Explain how an author develops the
point of view of the narrator or speaker in a
text.
RL 7: Compare and contrast the experience
of reading a story, drama, or poem to
listening to or viewing an audio, video, or
live version of the text, including contrasting
what they “see” and “hear” when reading the
text to what they perceive when they listen or
watch.
RL.9: Compare and contrast texts in
different forms or genres (e.g., stories and
poems, historical novels and fantasy stories)
in terms of their approaches to similar
themes and topics.
Writing Standards:
W 2: Write informative/explanatory texts to
examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and
information through the selection, organization,
and analysis of relevant content.
a. Introduce a topic; organize ideas, concepts,
and information, using strategies such as
definition, classification,
comparison/contrast, and cause/effect;
include formatting (e.g., headings),
graphics (e.g., charts, tables), and
multimedia when useful to aiding
comprehension.
b. Develop the topic with relevant facts,
definitions, concrete details, quotations, or
other information and examples.
c. Use appropriate transitions to clarify the
relationships among ideas and concepts.
d. Use precise language and domain-specific
vocabulary to inform about or explain the
topic.
e. Establish and maintain a formal style.
f. Provide a concluding statement or section
that follows from the information or
explanation presented.
Reading Informational Text Standards:
RI 1: Cite textual evidence to support analysis
of what the text says explicitly as well as
inferences drawn from the text.
RI 2: Determine a central idea of a text and
how it is conveyed through particular details;
provide a summary of the text distinct from
personal opinions or judgments.
RI 3: Analyze in detail how a key individual,
event, or idea is introduced, illustrated, and
elaborated in a text (e.g., through examples or
anecdotes).
RI 6: Determine an author’s point of view or
purpose in a text and explain how it is
conveyed in the text.
RI 7: Integrate information presented in
different media or formats (e.g., visually,
quantitatively) as well as in words to develop
a coherent understanding of a topic or issue.
RI 9: Compare and contrast one author’s
presentation of events with that of another
(e.g., a memoir written by and a biography on
the same person).
1
Supporting
Standards:
RL 4,5
RI 4,5
W 3,4,5,6,7,8
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Essential Questions:
RL 1 and RI 1
In citing, what is the difference between quoting and paraphrasing?
What is an inference?
How do readers make an accurate inference based on evidence in the text?
RL 2
How do readers figure out the message or moral or theme or underlying meaning of a poem or story?
How does a writer develop a theme?
How can summarizing help us to better understand text?
RL 3
How is the process of reading poetry different from reading stories and dramas?
What is important to notice about characters and events in a story or poem?
How do the characters in the story and the plot work together?
RL6
How does a poet develop the point of view of the narrator/speaker?
How does point of view affect the meaning of text?
RL7
How do the elements of poetry work to impact text?
How do the elements of poetry work to impact a live version/audio/video of text?
How is a play similar to and different from prose and poetry?
RL 9
How do different genres support similar themes?
RI 2
What do good readers do to help them understand what they are reading?
RI 3
How are authors’ ideas developed by particular sentences, paragraphs, or larger portions of informational text?
How does the structure of informational text contribute to the development of ideas?
How do readers connect ideas about a topic after they read?
RI 7
How do we use different sources to help in understanding a topic?
RI 9
How do authors develop point of view?
How can various authors interpret events differently?
W2
How is a topic introduced in explanatory writing?
How are concepts and information used and organized to support the topic?
What are the best strategies to use to explain the topic?
2
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Summative Unit Assessments:
Literature: Writing Prompt (W2)
Write an informative/explanatory multi-paragraph essay comparing and contrasting the short story “Eleven” by Sandra Cisneros to the poem “Nikki-Rosa” by
Nikki Giovanni. Use the following guidelines:
1. Focus the essay on the similarities and differences in how the authors develop the theme and the point of view of the narrators.
2. Introduce and state a topic.
3. Organize a body of two or three paragraphs to support the topic.
4. Use the similarities-to-differences strategy (a variation of the point-by-point method) to organize and format the essay.
a. Compare themes & points of view (1-2 paragraphs)
b. Contrast themes & points of view (1-2 paragraphs)
5. Use citations and evidence from the pieces.
6. Provide a conclusion.
The following graphic organizers can be used to assist in the writing process:
“Compare & Contrast: Similarities-to-Differences Strategy”, Appendix A, pp.30 & 31 and VENN Diagram, Appendix A, p.35
3
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Teacher Background Knowledge/Key Information about this Unit:
The unit has been revised to reflect the consensus of the ELA facilitators at our meeting on February 17. The theme of change remains, so you can tie all of the readings
back to it throughout the unit. Instead of reading about Egypt for the informational text in the first two weeks, you will find links to articles about environmental change
and wolves, and two poems that deal with change as a theme. Week three will entail a biography and interview about Nikki Giovanni. Week four remains the same,
reading the poem, “Nikki Rosa.” There has been a change in week five so that students will now read the poem “Vincent.” Week six will provide students the
opportunity to do a close read on a memoir and a biography on Sandra Cisneros as well as a writing task. In week seven, students will again read, “Eleven”. Week
eight is reserved for the summative writing task, which is the same as last year’s.
The priority, according to the 6th grade ELA facilitators, was to change the informational text portion and be extended some choice about what to read with their class.
This was accomplished in the first week by providing 3 groupings of articles to choose from. 2 groups of articles about environmental change/climate change are
offered. One collection has easier text and the other set has more challenging text. The 3rd group of articles comes from the ODELL unit: The Wolf You Feed. Choose
whichever group of articles suits your needs. The tasks are written generically, so that they can be used with any of the articles. Again, the choice is up to you as far as
which tasks you choose.
The challenge came when trying to figure out how to print classroom sets of the articles when all teacher s will not be reading the same set. Therefore, teachers will
need to copy their own articles for the first week. All other texts will be copied for you at the district and sent to your site.
As you can see, there is more prep work for you to do ahead of starting the revised unit.
To support the standards effectively, you will notice that informational text and literature are intertwined as opposed to doing the informational text first and then the
literature piece.
You will notice a decreased amount of tasks in most of the weeks. This is to accommodate the days that testing for SBAC will take place. Please note that a decrease in
the amount of tasks does not decrease the rigor and expectations of the tasks that are required. If you find that you are running of out materials and the students are
completing all tasks with mastery, please refer back to week one and choose another piece of informational text to read.
There are many opportunities for close reading in this unit. Keep in mind that not all close reading protocols are the same. Instead, they are dependent upon the type of
text being read and the content which is essential for that given piece. If students get confused remind them that they read different texts for different reasons and
therefore the strategies they use during close reading will be different with different texts. Students need to know why they are reading something. Teachers need to
identify what they want students to know or understand about the reading when they get done. As teachers, we need to provide our students with a focus or purpose for
reading.
Multiple opportunities are woven throughout the unit to practice informational writing (specifically compare/contrast) before the summative. You will need to teach
this type of writing to your students (Identifying similarities and differences is one of the most effective strategies to raise students achievement (Marzano, Pickering, &
Pollock, 2001). Here are three strategies to organize comparison and contrast papers:
1. Whole-to-Whole, or Block
In this structure, you say everything about one item then everything about the other. For instance, say everything about the presentation and/or what the student
experiences regarding the characters, setting, structure and/or plot for the read poem and then everything about the same for the video. Whole-to-Whole
comparison and contrast uses a separate section or paragraph for each item you're discussing. The points in each of the sections should be the same and they should
be explained in the same order (for instance, you might discuss the presentation of the character, setting, and plot for both, and in that order for both).
2. Similarities-to-Differences
In this structure, you explain all the similarities about the items being compared and then you explain all the differences. For instance, you might explain that the
presentation and/or what the student experiences regarding the characters and plot were similar in both the poem and video in the one section. In the next section,
you could explain that the presentation and/or what the student experiences regarding the characters and the plot were different. Similarities-to-Differences
comparison and contrast uses a separate section or paragraph for similarities and differences. In other words, the body of your paper would have two large sections:
one for similarities, and another for differences.
3. Point-by-Point
4
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
In this structure, you explain one point of comparison before moving to the next point. For instance, you would write about the presentation and/or the
student experiences regarding the characters in the poem and video in one section; then you would write about the presentation and/or the student’s
experiences regarding the setting in the poem and video in the next section. Point-by-Point comparison and contrast uses a separate section or paragraph
for each point. For consistency, begin with the same item in each section of your point-by-point paper.
5
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Week 1: Informational Text
Standards:
RI 1: Cite textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as
Learning Targets:
RI 1: Orally and in writing, students will cite several details and
inferences drawn from the text.
examples to support not only what the text explicitly says but through
RI 2: Determine a central idea of a text and how it is conveyed through particular details;
drawing inferences.
provide a summary of the text distinct from personal opinions or judgments.
RI 2: Students will distinguish between objectivity and subjectivity in
RI 3: Analyze in detail how a key individual, event, or idea is introduced, illustrated, and
the text as well as objectively summarizing the text.
elaborated in a text (e.g., through examples or anecdotes).
RI 3: Orally and in writing, students will analyze, in detail, how
RI 6: Determine an author’s point of view or purpose in a text and explain how it is conveyed
individuals, events or ideas in a text are introduced and change over the
in the text.
course of the text.
RI 7: Integrate information presented in different media or formats (e.g., visually,
RI 6: Students will determine an author’s point of view in an
quantitatively) as well as in words to develop a coherent understanding of a topic or issue.
informational text as well as how the author uses supporting details to
RI 9: Compare and contrast one author’s presentation of events with that of another (e.g. a
support that point of view. Orally and in writing, students will explain
memoir written by and a biography on the same person.).
how the point of view is conveyed in a text by evaluating what
W 2: Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and
information the author chooses to present, statements used within the
information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant content.
text and the use of language.
(2a,b,c,d,e,f)
RI 7: Given multiple sources of information, students will chart
information from those sources to present a coherent understanding of a
topic. Students will present their understanding both orally and in
writing.
RI 9: Students will compare how different authors portray the same
idea or event.
W 2: With the use of a graphic organizer, students will write a formal,
informative multiple paragraph piece to examine a topic. Students will
support the topic with important information and use various strategies
to examine the information about the topic.
Teacher Background Knowledge/Key Information Week 1:
You will find 3 sets of articles to choose from this week. Two groups of articles are about environmental change/climate change. One collection has easier text and the
other set has more challenging text. The 3rd group of articles comes from the ODELL unit: The Wolf You Feed. Choose whichever group of articles suits your needs. The
tasks are written generically, so that they can be used with any of the articles. Again, the choice is up to you as far as which tasks you choose to use.
Please be aware that you will need to copy your own sets of articles for this week.
Informational Text: Please choose one set of articles to use this week. If you choose to read the articles on environmental change, the compare and contrast will be
based on how the authors write about the topic of climate change and/or environmental change. If you choose to read the articles on wolves perhaps students will
compare how the authors convey that wolves fill an important role in the web of life, or that wolves exhibit a complex web of social relationships, or your own idea!
ReadWorks articles from www.readworks.org **Easier texts
Hook, Line, and Sinker: http://www.readworks.org/user/m/login/nojs?destination=passages/hook-line-and-sinker
Holy Cow!: http://www.readworks.org/user/m/login/nojs?destination=passages/holy-cow
Fuels of the Future: http://www.readworks.org/user/m/login/nojs?destination=passages/fuels-future
6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Dirty Job: http://www.readworks.org/user/m/login/nojs?destination=passages/dirty-job
Water from the Air: Cloud Forests: http://www.readworks.org/user/m/login/nojs?destination=passages/water-air-cloud-forests
High and Dry:
http://www.readworks.org/user/m/login/nojs?destination=passages/high-and-dry
Life Finds a Way: http://www.readworks.org/user/m/login/nojs?destination=passages/life-finds-way
Scholastic articles from http://www.scholastic.com/home/ **More challenging texts
Tomorrow’s Weather: http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=7571&print=1
Reefs at Risk: http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=7854
Protecting Polar Bears: http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=11271
Global Warming Report: http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=11487
An Inconvenient Truth for Kids: http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=12027
Plight of the Penguins: http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=3748563
Antarctica Breaking: http://www.scholastic.com/browse/article.jsp?id=3749276
Informational texts can also be found in the ODELL unit plan: The Wolf you Feed. You will find a PDF containing all of the texts for the unit by following this
link: http://odelleducation.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/04/RC-Unit-Texts-G6_The-wolf-you-feed.pdf
Please use the following titles:
A Brief History of Wolves in the United States, by Cornelia N. Hutt
All About Wolves: Pack Behavior, by John Vucetich and Rolf Peterson
All About Wolves: Hunting Behavior, by John Vucetich and Rolf Peterson
Alpha Status, Dominance, and Division of Labor in Wolf Packs, by David L. Mech
Optional Websites for your use, if you so choose: Living with Wolves http://www.livingwithwolves.org/index2.html
Lobos of the South West http://www.mexicanwolves.org/index.php/about-wolves
Tasks (Remember the tasks are listed as options. Choose the ones you would like to use with your article set.)
Discussion questions (apply to all texts):
What is the author’s personal relationship to the topic or themes?
What do you learn about the topic as you read?
How do the ideas relate to what you already know?
How are the details you read about related in ways that build ideas and themes?
Compare and Contrast Chart Graphic Organizers
http://www.readwritethink.org/files/resources/lesson_images/lesson275/compcon_chart.pdf
You will also find 2 more compare and contrast graphic organizers (A & B) in Appendix A
After your students complete 2 graphic organizers they should write 2 or more compare contrast paragraphs or a multiparagraph essay using their graphic
organizers, notes, a prewriting plan and the texts to guide them (RI 1,RI 3 RI 9, W2).
Integrating Information from a variety of authors or formats
Transmediations (McLaughlin, 2010) provide learners with essential, first-hand understanding of how various formats impact text. Students choose a text in its
original format and transform that text into another medium, such as a poem, or an electronic picture book, or song lyrics, or a work of art. This task might be
7
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
done after students have read all of the articles in the text set you chose. They can choose their favorite article to “transmediate.”
Glogster (www.edu.glogster.com) is an online tool for creating an interactive multimedia image that looks like a poster, but glog readers can interact with the
elements and content. A glog can contain photos, artwork, video clips, text descriptions, symbols, colors, and graphics. Students could use this tool to create
posters about what they have read in the article set.
Side by Side
After students have read and annotated at least 2 of the articles they can place both annotated articles side-by-side and begin to fill in a compare contrast graphic
organizer or a Venn diagram.
Stop and Jot
Students periodically stop and think about information that they are reading and jot down their thoughts. They might stop after each paragraph, each page, or
each section of reading. Students may write about something they learned, something they are wondering about, or a prediction about what they might learn
next. If students use sticky notes to do this, they can mark the sections of the book or article. Then, the notes can be added to a whole-class chart that will help
build content knowledge and understanding.
Golden Lines
What -This strategy engages readers to look for a specific point that “speaks” to them. "Golden Lines" are powerful quotes that automatically provide
interesting discussion material.
Why -Many students find it much easier to select something the author said than to come up with their own reactions. Therefore, Golden Lines are an easy and
effective strategy for students to determine important ideas, make connections, and visualize during reading.
How
Think: Have students read an article and choose a golden line – quotations or key statements that have special meaning or strike them as important.
Pair: With a partner, students share their golden lines and discuss their thoughts.
Share: Have students share ideas among table members and share out a few ideas within the room. (Optional: Group students in the room that selected the
same/similar passages and have them summarize the passage into 10 words or less)
Critical Reading Strategies
Number the paragraphs: Since common core requires students to refer to the text, they can start by numbering the paragraphs to make the text easier to
navigate.
Chunk the text: When faced with a full page of text, reading it can quickly become overwhelming for students. Breaking up the text into smaller sections (or
chunks) makes the page much more manageable for students. Students do this by drawing a horizontal line between paragraphs to divide the page into smaller
sections. It is important to understand that there is no right or wrong way to chunk the text, as long as there is justification for why certain paragraphs are
grouped together. At first, you might tell your students what paragraphs to chunk. Later, you can let go of that responsibility and ask your students to chunk the
text on their own.
Underline and circle…with a purpose: Telling students to simply underline “the important stuff” is too vague. “Stuff” is not a concrete thing that students can
identify. Instead, direct students to underline and circle very specific things. Think about what information you want students to take from the text, and ask
them to look for those elements. What you have students circle and underline may change depending on the text type. Circling specific items is also an effective
close reading strategy. If you have students circle “key terms” tell them that they are words that are 1. Defined, 2. Are repeated throughout the text. 3. If you
only circled five key terms in the entire text, you would have a pretty good idea about what the entire text is about.
Left margin: What is the author SAYING?: We must be very specific and give students a game plan for what they will write in the margins. This is where
the chunking comes into play. In the left margin, ask students to summarize each chunk. You may need to demonstrate how to summarize in 10-words or less.
The chunking allows the students to look at the text in smaller segments, and summarize what the author is saying in just that small, specific chunk.
8
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Right margin: Dig deeper into the text: Direct students to complete a specific task for each chunk. This may include:
Use a power verb to describe what the author is DOING. (For example: Describing, illustrating, arguing, etc..) Note: It isn’t enough for students to write
“Comparing” and be done. What is the author comparing? A better answer might be: “Comparing the character of Montag to Captain Beatty”.
Represent the information with a picture. This is a good way for students to be creative to visually represent the chunk with a drawing.
Ask questions. Students can begin to learn how to ask questions that dig deeper into the text. Try asking them to include one of the following terms in each
question: significance, trait, importance, value, purpose, reason, function, causation, change, connection, perspective.
Find connections: Ask students to find connections between the events and/or ideas in the text.
(adapted from iTeach.iCoach.iBlog.com)
CSI: Color, Symbol, Image
What- This strategy asks students to identify and distill the essence of ideas from reading, watching or listening in non-verbal ways by using a color, symbol, or
image to represent the ideas. CSI can be used to enhance comprehension of reading, watching or listening. It can also be used as a reflection about previous
events or learning. It is helpful if students have had previous experience with highlighting texts for important ideas, connections, or events. The synthesis
happens as students select a color, symbol, and image to represent three important ideas. This routine also facilitates the discussion of a text or event as students
share their colors, symbols, and images.
Why -Good readers sometimes use nonlinguistic representations (pictures instead of words) to identify big ideas while reading. These nonlinguistic
representations help readers to infer theme and that inference becomes generative knowledge they can use later to help them make decisions and solve
problems.
How
o As students are reading/listening/watching, they make note of things that they find interesting, important, or insightful.
o When finished, students choose 3 of these items that most stand out.
o For one of these, they choose a color that they feel best represents or captures the essence of that idea.
o For another one, they choose a symbol that they feel best represents or captures the essence of that idea.
o For the other one, they choose an image.
o With a partner or group, students share their color and then share the item from the reading that it represents. Students tell why they chose that color as a
representation of that idea. Repeat the sharing process until every member of the group has shared his or her Color, Symbol, and Image.
Adapted From: Visible Thinking ©, Harvard Project Zero
Point of View
Analyze the text to determine the author’s point of view about the topic. Discuss (or use as a short answer written assignment) How do we know the point of
view? How is the author’s point of view conveyed? Is the author’s point of view supported with evidence and
(reasons? What was the author’s purpose for writing this article? How do you know? Cite specific details from the text.
Another appealing way for students to focus on point of view or purpose is to use a comic strip generator. There are several free generators available online,
such as ToonDoo (www.toondoo.com), Chogger (www.chogger.com) and Make Beliefs Comix (www. makebeliefscomix.com). Students create comic strips
using characters, scenes, props, speech and thought bubbles, and captions to explain an author’s purpose for writing a text. When students cerate comic panels
to represent the retelling of a story or event and include speech and thought bubbles, they decide what the character or individual might think, say, and do. With
your guidance, students can think critically about text by analyzing point of view in order to create comic strips. (McLaughlin, Marueen, Overturf, Brenda J.
The Common Core: Teaching Students in Grade 6-12 to Meet the Reading Standards)
9
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Summarize
After each article, students should practice writing a summary, distinct from personal opinions or judgments, including a central idea of the text (RI 1 and RI 2).
Enrichment opportunity:
If you have learners who are very independent you might consider allowing them to do the following readwritethink lesson with a small group, while you are
guiding the rest of the class in other activities. The entire lesson can be found at: http://www.readwritethink.org/classroom-resources/lesson-plans/criticalliteracy-action-multimodal-1139.html?tab=3#resources
Or, you could simply use the following pieces from the overall lesson:
Evaluating Scientific Credibility: http://www.readwritethink.org/files/resources/lesson_images/lesson1139/evaluating_scientific.pdf
Representing Global Warming Discussion Guide: http://www.readwritethink.org/files/resources/lesson_images/lesson1139/representing_discussion.pdf
Self-Evaluation Rubric: http://www.readwritethink.org/files/resources/lesson_images/lesson1139/representing_rubric.pdf
Global Warming: Tying It All Together: http://www.readwritethink.org/files/resources/lesson_images/lesson1139/global_tying.pdf
10
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Weeks 2: “Autumn Movement” and “Nothing Gold can Stay”
Learning Targets:
RL 1: Orally and in writing, students will use several citations to support what
a text says explicitly and to make inferences
RL 2: Orally and in writing, students will determine a theme or central idea of
a literary text and describe how the theme is conveyed through particular
details (character, setting, events); students will provide a summary of the text
distinct from personal opinions or judgments
Grade: 6
Standards:
RL 1: Cite textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well
as inferences drawn from the text.
RL 2: Determine a theme or central idea of a text and how it is conveyed through
particular details; provide a summary of the text distinct from personal opinions or
judgments.
Week 2: Teacher Background Knowledge/Key Information: This week continues to focus on the theme of change but uses poetry to explain both changes in nature
as well as personal growth/changes in people. The poem “Autumn Movement” demonstrates change using the transition between Autumn and Winter. Thematically it
can be broadened to changes in life as well. The poem, Nothing Gold Can Stay, by Robert Frost does a lot of things well and therefore is a good model for readers who
aren’t quite sure what makes a good poem. For one thing, “Nothing Gold Can Stay” is only eight lines long, a few sentences. It is an apt example of the economic use of
words. Each word, each sound, is important. Yet in that short space, Frost conveys a theme that is a staple of many works of literature: the inevitability of change.
Nothing gold can stay, he tells us. And this is a theme students can relate to. They see change all around them, in their families, in their friends. They study it in science,
social studies, and literature. Other poems dealing with change or impermanence that can be used in conjunction with “Nothing Gold can Stay” are:
“Spring Storm,” by Jim Wayne Miller: https://sites.google.com/site/middleschoolpoetryunit/2-craft-and-structure/determining-the-meaning-of-words/spring-storm
Junkyards,” by Julian Lee Rayford: https://sites.google.com/site/middleschoolpoetryunit/key-ideas-and-details/determine-a-theme-of-a-story/junkyards
“Abandoned Farmhouse,” by Ted Kooser: http://www.poetryfoundation.org/poem/237648
“Deserted Farm,” by Mark Vinz: http://blogs.swa-jkt.com/swa/samanthapryse/2013/05/13/deserted-farm/
Theme is one of the more elusive literary terms to define. Consequently, many young readers have difficulty understanding it and knowing its role in a poem. Some
students have been taught that theme is the “meaning” of a poem, “what the poet is trying to say.” The problem is that explanations like these often distract readers from
the words of the poem, send them on a detour from experiencing the poem. Instead, lead your students to focus on what the poet is saying rather than what we think he
or she is “trying to say.” An important thing to remember about theme in a work of literature is that it is how one person sees it. No theme should be taken as a moral
certitude. Your students should feel free to disagree with how a poet sees the world.
“Autumn Movement” by Carl Sandburg (appendix D)
Tasks
Pre-reading
Note that standard L5a (Students will identify and interpret the use of personification, alliteration and onomatopoeia in text) is a target standard for quarter 4
(reference Sixth Grade Language/Speaking & Listening Learning Targets 2014-15). Instruction for these examples of figurative language (as well as a review
of those taught in previous grade levels) may be necessary during this week. As opposed to teaching figurative language in isolation, embed them as you teach
the poems (this can be during your grade level planning).
Read “Autumn Movement”
First Read: Have students read the poem “Autumn Movement” independently for the first reading. It’s okay for them to struggle with comprehension! Poetry
is difficult but they need to be able to struggle through it. Have students focus on their initial reaction to the poem and what they think it is about. In other
words, what is the ‘gist’ of the poem? They can take notes and annotate as needed.
11
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
o
After the first read, have students discuss with a shoulder partner what their initial reaction is to the poem and why (which line leads them to think that
way).
Second Read: Have students read the poem a second time. Have students focus on the figurative language that is being used in the poem. (6 th grade is not the
first time they have seen figurative language).
o After the second read, have students discuss with a partner the figurative language they found. Allow them time to discuss what they found. It is okay if
they are wrong. They need the chance to work with the text.
o Bring the class back together and discuss the figurative language. Allow students to provide their examples of the figurative language and at this time
explain why the student may be accurate or inaccurate in their interpretation of the language.
o Things to consider:
Lines 2 and 3: The field of cornflower yellow is a scarf at the neck of the copper sunburned woman, the mother of the year, the taker of seeds. … What
are they comparing the field to?
Third Read: Have students read the poem a third time. Have students make notations on the text about what they understand (!) or what they are still confused
about (?). Give them the following questions to think about prior to reading: What is does “the field of cornflower yellow” represent? (sunflowers? corn?) What
is the copper woman, the mother of the year, the taker of seeds? (earth/mother earth). What does yellow is torn full of holes mean? (the plants dying because
winter is coming). What do you think the new beautiful things are? (winter, snow).
o After the third read, have students work with their partner in discussing the questions. Allow them to discuss what they know and what they are still
struggling with.
o Bring the class back together and discuss the questions whole group. It may be necessary to go line by line with the students:
I cried over beautiful things knowing no beautiful thing lasts. (narrator is upset that change is coming even though they know that nothing lasts and
change in inevitable.)
The field of cornflower yellow is a scarf at the neck of the copper sunburned woman, the mother of the year, the taker of seeds. (The fields of corn is
like a scarf on mother earth-copper sunburned woman, mother of the year, taker of seeds is earth )
The northwest wind comes and the yellow is torn full of holes (harvest season is over, the colder weather changes the field and plants)
new beautiful things come in the first spit of snow on the northwest wind (the new things are winter- rain, snow)
and the old things go, not one lasts. (the old things- Autumn, the plants)
Group Work
Place students into groups of three or four. Give each student a TP-CASTT analysis protocol (appendix A). Have students work in their groups to complete each
component of the protocol (either on notebook paper, chart paper, word processing, PowerPoint, etc.). Each student should complete/turn in/post their own work but
the work is done collectively in the group.
“Nothing Gold can Stay” by Robert Frost (appendix D)
Tasks
Pre-Reading Discussion Questions:
Write the title of the poem on the board and ask the students what they make of it as a title of a poem. What do they think it means? You might draw their
attention to the apparent contradiction: doesn’t gold stay gold forever? How can it be that gold cannot/does not stay the same?
Exploring Change-Small and Large group activities
After students have suggested some possible explanations for the title, break the class into groups of three or four students and give each group a copy of
the Change organizer (Appendix A??). Have them use it to map out some of their thoughts about cycles and change, which is the theme of Frost’s poem.
12
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
When the groups have completed their organizers, ask them to give examples of things people do to avoid change. For example, to stay healthy, some
people exercise, others take vitamins and supplements. Others choose to have cosmetic surgery in order to remain young looking. Do these practice stop
change? Slow it down? Can you think of things that groups---families, teams, nations---do to avoid change?
Close Reading: Getting to Know the Poem
Noticing Figurative Language: We can understand the theme of this short poem by examining its metaphors, especially in the first stanza, where Frost lays
out one of his beliefs about life. The metaphors in this poem may be challenging for your more literal-minded students, but you can help them by looking at
the stanza line by line and asking some leading questions
Nature’s first green is gold. How can green be gold? (It helps if your students understand that gold is a symbol of something precious and valuable.
Those first shoots and leaves symbolize rebirth and new life and are equally precious, and therefore gold.)
Her hardest hue to hold. What is Frost saying here? (Frost is not speaking literally, of course. He means that the first green is the stage of growth that
goes by the most quickly.)
Her early leaf’s a flower;/But only so an hour. How do these two lines reinforce what Frost has stated in the title and the opening lines? (The quick
passing of time, the impermanence of the fresh green shoots and leaves of spring…Again, only an hour isn’t literal; Frost is using hyperbole to make
his point.
The first stanza introduces the theme of this poem: things of life change very quickly. Frost continues in this vein in the second stanza with references
to Eden ending sadly---it sank to grief—and every day passing quickly---So dawn goes down to day---and finally his repetition of the title in the
final line---Nothing gold can stay. Continue questioning the students about the second stanza in the same way you did for the first stanza. For example:
Then leaf subsides to leaf. What is Frost implying here?
How do the first three lines connect? Then leaf subsides to leaf. So Eden sank to grief/ So dawn goes down to day. (So = likewise, or just as)
What is the significance of repeating the title at the end of the poem?
Noticing Sound: Frost does a number of interesting things with sound in this poem. The students are likely to recognize that the poem is written in
couplets—pairs of lines with end rhymes—with the rhyme scheme aabb ccdd. These end rhymes help hold the poem together. Also point out that the final
couplet brings the poem to a firm conclusion.
Have your students find the alliteration (repetition of the initial consonant sounds) that Frost uses:
Line 1: green/gold
Line 2: her/hardest/hue/hold, continued to line 3: her
Line 7: dawn, down, day
He also repeats other sounds skillfully:
Line 3: er as in her early
Line 4 o as in only so
Line 7 o as in so/goes
Say It Out Loud: Students can perform the poem as responses between 2 voices:
Nature’s first green is gold,
Her hardest hue to hold,
Her early leaf’s a flower;
But only so an hour.
Then leaf subsides to leaf.
So Eden sank to grief,
So dawn goes down to day.
13
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Nothing gold can stay.
Events in the plot-partner work
Ask students what the events of this poem are (ie; Fall-green is now gold, Trying to hold on to the leaves, but it doesn’t work, the leaves fall anyway—
leading to winter. Spring is the early leaf’s blossoming as flowers, the late spring and the flowers die and only the green leaves are left---eventually leading
back to the fall). Have students use the cyclic events graphic organizer with a partner and fill in the events as they see them happening in the poem.
Using the cyclic event graphic organizer (Appendix A), students work in partners to write a summary without giving their opinions or feelings about it.
(Lesson adapted from: Janeczko, Paul B., Reading Poetry in the Middle Grades, Heinemann, Portsmouth, NH)
Exploring the theme
Use some of the following questions in a class discussion to explore theme: What message is the poet trying to send or help you understand? Does it relate
to your life in any way? What does the poem say to you?
Using the “What it’s REALLY All About” graphic organizer students will either write their own suggestion for the theme of the poem, Nothing Gold Can
Stay, or be provided with one from the teacher (possibilities: Life is such a fragile thing and most of it is taken for granted. The most precious time in life
generally passes in what could be the blink of an eye. Change is eminent and will happen to all living things).
14
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Week 3: Nikki Giovanni
Standards:
RI 1: Cite textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well as
Learning Targets:
RI 1: Orally and in writing, students will cite several details and
inferences drawn from the text.
examples to support not only what the text explicitly says but through
RI 2: Determine a central idea of a text and how it is conveyed through particular details;
drawing inferences.
provide a summary of the text distinct from personal opinions or judgments.
RI 2: Students will distinguish between objectivity and subjectivity in
RI 3: Analyze in detail how a key individual, event, or idea is introduced, illustrated, and
the text as well as objectively summarizing the text.
elaborated in a text (e.g., through examples or anecdotes).
RI 3: Orally and in writing, students will analyze, in detail, how
RI 6: Determine an author’s point of view or purpose in a text and explain how it is conveyed
individuals, events or ideas in a text are introduced and change over the
in the text.
course of the text.
RI 7: Integrate information presented in different media or formats (e.g., visually,
RI 6: Students will determine an author’s point of view in an
quantitatively) as well as in words to develop a coherent understanding of a topic or issue.
informational text as well as how the author uses supporting details to
RI 9: Compare and contrast one author’s presentation of events with that of another (e.g. a
support that point of view. Orally and in writing, students will explain
memoir written by and a biography on the same person.).
how the point of view is conveyed in a text by evaluating what
W 2: Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and
information the author chooses to present, statements used within the
information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant content.
text and the use of language.
(2a,b,c,d,e,f)
RI 7: Given multiple sources of information, students will chart
information from those sources to present a coherent understanding of a
topic. Students will present their understanding both orally and in
writing.
RI 9: Students will compare how different authors portray the same
idea or event.
W 2: With the use of a graphic organizer, students will write a formal,
informative multiple paragraph piece to examine a topic. Students will
support the topic with important information and use various strategies
to examine the information about the topic.
Week 3 Teacher Background Knowledge/Key Information: Students will read two texts about the life of Nikki Giovanni. One is a biography and one is an
interview. They will read and respond to these texts by making notes, underlining, highlighting and annotating the texts. Students may consult dictionaries and
thesauruses if needed.
Nikki Rosa Biography (appendix D)
Guided Reading Activity
Text 1: The biography
o Before reading the biography from www.nikki-giovanni.com/bio.shtml, instruct students to preview the text and then discuss any thoughts and questions
they have about the text based on the features they noticed.
o What predictions can they make about the text?
o During the reading of the text, students will stop after every paragraph to take notes using a 3 column note-taking format. One column is for questions and
predictions, the next section is for answers to the questions and confirmation of predictions, and the final column is for key ideas, interesting language and
their feelings about what they read. Or, follow the directions for Critical Reading Strategies outlined in week one.
o After reading the entire text, students will record any additional thoughts about the text on the back of the 3 column chart.
15
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Class Discussion
Nikki Rosa: Interview (appendix D)
Text 2: The interview
o Before reading the Nikki Giovanni Interview Transcript instruct students to preview the text and then discuss any thoughts and questions they have about
the text based on the features they notice. How is the format of this text different from the format of the biography?
o What predictions can they make about the text?
o During the reading of the text, students will stop after each page to take notes using a 3 column note-taking format. One column is for questions and
predictions, the next section is for answers to the questions and confirmation of predictions, and the final column is for key ideas, interesting language and
anything else they find interesting. Or, follow the directions for Critical Reading Strategies outlined in week one.
Comparing the texts
o Next, students will consider any connections between the two texts using a Venn Diagram or the Compare/Contrast graphic organizer in Appendix A.
o In small groups or partners students will answer the following questions:
How are the biography and the interview alike? You may want to look at the ideas you wrote in the graphic organizer, your notes, and the texts.
How are the biography and the interview different? You may want to look at the ideas you wrote in the graphic organizer, your notes, and the texts.
What connections can you make between the 2 texts? In other words, what ideas come to you when you think about the similarities and differences
between these 2 texts? Write your thoughts and ideas in a paragraph.
Class Discussion
Class Discussion: How do the biography and the interview provide insight into Nikki Giovanni? How is the information alike? Different? Why would the
information be different when it was about the same person? Cite specific information from the texts to justify your response.
Writing Choices
QuIP Strategy (McLaughlin, E.M. (1987)
The QuIP is a simple strategy to get students asking their own questions and writing about their findings. The graphic organizer is included in
Appendix A. Students will first generate questions they have about Nikki Giovanni. Find the answers to their questions in both texts (they may need
to do further research online) and write a brief summary of their findings in a paragraph or two.
Compare/Contrast essay
o Using the information from their graphic organizers, notes and the two texts, students will write a compare/contrast multiparagraph essay. The goal is
to move students away from the obvious comparisons (one was written by an adult, the other was written by students, one was written in paragraph
form, the other in a question/answer format) to more in depth work. Encourage students to address both the content and the mediums, their feelings
and their thoughts when they read each text, and how and why each text emphasized different things about her life.
Compare/Contrast organization
1. Whole-to-Whole, or Block
In this structure, you say everything about one item then everything about the other. For instance, say everything about the presentation
and/or what the student experiences regarding the biography and then everything about the same for the memoir. Whole-to-Whole
comparison and contrast uses a separate section or paragraph for each item you're discussing. The points in each of the sections should be the
same and they should be explained in the same order.
2. Similarities-to-Differences
In this structure, you explain all the similarities about the items being compared and then you explain all the differences. For instance, you
might explain that the presentation and/or what the student experiences were similar in both the biography and memoir in the one section. In
the next section, you could explain how the presentation and/or what the student experiences were different. Similarities-to-Differences
comparison and contrast uses a separate section or paragraph for similarities and differences. In other words, the body of your paper would
16
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
have two large sections: one for similarities, and another for differences.
Point-by-Point
In this structure, you explain one point of comparison before moving to the next point. For instance, you would write about the presentation
and/or the student experience regarding one piece of both the biography and the memoir in one section; then you would write about the
presentation and/or the student’s experiences regarding another piece for both the biography and the memoir in another section. Point-byPoint comparison and contrast uses a separate section or paragraph for each point. For consistency, begin with the same item in each section
of your point-by-point paper.
Enrichment Opportunity
Living Legend? Or Not?
“…and over the course of more than three decades of publishing and lecturing she has come to be called both a “national Treasure” and, most recently, one of Oprah
Winfrey’s twenty-five “Living Legends.” (http://nikki-giovanni.com/print_bio.shtml)
3.
Do you agree or disagree that Nikki Giovanni is considered a “national Treasure” and one of twenty-five “Living Legends?”
Fill in the Persuasive Essay: Graphic Organizer to plan your essay.
State your claim (What is your opinion on this topic?) and then provide reasons and evidence that support your claim from the biography and interview texts.
Write (or type) your essay. Refer to your plan and the texts as you write. Don’t forget to note where you got your evidence from.
17
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Weeks 4: “Nikki-Rosa”
Learning Targets:
RL1: Orally and in writing, students will cite several details and examples of
textual evidence to support what the text explicitly says and by drawing
inferences.
RL2: Students will distinguish between objectivity and subjectivity when
analyzing a text, consider literary elements as well as facts when determining
the theme and provide an objective summary of the text.
RL6: Students will distinguish between the author and narrator/speaker in a
text as well as identify the point of view of a narrator or speaker in a text.
RL 7: Students will compare/contrast their experience when text is read verses
audio or video of the same text.
Standards:
RL 1: Cite textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well
as inferences drawn from the text.
RL 2: Determine a theme or central idea of a text and how it is conveyed through
particular details; provide a summary of the text distinct from personal opinions or
judgments.
RL 3: Describe how a particular story’s or drama’s plot unfolds in a series of episodes
as well as how the characters respond or change as the plot moves toward a resolution.
RL 6: Explain how an author develops the point of view of the narrator or speaker in a
text.
RL 7: Compare and contrast the experience of reading a story, drama, or poem to
listening to or viewing an audio, video, or live version of the text, including
contrasting what they “see” and “hear” when reading the text to what they perceive
when they listen or watch.
Week 4 Teacher Background Knowledge/Key Information: In her poem "Nikki-Rosa," Nikki Giovanni describes specific moments from her childhood. A close
reading of a poem helps students go beyond identifying simple and obvious characteristics to explore the poet and in this poem, also the narrator, in more depth. In the
case of this poem by Nikki Giovanni, for instance, students can move from "identify[ing] the speaker as black and from the country" to "think[ing] about what they can
tell from the poem about [the speaker's] attitudes, about what they think might be [the speaker's] priorities in life." The images she recalls are more than biographical
details; they are evidence to support her premise that growing up black doesn't always mean growing up in hardship.
This is a link to resources about Nikki Giovanni, the poet: http://www.readwritethink.org/classroom-resources/calendar-activities/poet-nikki-giovanni-born20729.html
“Nikki-Rosa”
Tasks
Pre-Reading Review
Review types of figurative language: personification, metaphors, similes, onomatopoeia
Review 1st person and 3rd person narration
Review the difference between subjectivity and objectivity (1.Objective and subjective statements are used by speakers to get their points across.
2.Objective statements are facts that can be verified by third parties while subjective statements may or may not be entirely true as they are colored by the
opinions of the speaker.) Read more: http://www.asdatoz.com/Documents/Website-%20Objective%20vs%20subjective%20ltr.pdf
Pre-Reading Discussion (“Nikki-Rosa” by Nikki Giovanni)
What comes to your mind when you say or hear that someone has had a “hard childhood?”
When you think about some of the things you have experienced as children, what might make some people feel sorry for you, but were actually pleasurable to
you? (Students might recall having to share a bed with a sibling where there was plenty of squabbling over space but also many sweet secrets shared. Or a
student might remember weekly chores like ironing her father’s shirts which, though she would never admit it to her mother, made her feel closer to her dad.
Students might offer memories of hand-me-down clothes, errands to the store, or leftover dinners.) Create a cluster on the board of all the features of this
condition from your students’ point of view.
18
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
First & Second Reading: Connecting personally with the poem
Pass out copies of “Nikki-Rosa.” Ask students to read the poem independently and while they read to take notes on a T chart: What I visualized while I read--What I experienced (or felt, heard, remembered, connected to, wondered about…) while I read.
Next they should discuss their T chart findings with a small group of peers.
Play the video of Giovanni reading her poem “Nikki-Rosa” for students (the video loads automatically, but you need to click the play arrow to start the video).
http://nikki-giovanni.com/nikkirosa.shtml Because of the small size of the image you may want to structure small groups of students, gathered around a single
computer if projection equipment is not available. First, allow them to watch and listen without taking notes. Then allow them to watch and listen again while
they reflect, using the same type of T chart (What I visualized while I listened and watched---What I experienced (or felt, heard, remembered, connected to,
wondered about…) while I listened and watched.
Next they should discuss their T chart findings with a small group of peers.
Hold a whole class discussion comparing and contrasting the experience of reading the poem independently to listening to and viewing the video of the text. Then
discuss any connections they can make to what they read about Nikki Giovanni last week.
Third Reading: From the author’s point of view
Finally, have them read the poem a third time, underlining or highlighting all the words and phrases that describe the various pleasures the speaker in the poem
remembers experiencing in her “hard” childhood. Remind students that while this poem may seem to be obviously autobiographical-the title is reasonably
strong evidence-a careful reader always considers the speaker in a poem to be separate from the author.
Initiate a discussion of the poem. The questions below can be starters for the discussion, but encourage the conversation to roam where it will. Requiring
students to answer a list of questions could make them hate the poem forever.
o Did any of the phrases that you marked in “Nikki-Rosa” remind you of your own childhood experiences? Cite these phrases and tell how that made you
feel about what you read.
o How would you describe the speaker’s attitude toward her childhood? Cite evidence directly from the text to support your answer. Why do you think that
she is worried that a biographer will “never understand”?
o What do you think you “understand” about the circumstances of the speaker’s childhood? Cite the text as you speak. (Push students to be very specific here
in order to help them recreate the world in which these childhood remembrances existed.)
o Why do you think Nikki Giovanni chooses to address the reader directly as “you”? What effect did this have on you as a reader? What assumption does
this use of the second person make about Giovanni’s expectation of who her readers will be?
o How did you interpret the line “And though you’re poor it isn’t poverty that / concerns you”? If it wasn’t poverty that concerned the speaker, what was it
that concerned her?
o Note that the line “and I really hope no white person ever has cause / to write about me / because they never understand” might cause some students to feel
that Giovanni is casting them as the “bad guys” in the poem. Encourage students to think about how Giovanni’s experience as a black person might lead
her to make this generalization about white people. Discourage students from relegating such generalizations to the “bad old days” before the Civil Rights
movement. If the issue comes up, it is important to discuss the pervasive presence of racism in our own society and how this shapes our generalizations
about who we expect will “understand” us and who we expect never will.
Summarize
Write a summary of the poem in your own words.
(This lesson was adapted from the readwritethink.org lesson plan by Traci Gardner, Childhood Remembrances: Life and Art Intersect in Nikki Giovanni’s “NikkiRosa.”)
19
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Small Group Work
After reading and discussing “Nikki-Rosa” what is the most important idea that Giovanni is trying to express about her childhood? Work cooperatively with a
small group of students to find quotes that reveal Giovanni’s thoughts and feelings about her childhood. Justify your choice. Use the worksheet “Quote Me.”
(Appendix A).
Meet as a whole class to discuss the quotes and justifications from the small group work done on “Quote Me.”
Interpreting the Theme
Using the “What it’s REALLY All About” graphic organizer (Appendix A) students will either write their own suggestion for the theme of the poem, Nikki
Rosa, or be provided with one from the teacher (you might consider: money doesn’t equal happiness, happiness is in the eye of the beholder, family and
community bonds create “wealth”, you must wear my shoes to understand my life, adversity is a state of mind rather than a set of circumstances).
CFA
Use the poem, speak up, by jamaya ewing (see appendix D). Students can do the following activities independently.
After reading the poem, have students find the 3 quotes that they feel best express the importance of speaking up. Use the “Quote Me” worksheet to write
their quotes and to justify their thoughts. (RL 6.1)
Using the :What it’s REALLY All About” graphic organizer students will either write their own suggestion for the theme of the poem, “speak up,” or be
provided with one from the teacher (you might consider: life is too short to hide who you really are, your own unique expression must be heard, be
courageous enough to be yourself)
20
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Week 5: “Vincent”
Standards:
RL 1: Cite textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well
Learning Targets:
RL1: Orally and in writing, students will cite several details and examples of
as inferences drawn from the text.
textual evidence to support what the text explicitly says and by drawing
RL 7: Compare and contrast the experience of reading a story, drama, or poem to
inferences.
listening to or viewing an audio, video, or live version of the text, including
RL 7: Students will compare/contrast their experience when text is read verses contrasting what they “see” and “hear” when reading the text to what they perceive
audio or video of the same text.
when they listen or watch.
W 2: With the use of a graphic organizer, students will write a formal,
W 2: Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas,
informative multiple paragraph piece to examine a topic. Students will support
concepts, and information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant
the topic with important information and use various strategies to examine the
content. (2a,b,c,d,e,f)
information about the topic.
Week 5 Teacher Background Knowledge/Key Information: This week students will be focusing on the poem “Vincent” by Tim Burton. Students will read a
biography about Tim Burton to build background knowledge and then do a close read of the poem. It is important to give students time to work in collaborative
groupings. Students will also view the poem “Vincent” as it is read and illustrated in a video. If you do not have immediate access to technology in your classroom,
please make arrangements to watch it in another classroom/computer lab that had technology available. Students will then be required to write a short compare/contrast
(4 paragraph) paper on the presentation/experience of the reading the poem and watching the video.
Tasks
Building Background
Ask students if they know Tim Burton? Do they know of his movies? Chart on the board or chart paper their responses.
Read “Tim Burton: Biography” (appendix D). This text is meant to give the students an idea of who Tim Burton is but they will not be expected to do a close
read on the text.
Discussion Questions
o Have any of you seen one or more of the movies listed in the biography? What are his movies like?
o What types of films did Burton like to watch as a child? (horror films) How do you think this influenced his film making later in life?
o Who was Vincent Price? (Reference text). Explain that famed actor Vincent Price played a key role in Burton’s upbringing.
“Vincent” (poem)
Read “Vincent” by Tim Burton
First Read: Have students read the poem “Vincent” independently for the first reading. It’s okay for them to struggle with comprehension. Have students focus
on their initial reaction to the poem and what they think it is about. In other words, what is the ‘gist’ of the poem? They can take notes and annotate as needed.
After the first read, have students discuss with a shoulder partner what their initial reaction is to the poem and why (which line leads them to think that
way).
Second Read: Have students read the poem a second time. Have students focus on the vocabulary that is difficult. Although this should not be a difficult read
for most, words like ghoulish, gruesome, portrait, encased, tomb and possessed may be difficult specifically with ELs. After the second read, chart the words
that students do not know on the board or chart paper.
After the second read, discuss how the author uses vocabulary in the poem.
What do students imagine or ‘see’ when they read the poem? How does the vocabulary influence those images in their mind?
What text structures the poem for the ease of reading? (rhyming, short sentences, use of adjectives, dialogue, etc.).
21
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Third Read: Have students look deeper into the poem and the meaning. Students will read the poem a third time and being to take the poem apart.
o Some examples of things to point out if the students are not able to do it:
o Line 8: And wander dark hallways, alone and tormented (wanders- does not have a purpose to be there, tormented- he is a pain)
o Lines 14 and 15: Could go searching for victims in the London fog; His thoughts, though, aren’t only of ghoulish crimes (what is he thinking about?
Hurting others- victims would be his victims- he is thinking of committing a ghoulish crime)
o Line 29: While alone and insane encased in his tomb (Where is he actually? Where is he pretending to be?)
o Line 36: “I am possessed by this house, and can never leave it again”
o Lines 45-46: The room started to swell, to shiver and creak; His horrid insanity had reached its peak
o Lines 51-52: Every horror in his life that had crept through his dreams; Swept his mad laughter to terrified screams!
Discussion Questions
Who is the character trying to be like? (Line 4). How is this significant to the author Tim Burton? (refer back to his biography which stated he grew up
watching horror movies and his favorite actor Vincent Price). Reread the first four lines of the poem. What do we learn about the boy Vincent in these first
four lines?
What technique does the author use to tell Vincent’s story and show what Vincent is thinking? (He weaves reality and imagination together throughout the
text). What are some examples of this technique? (this can be turned into a group task where students together identify the examples)
How do you know that Vincent is imagining a different life? (Student identify the lines: example- line 22 talks about his beautiful wife being dead but he is
only seven years old, he doesn’t have a wife).
Graphic Organizer
o Have students complete the “poem” side of the graphic organizer Compare and Contrast: Poem/Video(appendix A) Save to use later
Group Task
o Place students into groups of three or four. Give each student a TP-CASTT analysis protocol (appendix A). Have students work in their groups to complete
each component of the protocol (either on notebook paper, chart paper, word processing, PowerPoint, etc.). Each student should complete/turn in/post their
own work but the work is done collectively in the group.
“Vincent” (video)
Watch the short video of “Vincent” being read by Vincent Price
http://shortsbay.com/film/vincent
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BIS04fIoUGA
IF neither of these links work, please log in to your active directory and go to www.youtube.com. Search “Vincent by Tim Burton” and a list of options
will become available for you to choose.
Discussion
o Allow students to talk with a partner about their first experience watching the video. The following questions can be answered whole group, with a partner
or in a small group:
How do the sound effects enhance the poem?
How do the visual images enhance the poem?
Why do you think the video is in black and white?
What technique does the video use to show the difference between what is real and what Vincent imagines? (real time the video is lighter, music is
usually happier, Vincent’s hair is ‘normal’ but during the imaginary time, the music is scarier, the images darker, hair is messy).
22
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Does the video match what you imagined?
How does the voice of Vincent Price reading the poem make you feel?
Why do you think Tim Burton wanted/had Vincent Price read the poem? What is the significance?
Graphic Organizer
o Have students complete the “video” side of the graphic organizer they worked on previously. (Titled: Compare and Contrast: Poem/Video(appendix A)).
Writing
o Students are going to write a short compare and contrast paper based on the poem “Vincent”. Explain to students that they are comparing and contrasting
how the poem was presented and their experience with both in each format. During the reading of the poem, students had to rely on the words and
descriptions to conjure images of what the poem was about. For the video, the music, sound and lighting effects played a role in the students understanding
of the poem as well as the voice of the narrator. Remind students that they aren’t comparing and contrasting the events or plot of the poem and video
because that is the same but more the presentation and their experiences of the poem in the two differing formats.
o Remind students that as they begin to organize their writing, it's important to make sure that they balance the information about the items that they're
comparing and contrasting. They will need to be sure to give both items equal time in what they write.
o There are three strategies to organize comparison and contrast papers:
1. Whole-to-Whole, or Block
o In this structure, you say everything about one item then everything about the other. For instance, say everything about the presentation
and/or what the student experiences regarding the characters, setting, structure and/or plot for the read poem and then everything about
the same for the video. Whole-to-Whole comparison and contrast uses a separate section or paragraph for each item you're discussing.
The points in each of the sections should be the same and they should be explained in the same order (for instance, you might discuss the
presentation of the character, setting, and plot for both, and in that order for both).
2. Similarities-to-Differences
o In this structure, you explain all the similarities about the items being compared and then you explain all the differences. For instance,
you might explain that the presentation and/or what the student experiences regarding the characters and plot were similar in both the
poem and video in the one section. In the next section, you could explain that the presentation and/or what the student experiences
regarding the characters and the plot were different. Similarities-to-Differences comparison and contrast uses a separate section or
paragraph for similarities and differences. In other words, the body of your paper would have two large sections: one for similarities, and
another for differences.
3. Point-by-Point
o In this structure, you explain one point of comparison before moving to the next point. For instance, you would write about the
presentation and/or the student experiences regarding the characters in the poem and video in one section; then you would write about the
presentation and/or the student’s experiences regarding the setting in the poem and video in the next section. Point-by-Point comparison
and contrast uses a separate section or paragraph for each point. For consistency, begin with the same item in each section of your pointby-point paper. For instance, for each point that you discuss, explain the information about the poem first and then about the video.
o Students will begin writing their compare/contrast paper. It should be at least four paragraphs long with short introductory/conclusion paragraphs and two
paragraphs for the body.
23
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Week 6: Sandra Cisneros
Learning Targets:
RI 9: Compare and contrast one author’s presentation of events with
that of another (e.g., a memoir written by and a biography on the same
person).
W 2: With the use of a graphic organizer, students will write a formal,
informative multiple paragraph piece to examine a topic. Students will
support the topic with important information and use various strategies
to examine the information about the topic.
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Standards:
RI 9: Compare and contrast one author’s presentation of events with that of another (e.g., a
memoir written by and a biography on the same person).
W 2: Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas, concepts, and
information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant content.
(2a,b,c,d,e,f)
Week 6: Teacher Background Knowledge/Key: This week students will read a memoir by Sandra Cisneros and a biography about her. Students will compare and
contrast the information they learn about Sandra Cisneros in both the memoir and the biography. It is important to explain to students the differences between a memoir
and a biography and explain that as they read the text their role as a reader is different and therefore the information they may learn and what they learn will be different.
The week will conclude with a short, four paragraph writing task in which the students will compare and contrast the author’s presentation of information in the
biography and the memoir.
Sandra Cisneros: Biography
Tasks
Reading a biography: Provide instruction on the definition and characteristics of a biography.
Ask students what they think of when they hear the word biography. Chart answers on board.
Explain that a biography is a narrative nonfiction/historical nonfiction which presents the facts about an individual's life and makes an attempt to interpret those
facts, explaining the person's feelings and motivations.
Explain that good biographers (authors of biographies) use many research tools to gather and synthesize information about their subject, including the person’s
words, actions, journals, reactions, related books, interviews with friends, relatives, associates and enemies, historical context, psychology, primary source
documents.
Explain that the purpose of a biography is often to understand the person and the events and history affected by that person. It is important to note that
biographers possess a point of view, a larger agenda and/or a purpose in reporting and writing on the person’s life.
Explain that a biography has a number of characteristics including:
o often starts with birth or early life and often covers birth-to-death
o often delves in to a person's formative years, exploring early influences on a subject's later life
o situates person’s life in historical terms and a cultural context
o uses direct quotes from person and those who knew her
o sometimes uses fictionalized scenes/dialogues but always based on what is known about the person and the events described,
o often uses pictures, maps, photographs, or other historically available documents.
The role of the reader: Explain that as a reader of a biography, one should consider author’s purpose in presenting the biography. Is it idealized? fair? Why or
why not? Who is the biographer? When was this biography written? How does this affect my reading of it? How does this help me to understand the influence
of this person on history, and history and culture’s effect on her? How might this person be a model for things to do or not do in my own life?
24
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Read: Sandra Cisneros: Biography (appendix D)
Close Reading of Sandra Cisneros: Biography
o When doing a close read on a biography,
First Read: Explain to students the purpose for reading the biography is to gain knowledge about the life and career of Sandra Cisneros. Have students read
text as independently as possible. Depending on the text complexity and the readers, the first read may be done independently, as a read aloud/think aloud, or
paired or shared reading. The first read should be without building background; students should be integrating their background knowledge with the text as they
read. Focus on the key ideas and details in the text, making sure that readers know the main idea, story elements, or key details that the author includes. What’s
the gist of the biography? As they identify the main idea and details tell them to think about what type of information is being provided in the biography. They
may mark/annotate the text as needed.
o After the first read, have students discuss (with a shoulder partner) the key ideas and details they learned about Sandra Cisneros. Have them discuss the
type of information: Personal? Professional? Feelings? If they are Cisneros feelings, how does the text explain her feelings? (ex- quotes). Etc.
Second Read: Students read the biography a second time. Have them underline words or phrases that they are unfamiliar with or need clarification.
o After the second read, have the students discuss (with a shoulder partner) the vocabulary- words and phrases that they found confusing or unfamiliar. Let
the pairs discuss what they found confusing and give them an opportunity to help each other with comprehension.
o As a whole class, go back to the text and ask the students what they are struggling with and clarify information they are struggling with.
Third Read: Have students read the biography a third time. Tell the students to think about the following questions as they read: What childhood experiences
helped shape Cisneros writing career? What does Cisneros mean when she said that at school she learned “what I didn’t want to be, how I didn’t want to
write.”? How does the structure of the text (events are in chronological order) help you understand her life and career? What might be missing (lead the
students to understand that this biography covers her entire life on one page and it gives key events in her life but doesn’t tell the whole story)- is this biography
her entire life story or just the important parts? Who decided on the important parts? (author). This would be a good place to explain that the author of the
biography plays a key role in deciding what information is included and what information is not.
o Have students answer the following questions with their shoulder partners after they are done reading for the third time. After they have answered and
discussed these questions with their partners, bring the class back together and discuss whole group.
Graphic Organizer
o With a partner or in groups, have students complete the Biography/Memoir Graphic Organizer (appendix A). Students should be able to work
independently if the close reading was done prior and discussions were supported after each read.
“Only Daughter” by Sandra Cisneros
Tasks
Reading a memoir: Provide instruction on the definition and characteristics of a memoir.
Ask students what they think of when they hear the word memoir. Chart answers on the board. If they don’t say memory, direct them to that example.
Explain that a memoir is a personal narrative that focuses on a specific period in the author’s life and describes in some detail the persons, events, or times
known to author.
Explain that a memoir is different than an autobiography in that it provides a detailed snapshot of a certain time in the writer’s life, rather than an account of the
writer’s entire life. Another difference between a memoir and an autobiography is that memoirists (the person who writes the memoir) are usually persons who
have played roles in, or have been close observers of, historical events. The memoirist takes it upon himself or herself to describe those events in some detail
while at the same time reflecting upon their influence and effects.
The role of the author/memoirist: Explain that a memoirist writes with two general purposes in mind: to tell a compelling story of a part of his or her life, and to
tell about the people, places, and times that had an influence on his or her life/personality.
25
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
The role of the reader: Explain that as a reader of a memoir, the purpose is to understand all that the author describes. In addition, a reader should derive some
enjoyment from the writing and perhaps learn something about himself or herself. Also, the reader should try to make a personal connection to a memoir.
Explain to students that connecting to the people, places, and events the writer describes can make the writer’s reactions easier to understand. It can also help
students more thoughtfully reflect upon the “portrait” the writer has created.
Read “Only Daughter” by Sandra Cisneros
Close Reading of “Only Daughter”
o When doing a close reading of a memoir, students need to identify the events and feelings of the author in order to understand the life lesson or author’s
purpose for writing the memoir. Therefore, the first close read will look at the events, the second read will focus on the feelings and the third will focus on
the overarching life experiences, life lessons and/or purpose for the memoir).
o Point out text features. Notice that the memoir is written in two columns and vocabulary support is in the footnotes. You may need to point out how to use
the footnotes: the first word ‘anthology’ is in line 4 and it has a small number 1 next to the ‘y’. This corresponds to the vocabulary at the bottom. Also
point out that Sandra Cisneros, as a bilingual author, includes words and phrases in Spanish within her writing. It’s okay for the students to try and even
struggle with the words in Spanish.
o Differentiation: If the passage is too long for your students to read in one sitting- divide the paragraphs. Have all students read the first four paragraphs
following the close reading procedures (first, second, third read) and then later or the next day move onto the next set of paragraphs. It is okay to break up
the reading into multiple days.
First Read: Have students read the memoir independently for the first reading. It’s okay for them to struggle with comprehension. Have students focus on the
setting (time and place) of the memoir as well as the experiences in the person’s life the story describes. They can take notes and annotate as needed.
o After the first read, have students discuss (with a shoulder partner) the setting of the memoir and identify the experiences in the person’s life the story
describes. Provide support if the students are struggling understanding the setting but full analysis will come after the last reading.
Second Read: Have students read the memoir independently the second time. Have students focus on the words and phrases that express the feelings of the
author.
o After the second read, have students discuss (with a shoulder partner) the words and phrases they circled regarding the feelings of the author. Let the pairs
discuss what they found confusing and give them an opportunity to help each other with comprehension. Bring the class back together to discuss whole
group what the students circled and their discussion. Prompt with the questions: how does she (Cisneros) feel? How do you know? What words/phrases
indicate that is how she feels? Make sure to emphasize that the memoir reflects the feelings the author experienced during the time she is describing.
Third Read: Have the students read a third time. Students will be picking out details that help support the experience that Cisneros is writing about. Remind
the students to think about the following ideas/questions as they read: the author is writing to describe something wonderful that happened to her: What is it?
Why is it wonderful? Why does Cisneros w Why does Cisneros write many words and phrases in Spanish? (cultural connection, pride, bilingualism, etc). What
does that tell us how she feels about her heritage and culture? What were Cisneros’ father’s expectations for her? What did he want her to do? How are we able
to learn so many personal things about Cisneros? What do you feel while reading her memoir? What techniques does she use to make you feel her story?
o After the second read, have students discuss (with a shoulder partner) the questions. After partner discussion, bring the class back together and have a class
discussion on the questions. Point out that reading a memoir allows us to look into a person’s heart and really learn about how they feel about her life
experiences.
o Ensure that students realize that Cisneros wrote very personal information in her memoir- almost like a diary. Students may need to be given examples
such as – would you want everyone in this room to read what you put in your diary? Or would you want them to know about your most personal fears? Or
insecurities?
Graphic Organizer
With a partner or in groups, have students complete the Biography/Memoir Graphic Organizer (appendix A). Students should be able to work independently if
26
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
the close reading was done prior and discussions were supported after each read. This is just to support and further their understanding of the information
provided by the text.
T-Chart (save to use with the writing)
Either with a partner/group or whole class depending on your students, complete a T-Chart about what the students experienced while reading the biography
and what they experienced by reading the memoir. Example items for the biography: lots of information, factual, chronological. etc. Example for the memoir:
personal insight, focused on one event but used flashbacks, reader could feel how she felt, etc.
Writing
Students are going to write a short compare and contrast paper based on the biography about Cisneros and her memoir. Explain to students that they are
comparing and contrasting how the biography was presented, how the memoir was presented and their experience reading both. During the reading of the
biography, students had to rely on the facts and information the author choice to present in a chronological order. Students got an idea of who Cisneros was
based on that information. They were able to learn how Cisneros felt through the use of quotes. In the memoir, students learned about Cisneros through reading
about a very personal experience she had with her father. She expressed her feelings and told the read about personal experiences she had growing up (her point
of view). Remind students that they aren’t comparing and contrasting the events in the biography and memoir but the presentation of each and their experiences
reading the two differing formats.
Remind students that as they begin to organize their writing, it's important to make sure that they balance the information about the items that they're comparing
and contrasting. They will need to be sure to give both items equal time in what they write.
There are three strategies to organize comparison and contrast papers:
1. Whole-to-Whole, or Block
In this structure, you say everything about one item then everything about the other. For instance, say everything about the presentation and/or what
the student experiences regarding the biography and then everything about the same for the memoir. Whole-to-Whole comparison and contrast uses a
separate section or paragraph for each item you're discussing. The points in each of the sections should be the same and they should be explained in the
same order.
2. Similarities-to-Differences
In this structure, you explain all the similarities about the items being compared and then you explain all the differences. For instance, you might
explain that the presentation and/or what the student experiences were similar in both the biography and memoir in the one section. In the next section,
you could explain how the presentation and/or what the student experiences were different. Similarities-to-Differences comparison and contrast uses a
separate section or paragraph for similarities and differences. In other words, the body of your paper would have two large sections: one for
similarities, and another for differences.
3. Point-by-Point
In this structure, you explain one point of comparison before moving to the next point. For instance, you would write about the presentation and/or the
student experience regarding one piece of both the biography and the memoir in one section; then you would write about the presentation and/or the
student’s experiences regarding another piece for both the biography and the memoir in another section. Point-by-Point comparison and contrast uses a
separate section or paragraph for each point. For consistency, begin with the same item in each section of your point-by-point paper.
Students will begin writing their compare/contrast paper. It should be at least four paragraphs long with short introductory/conclusion paragraphs and two
paragraphs for the body.
27
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Weeks 7: “Eleven”
Learning Targets:
RL2: Students will distinguish between objectivity and subjectivity when
analyzing a text, consider literary elements as well as facts when determining
the theme and provide an objective summary of the text.
RL 3: Using a graphic organizer, students will describe how the plot of a story
or drama develops sequentially as conflict drives the action. Students will
describe how the characters respond or change as the plot moves toward a
resolution.
Grade: 6
Standards:
RL 1: Cite textual evidence to support analysis of what the text says explicitly as well
as inferences drawn from the text.
RL 2: Determine a theme or central idea of a text and how it is conveyed through
particular details; provide a summary of the text distinct from personal opinions or
judgments.
RL 3: Describe how a particular story’s or drama’s plot unfolds in a series of episodes
as well as how the characters respond or change as the plot moves toward a resolution.
.
Teacher Background Knowledge/Key Information Weeks 7 and 8: Weeks 7 and 8 focus on short stories and the summative writing assignment.
If you have a Russian nesting doll, or something like that, or a tree stump with rings you could use these things to help your students visualize the theme of her
poem.
Cisneros creates word pictures that appeal to the senses. Her images connect to sight, touch and hearing. You may want to use this poem to discuss how authors
vivid, descriptive language in their writing.
The author uses many interesting and vivid comparisons throughout the poem as well. You may want to review similes and other figurative language as you
find it in the text.
Some of the discussion questions lend themselves very well to a Socratic Seminar and/or Accountable Talk sessions. Use these links to learn more about
Socratic Seminars:
http://www.readwritethink.org/professional-development/strategy-guides/socratic-seminars-30600.html#related-resources
http://www.authenticeducation.org/documents/WhatSeminar04.pdf
http://www.scholastic.com/teachers/top-teaching/2010/11/higher-order-comprehension-power-socratic-seminar
Use these links to learn more about Accountable Talk:
http://msopage.weebly.com/uploads/3/8/5/1/3851505/203_accountable_talk_toolkit_10-09.pdf
http://ifl.lrdc.pitt.edu/ifl/index.php/resources/other_resources
Accountable Talk Rubric:
http://www.guilford.k12.ct.us/sites/rebhunj/documents/modACCOUNTABLETALKRUBRIC_000.pdf
Develop Vocabulary & Concepts: The vocabulary in this short story is not difficult, but there are concepts that you might explore with your students regarding the
passage of time…such as rings inside a tree and other ways to measure time passing)
“Eleven” by Sandra Cisneros
Tasks
Read “Eleven” by Sandra Cisneros
Post Reading-Discussion Questions (these questions can serve as Socratic Seminar starters, quick writes, journal topics, small group sharing, etc.):
Why doesn’t Rachel want to be eleven in the story?
What are some of the life experiences you have had that are significant in the “rings” of your life?
How did Sandra Cisneros write the story so that it seems as though it was written by Rachel herself?
28
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Have you ever had an experience that could relate to Rachel’s?
How does the author use vivid, specific, sensory details and figurative language to evoke a child’s perspective to help the reader understand Rachel’s feelings?
What is the effect that age and authority have on the relationship between a student and a teacher?
What is the simile and other vivid details the author uses to make Rachel’s feelings about the sweater clear?
Rachel’s words in paragraph 10 contain an ellipsis (…). What is the author probably trying to show? (Rachel is unable to express herself to Mrs. Price.)
How does the event in class affect her feelings about her eleventh birthday?
What assumptions does Mrs. Price seem to make about Rachel? Why didn’t Rachel just refuse to put on the sweater? If you were Rachel, what would you have
done?
Explain whether you think Rachel makes her situation worse by how she acts over the sweater.
At the end of the story, Rachel says that “everybody will sing Happy birthday,…only it’s too late.” What is “too late”? What can you infer about Rachel and
about how the situation has affected her?
What does Rachel want more than anything else? Why does she want that? What factors directly and indirectly influence the behavior of Rachel in this
situation? How does her behavior reveal her character? What choices are available to her?
How should authority figures treat/interact with those they have power/influence over? Does higher age imply more wisdom? What is the worst thing that Mrs.
Price did? Why?
Sequence of Events
After beginning with Rachel’s reflections on growing up, the passage describes a single morning’s events in chronological order. Markers in paragraph 5 such
as “Only today I wish...” and “Today I wish...” signal the transition from reflection to action. Have students trace the events in this section using the bottom half
of the “Change Character Continuum” organizer (keep to use for a CFA later on). Ask students what conflict drives all of this action.
Making Inferences
Writers seldom explain everything. You must figure out some things by making inferences: combining clues in the text with what you know to make an
educated guess. To practice determining implicit meaning from ideas in context discuss the Implicit Meaning graphic organizer (Appendix A)
Class Discussion-Making Inferences
In the story, Rachel thinks of herself as being ages ten, nine, eight, and so on. What does this suggest to the reader about Rachel? (She is the product of
everything that happened to her.)
When Rachel moves the red sweater to the corner of her desk, as far away as possible from everything what does this imply about her feelings
towards the sweater? How do you know? What makes you think so?
In paragraph 5, why does Rachel say that she wishes she was “one hundred and two instead of eleven”? (She wishes she had more life experience.)
In paragraph 19 why does Rachel start to cry?
Small Groups-Identifying Explicit Information
Write the following questions on the white board and assign small groups to discuss the answers and be ready to tell where they found their answers in the text:
According to Rachel, “the part of you that’s five” sometimes needs to ______ ? Where did you find this answer?
Rachel compares “growing old” to __________. Where did you find this answer?
What does Mrs. Price put on Rachel’s desk? What mistake has Mrs. Price made?
For Rachel, when is the worst part of her day?
Hold a class discussion. Ask students to cite the part of the text where they found their answers.
29
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Characterization
A writer may directly tell you that a character is shy or sad, or he or she may make it obvious by revealing a character’s shy actions, or sad thoughts or physical
appearance. A writer may also hint at a character’s traits by how other characters respond to her. Write the following questions on the white board for students
to refer to as they fill in the “It says, I say, And so” graphic organizer (Appendix A)
How does Sandra Cinsneros reveal Rachel’s character through her actions and thoughts and physical appearance?
How do other characters in the story respond to Rachel?
What does this tell you about her?
Cite specific examples from the story as you and your partner complete the “It Says/I Say/And so” graphic organizer (Appendix A).
Quick Write or Journal Entry
Explain what Rachel means by this statement from paragraph 3: “Because the way you grow old is kind of like an onion or the rings inside a tree trunk
or like my little wooden dolls that fit one inside the other, each year inside the next one.” Use relevant and specific information from the story to support your
answer.
What does Rachel most likely mean by this statement from paragraph 13: “But when the sick feeling goes away and I open my eyes, the red sweater’s still
sitting there like a big red mountain.”
Exploring Theme
A theme is a main or central idea, concern or purpose in a literary work. It is a "big" statement that a piece of literature makes about particular subjects. Works
can have many subjects and many themes and both are open to interpretation. It is best to express a theme in a full sentence. Discuss some subjects of
“Eleven”: growing up, childhood and the influence people’s experiences have on them. Sometimes a good way of determining a theme of a story is to ask:
What lessons do the characters learn? What are TWO lessons Rachel learns?
Use the “What’s This REALLY All About” graphic organizer (Appendix A) to explore themes in “Eleven.”
CFA
Using the character continuum graphic organizer (the bottom half was already completed in class), students will add words to the top of the continuum line to
describe how Rachel responds or changes as the plot moves towards a resolution.
How do you think Rachel gets along with the other students? How does she feel about her-self? Use the It Says/I Say/And So graphic organizer to make
inferences about both questions.
Extension Activities:
Write an essay describing your most embarrassing moment. Use vivid details to bring your experience to life for the reader.
Write a story from the point of view of someone who is a least five years younger than you.
Take Rachel’s story and turn it into a poem.
Continue the story, describing what happened when Rachel returned home at the end of her school day.
Write a poem about Rachel using the following template:
If Rachel were an object she would be an ___________________ because ___________________________________________________.
If Rachel were a song she’d be ___________________________ because _________________________________________________________.
If Rachel were an emotion it would be ___________________ because ________________________________________________________.
If Rachel were an animal it would be a _________________________ because _________________________________________________.
30
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Theme Collage: Complete a collage which demonstrates your understanding of one of the themes from “Eleven.” Tor create the collage, use a sheet of
construction paper or poster board. You will also need access to pictures and words from magazines and/or the computer. Include your theme statement on your
collage.
31
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Weeks 8: Summative
Learning Targets:
RL 9: Students will distinguish between different forms of a text (e.g. stories,
poems, dramas) as well as different types of genres (e.g. historical fiction,
fantasy, science fiction) with a focus on the devices authors use in each (e.g.
figurative language, voice, character interaction). Students will discuss and
chart the characteristics of each. Students will compare and contrast the
characteristics of different forms and genres.
W 2: With the use of a graphic organizer, students will write a formal,
informative multiple paragraph piece to examine a topic. Students will support
the topic with important information and use various strategies to examine the
information about the topic.
Teacher Background Knowledge/Key Information Weeks 8:
Grade: 6
Standards:
RL 9: Compare and contrast texts in different forms or genres (e.g., stories and poems,
historical novels and fantasy stories) in terms of their approaches to similar themes
and topics.
W 2: Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas,
concepts, and information through the selection, organization, and analysis of relevant
content. (2a,b,c,d,e,f)
Summative Assessment
Write an informative/explanatory multi-paragraph essay comparing and contrasting the short story “Eleven” by Sandra Cisneros to the poem “Nikki-Rosa” by
Nikki Giovanni. Use the following guidelines:
7. Focus the essay on the similarities and differences in how the authors develop the theme and the point of view of the narrators.
8. Introduce and state a topic.
9. Organize a body of two or three paragraphs to support the topic.
10. Use the similarities-to-differences strategy (a variation of the point-by-point method) to organize and format the essay.
4. Compare themes & points of view (1-2 paragraphs)
5. Contrast themes & points of view (1-2 paragraphs)
11. Use citations and evidence from the pieces.
12. Provide a conclusion.
The following graphic organizers can be used to assist in the writing process:
1. “Compare & Contrast: Similarities-to-Differences Strategy”, Appendix A
2. VENN Diagram, Appendix A
32
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
NOTES
33
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Appendix A
Graphic Organizers
34
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Compare / Contrast Organizer (RI6.9) “A”
Similarities:
Biography
Differences:
Biography
Interview
Category
Interview
_______________________
_______________________
_______________________
_______________________
_______________________
Conclusion: (What trends or patterns did you discover in the similarities and differences?)
35
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
TP-CASTT
Analysis Protocol
TITLE: Examine the title on an interpretive level. What does the title mean?
PARAPHRASE: Translate the poem line by line into your own words on a literal level. Look for
complete thoughts (sentences may be invented) and examine unfamiliar words.
CONNOTATION: Examine the poem for meaning beyond the literal. Look for figurative
language, imagery, and sound elements.
ATTITUDE/TONE: Notice the speaker’s tone and attitude. Humor? Sarcastic? Awe? How do
you know?
SHIFTS: Note any shifts or changes in speaker and attitude. Look for key words, time change,
and punctuation.
THEME: Briefly state in your own words what the poem is about then what the poet is saying
about the subject.
36
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Prompt
Person’s name, time
period, and place
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Biography/Memoir Graphic Organizer
Information
Personal Background
Personality Traits
Significance
Obstacles
Important Quote
37
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
QuIP Strategy
(Questions into Paragraphs)
Answers
Questions
Source 1
Source 2
a.
b.
c.
38
Summary
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Compare and Contrast Graphic Organizer (RI.6.9) “B”
A way to compare 2 or more concepts/texts by looking at similarities and differences. Choose two different texts about a similar topic
with two different authors (Adapted from Marzano, 2001)
↓
↓
↓
↓
Main Topic
→
←
↑
↑
39
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
40
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
41
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Implicit Meaning Organizer
In the story it says…
I say…(what you know)
Rachel thinks of herself as being ages
ten, nine, eight and so on.
that Rachel moves the red sweater to the
corner of her desk, as far away as
possible from everything.
that Rachel wishes she was “one
hundred and two instead of eleven”
that Rachel starts to cry.
42
And so…(inference)
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
It Says/I Say/And so
In the story it says…
I say…
And so…
43
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
COMPARE & CONTRAST
Similarities-to-Differences Strategy
INTRODUCTION
(1 paragraph)
SIMILARITIES
(1-2 paragraphs)
Theme: “Nikki-Rosa”
Point of View: “Nikki-Rosa”
Theme: “Eleven”
Point of View: “Eleven”
DIFFERENCES
(1-2 paragraphs)
Theme: “Nikki-Rosa”
Point of View: “Nikki-Rosa”
Theme: “Eleven”
Point of View: “Eleven”
CONCLUSION
(1 paragraph)
With this structure, the writer uses separate sections of the paper to discuss similarities
and differences.
So, the body of the essay will have two large sections: one for similarities and one for
differences.
First, explain all the similarities between “Nikki-Rosa” (poem) and “Eleven” (short
story), regarding theme and point of view.
Then, discuss all of the differences found in “Nikki-Rosa” and “Eleven”, regarding
those same areas of theme and point of view.
44
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
COMPARE & CONTRAST
Similarities-to-Differences Strategy
INTRODUCTION
CONCLUSION
45
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
46
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
47
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
48
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
49
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
50
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Character Change Continuum
Copyright 2005 IRA?NCTE. All rights reserved.
ReadWriteThink materials may be reproduced for educational purposes.
51
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Character Change Continuum
Thank You, Mr. Falker by Patricia Polacco
(How the character changes as the events of the plot unfold.)
Self-Confident
↓
↓
Losing Self-Confidence
↓
No Self-Confidence
↓
↓
↓
Self-Confident
↓
↓
Trisha works
Trisha can
Trisha
Trisha goes
Trisha is in
Trisha’s
Trisha is
Trisha gets a
believes she
to
grade one
family moves
bullied
new teacher
with Mr.
will learn to
kindergarten
and begins to
and she goes
because she
who tells her
Falker and
read.
and likes to
feel “dumb”
to a new
can’t read.
draw but
because she
school.
doesn’t learn
can’t read.
(The main events of the plot.)
Copyright 2005 IRA?NCTE. All rights reserved.
ReadWriteThink materials may be reproduced for educational purposes.
52
she is not
Miss Plessie
d umb.
to learn to
read.
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Quote Me!
When the author of a poem is also the narrator inside the poem, we can tell a lot about his
or her thoughts, ideas and feelings. Your job is to select 3 quotes from the poem, “Nikki
Rosa” and explain what important idea Giovanni is trying to express about her childhood.
Quote #1
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
In this quote, Nikki Giovanni is trying to say ___________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
I think this because________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
Quote #2
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
In this quote, Nikki Giovanni is trying to say ___________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
I think this because________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
Quote #3
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
In this quote, Nikki Giovanni is trying to say ___________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
I think this because________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
53
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Making Inferences about Eleven
In the story it says…
Rachel thinks of herself as being
ages ten, nine, eight and so on.
I say…(what you know)
that Rachel moves the red sweater to
the corner of her desk, as far away
as possible from everything.
that Rachel wishes she was “one
hundred and two instead of eleven”
that Rachel starts to cry.
54
And so…(inference)
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
What’s it REALLY All About?
Theme
Supporting evidence from text
So what? What does this theme mean to me? How does this relate to my life?
55
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Appendix C
Samples
56
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
57
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
58
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Appendix D
Resources
59
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Autumn Movement
I cried over beautiful things knowing no beautiful thing lasts.
The field of cornflower yellow is a scarf at the neck of the copper
sunburned woman, the mother of the year, the taker of seeds.
The northwest wind comes and the yellow is torn full of holes,
new beautiful things come in the first spit of snow on the northwest wind,
and the old things go, not one lasts.
60
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Sandra Cisernos:
Biography
Sandra Cisneros was born in Chicago, Illinois, on December 20, 1954. The only daughter in a family of
seven children, she grew up speaking both English and Spanish. Her mother, Elvira Cordero Anguiano, was a selfeducated Mexican American who kindled her children’s enthusiasm for reading by taking them to libraries. Her
father, Alfredo Cisneros Del Moral, was a Mexican upholsterer. With a Mexican American mother, a Mexican
father, and six brothers, she described her circumstances as being similar to having seven fathers. Because of close
familial and cultural ties with Mexico, the Cisneros family moved back and forth between a series of cramped
apartments in Chicago and the paternal grandmother’s home in Mexico City. The concept of home or the lack of
one would later weigh heavily in Cisneros’ writing. The combination of an uprooted lifestyle and an ever-changing
circle of friends, schools, and neighborhoods, as well as the isolation that resulted from her brothers’ unwillingness
to let a girl join in their play, led Cisneros to turn inward to a life of books. That time spent alone allowed an
observant, creative voice to take root in the author.
In Chicago Catholic schools, where expectations for Mexican American girls were low, Cisneros was a
below-average student, but she read voraciously and began writing early. After graduating from Loyola University
in Chicago in 1976, she earned a master’s degree at the prestigious Iowa Writers Workshop, where she learned
“what I didn’t want to be, how I didn’t want to write.”
Upon returning from graduate study to Chicago, she awakened to what she called the “incredible deluge of
voices” that has become the hallmark of her writing. Her stories and poems reveal a variety of voices, Mexican
American voices mainly, telling their stories in exuberant mixture of English and Spanish. Her writing career
started slowly. She earned her living as a teacher, college recruiter, arts administrator, writing teacher, and lecturer.
Her choice to remain poor in order to write has puzzled her father and brothers and often caused her to wonder
whether she was betraying her beloved Mexican American culture by choosing a nontraditional life.
Cisneros's work crosses genres, falling into the various categories of fiction, poetry, and memoir. Her first
and most noted work, The House on Mango Street, was published in 1984 and soon won a selection of prestigious
awards, such as the Columbus Foundation's American Book Award in 1985, which led to fellowships and grants
from the National Endowment for the Arts and teaching/lecturing positions across the country. During this time of
discovery, Cisneros divided her time between California and Texas, constantly returning to her roots in Chicago.
Cisneros has written a substantial amount of material, all garnering significant praise and respect. Her first
book of poetry, My Wicked, Wicked Ways was published in 1987, followed by a book of short stories, Woman
Hollering Creek, published in 1991, and Loose Woman in 1994. It was this final collection of short fiction that
guaranteed Cisneros a place amongst the American Writers of the 20th century, winning the PEN Center West
Award for Best Fiction, Quality Paperback Book Club New Voices Award, Anisfield-Wolf Book Award, and the
Lannan Foundation Literary Award. Cisneros's work has been highlighted and lauded by The New York Times and
American Library Journal.
Cisneros continues to write and currently lectures at youth centers, community colleges, and universities
around the country, just like her central character Esperanza vows to do in The House on Mango Street. The
character of Esperanza in The House on Mango Street has been compared to such literary icons of Americana as
Huckleberry Finn.
61
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
“Vincent”
Vincent Malloy is seven years old
He’s always polite and does what he’s told
For a boy his age, he’s considerate and nice
But he wants to be just like Vincent Price
He doesn’t mind living with his sister, dog and cats
Though he’d rather share a home with spiders and bats
There he could reflect on the horrors he’s invented
And wander dark hallways, alone and tormented
Vincent is nice when his aunt comes to see him
But imagines dipping her in wax for his wax museum
He likes to experiment on his dog Abercrombie
In the hopes of creating a horrible zombie
So he and his horrible zombie dog
Could go searching for victims in the London fog
His thoughts, though, aren’t only of ghoulish crimes
He likes to paint and read to pass some of the times
While other kids read books like Go, Jane, Go!
Vincent’s favorite author is Edgar Allen Poe
One night, while reading a gruesome tale
He read a passage that made him turn pale
Such horrible news he could not survive
For his beautiful wife had been buried alive!
He dug out her grave to make sure she was dead
Unaware that her grave was his mother’s flower bed
His mother sent Vincent off to his room
He knew he’d been banished to the tower of doom
Where he was sentenced to spend the rest of his life
Alone with the portrait of his beautiful wife
While alone and insane encased in his tomb
Vincent’s mother burst suddenly into the room
She said: “If you want to, you can go out and play
It’s sunny outside, and a beautiful day”
Vincent tried to talk, but he just couldn’t speak
The years of isolation had made him quite weak
So he took out some paper and scrawled with a pen:
“I am possessed by this house, and can never leave it again”
His mother said: “You’re not possessed, and you’re not almost dead
62
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
These games that you play are all in your head
You’re not Vincent Price, you’re Vincent Malloy
You’re not tormented or insane, you’re just a young boy
You’re seven years old and you are my son
I want you to get outside and have some real fun.”
Her anger now spent, she walked out through the hall
And while Vincent backed slowly against the wall
The room started to swell, to shiver and creak
His horrid insanity had reached its peak
He saw Abercrombie, his zombie slave
And heard his wife call from beyond the grave
She spoke from her coffin and made ghoulish demands
While, through cracking walls, reached skeleton hands
Every horror in his life that had crept through his dreams
Swept his mad laughter to terrified screams!
To escape the madness, he reached for the door
But fell limp and lifeless down on the floor
His voice was soft and very slow
As he quoted The Raven from Edgar Allen Poe:
“and my soul from out that shadow
that lies floating on the floor
shall be lifted?
Nevermore…”
63
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Tim Burton:
Biography
Synopsis
Tim Burton was born on August 25, 1958, in Burbank, California. After majoring in animation at the California
Institute of Arts, he worked as a Disney animator for less than a year before striking out on his own. He became
known for creating visually striking films that blend themes of fantasy and horror, including Beetlejuice, Edward
Scissorhands, Batman, and The Nightmare Before Christmas.
Early Films
Famed director, producer and screenwriter Tim Burton was born Timothy Walter Burton on August 25, 1958, in
Burbank, California. As a child, Burton was engrossed with the classic horror films of Roger Corman—many of
which featured quintessential screen villain Vincent Price. Burton also developed a penchant for drawing and
enrolled at the California Institute of Arts, where he majored in animation. In 1980, upon his graduation, he began
working as an apprentice animator for Walt Disney Studios. Within a year, Burton grew tired with his work at
Disney and decided to strike out on his own. In 1982, he released the award-winning short Vincent, which paid
homage to the enduring work of his childhood idol.
In 1984, Burton created a unique version of the Frankenstein story with the live-action short Frankenweenie.
Impressed with Frankenweenie, Paul Reubens commissioned Burton to direct the wildly inventive comedy Peewee's Big Adventure (1985). The success of Pee-wee's Big Adventure brought about other opportunities, including
the 1988 ghost story Beetlejuice starring Michael Keaton, Alec Baldwin, and Geena Davis. Often considered the
prototypical Burton film, Beetlejuice was recognized for its visual flair and interwoven themes of fantasy and
horror.
After forming his own production company, Burton directed the lavish production Batman (1989). With a cast that
included Jack Nicholson, Michael Keaton, and Kim Basinger, the stylized feature became the first film to sell $100
million in the first 10 days of release. The following year, Burton helmed the bizarre but touching film Edward
Scissorhands. Featuring notable performances by up-and-coming stars Johnny Depp and Winona Ryder (as well as
Price's final feature role as the eccentric inventor), Edward Scissorhands was acclaimed for being both a social
satire and a simple tale of love and intolerance.
Batman and Beyond
Directing an ensemble that included Michelle Pfeiffer, Danny DeVito, and Christopher Walken, Burton reteamed
with Keaton for the 1992 Batman sequel, Batman Returns. The following year, he produced the animated musical
Tim Burton's The Nightmare Before Christmas. Created with the painstaking process of stop-motion animation,
the film became a critical and commercial success, while Burton was credited for his technical prowess.
In 1994, Burton cast Johnny Depp as the title character in Ed Wood—a black-and-white portrait of a middling
filmmaker and his all-consuming passion to succeed. Although critically praised (Martin Landau won a Best
Supporting Actor Oscar for his portrayal of a drug-addicted Bela Lugosi), the film failed to appeal to mass
audiences. After producing the third installment Batman Forever (1995) and the animated feature James and the
Giant Peach (1996), Burton directed the sci-fi spoof Mars Attacks! The film flopped at the box office despite an
all-star cast that included Jack Nicholson, Glenn Close, Annette Bening, and Pierce Brosnan.
In 1999, Burton directed a freely adapted film version, Sleepy Hollow, of Washington Irving's haunting tale The
Legend of Sleepy Hollow, in which Johhny Depp offered a notable performance as the heroic Ichabod Crane. In
2001, Burton took on an ambitious remake of the 1968 cult classic Planet of the Apes starring Mark Wahlberg and
Helena Bonham Carter. In 2005, he released a remake of Charlie and the Chocolate Factory starring Johnny Depp
and a stop-motion animated feature called The Corpse Bride, which received an Oscar nod for Best Animated
Feature Film.
Recent Projects
Continuing with his interest in ghoulish subjects, Burton directed the film adaptation of the popular musical
Sweeney Todd: The Demon Barber of Fleet Street in 2007. The film reunited Burton with longtime friend Johnny
Depp and Helena Bonham Carter. All three received critical praise for their work on the film, including several
64
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Golden Globe nominations. In 2010, they reunited again in Tim Burton's adaptation of Lewis Carrol's Alice In
Wonderland, wherein Depp played the role of The Mad Hatter and Carter, the Red Queen.
In 2012, Burton worked with Depp on a film adaptation of the cult television series Dark Shadows. Writer Seth
Grahame-Smith penned the script for this humorous look at a vampire living among his descendants. Burton also
mined his own childhood for the animated film Frankenweenie that same year. The title character—a dog brought
back to life—was inspired by one of his own pets. Pepe "just had a good spirit, that dog," Burton told
Entertainment Weekly. "The Frankenweenie character wasn’t meant to look like him. It was more just the memory
and the spirit of him."
In addition to his filmwork, Burton exhibited over 700 drawings, paintings, and other artwork at New York City's
Museum of Modern Art in 2009 and 2010.
Adapted from: http://www.biography.com/people/tim-burton-9542431
65
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
“Only Daughter”
Sandra Cisneros
Once, several years ago, when I was just starting out my writing career, I was asked to write my own
contributor’s note for an anthology1 I was part of. I wrote: “I am the only daughter in a family of six sons. That explains
everything.”
Well, I’ve thought about that ever since, and yes, it explains a lot to me, but for the reader’s sake I should have
written: “I am the only daughter in a Mexican family of sic sons.” Or even: “I am the only daughter of a Mexican father
and a Mexican-American mother.” Or: “I am the only daughter of a working-class family of nine.” All of these had
everything to do with who I am today.
I was/ am the only daughter and only a daughter. Being an only daughter in a family of six sons forced me by
circumstance to spend a lot of time by myself because my brothers felt it beneath them to play with a girl in public. But
that aloneness, that loneliness, was good for a would-be writer—it allowed me time to think and think, to imagine, to
read and prepare myself.
Being only a daughter for my father meant my destiny would lead me to become someone’s wife. That’s what
he believed. But when I was in the fifth grade and shared plans for college with him, I was sure he understood. I
remember my father saying, “Que Bueno, mi’ha, that’s good.” That meant a lot to me, especially since my brothers
thought the idea hilarious. What I didn’t realize was that my father thought college was a good idea for girls—good for
finding a husband. After four years in college and two more in graduate school, and still no husband, my father shakes
his head even now and says I wasted all that education.
In retrospect2, I’m lucky my father believed daughters were meant for husbands. It meant it didn’t matter if I
majored in something silly like English. After all, I’d find a nice professional eventually, right? This allowed me the
liberty to putter about embroidering3 my little poems and stories without my father interrupting with so much as a
“What’s that you’re writing?”
But the truth is, I wanted him to interrupt. I wanted my father to understand what it was I was scribbling, to
introduce me as “My only daughter, the writer.” Not as “This is my only daughter. She teachers.” Es maestro—teacher.
Not even profesora.
In a sense, everything I have ever written has been for him, to win his approval even though I know my father
can’t read English words, even though my father’s only reading includes the brown-ink Esto sports magazines from
Mexico City. Or the fotonvelas, the little picture paperbacks with tragedy and trauma erupting from the characters’
mouth in bubbles.
My father represents, then, the public majority. A public who is disinterested in reading, and yet one whom I
am writing about and for, and privately trying to woo4.
When we were growing up in Chicago, we moved a lot because of my father. He suffered bouts of nostalgia 5.
Then we’d have to let go of our flat6, store the furniture with mother’s relatives, load the station wagon with baggage
and bologna sandwiches and head south. To Mexico City.
We come back, of course. To yet another Chicago flat, another Chicago neighborhood, another Catholic school.
Each time, my father would seek out the parish priest in order to get a tuition break7, and complain or boast: “I have
seven sons.”
He meant siete hijos, seven children, but he translated it as “sons.” “I have seven sons.” To anyone who would
listen. The Sears Roebuck employee who sold us the washing machine. The short-order cook where my father ate his
ham-and-egg breakfasts. “I have seven sons.” As if he deserved a medal from the state.
1
anthology: collection of stories and other literature in a book.
retrospect: thinking about things in the past
3 embroidering: adding details to
4 woo: attract, interest
5 nostalgia: short periods of time with homesickness
6 flat: apartment
7 Tuition break: a decrease in the cost of going to a private school
2
66
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
My papa. He didn’t mean anything by that mistranslation, I’m sure. But somehow I could feel myself being
erased. I’d tug my father’s sleeve and whisper: “Not seven sons. Six! And one daughter.”
When my oldest brother graduated from medical school, he fulfilled my father’s dream that we study hard and
use this—our heads, instead of this—our hands. Even now my father’s hands are thick and yellow, stubbed by a history
of hammer and nails and twine and coils8 and springs. “Use this,” my father said, tapping his head, “and not this,”
showing us those hands. He always looked tired when he said it.
Wasn’t college a investment? And hadn’t spent all those years in college? And if I didn’t marry, what was it all
for? Why would anyone go to college and then choose to be poor? Especially someone who had always been poor.
Last year, after ten years of writing professionally, the financial rewards9 started to trickle in. My second
National Endowment for the Arts Fellowship. A guest professorship at the University of California, Berkley. My book,
which sold to a major New York publishing house.
At Christmas, I flew home to Chicago. The house was throbbing10, same as always: hot tamales and sweet
tamales hissing in my mother’s pressure cooker, and everybody—my mother, six brothers, wives, babies, aunts,
cousins—talking too loud and at the same time. Like in a Fellini11 film, because that’s just how we are.
I went upstairs to my father’s room. One of my stories had just been translated into Spanish and published in an
anthology of Chicano12 writing and I wanted to show it to him. Ever since he recovered from a stroke two years ago, my
father likes to spend his leisure hours horizontally13. And that’s how I found him, watching a Pedro Infante movie on
Galavision and eating rice pudding.
There was a glass filled with milk on the bedside table. There were several vials of pills and balled Kleenex.
And on the floor, one black sock. Pedro Infante was about to burst into song, and my father was laughing.
I’m not sure if it was because my story was translated into Spanish, or because it was published in Mexico, or
perhaps because the story dealt with Tepeyac, the colonia my father was raised in and the house he grew up in, but at
any rate, my father punched the mute button on his remote control and read my story.
I sat on the bed next to my father and waited. He read it very slowly. As if he were reading each line over and
over. He laughed at all the right places and read lines he liked out loud. He pointed and asked questions: “Is this Soand-so?” “Yes,” I said. He kept reading.
When he was finally finished, after what seemed like hours, my father looked up and asked: “Where can we get
more copies of this for the relatives?”
Of all the wonderful things that happened to me last year, that was the most wonderful.
8
Twines and coils: strings and loops
Financial rewards: money
10 Throbbing: beating
11 Fellini: an Italian movie director
12 Chicano: Mexican-American
13 Horizontally: laying down
9
67
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Nikki-Rosa
childhood remembrances are always a drag
if you're Black
you always remember things like living in Woodlawn
with no inside toilet
and if you become famous or something
they never talk about how happy you were to have
your mother
all to yourself and
how good the water felt when you got your bath
from one of those
big tubs that folk in chicago barbeque in
and somehow when you talk about home
it never gets across how much you
understood their feelings
as the whole family attended meetings about Hollydale
and even though you remember
your biographers never understand
your father's pain as he sells his stock
and another dream goes
And though you're poor it isn't poverty that
concerns you
and though they fought a lot
it isn't your father's drinking that makes any difference
but only that everybody is together and you
and your sister have happy birthdays and very good
Christmasses
and I really hope no white person ever has cause
to write about me
because they never understand
Black love is Black wealth and they'll
probably talk about my hard childhood
and never understand that
all the while I was quite happy
Retrieved from: http://nikki-giovanni.com/page_52.shtml
68
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Nikki Giovanni:
Biography
Nikki Giovanni is a world-renowned poet, writer, commentator, activist, and educator. Over the past thirty
years, her outspokenness, in her writing and in lectures, has brought the eyes of the world upon her. One of the
most widely-read American poets, she prides herself on being "a Black American, a daughter, a mother, a
professor of English." Giovanni remains as determined and committed as ever to the fight for civil rights and
equality. Always insisting on presenting the truth as she sees it, she has maintained a prominent place as a strong
voice of the Black community. Her focus is on the individual, specifically, on the power one has to make a
difference in oneself, and thus, in the lives of others.
Nikki Giovanni was born in Knoxville, Tennessee, and grew up in Lincoln Heights, an all-black suburb of
Cincinnati, Ohio. She and her sister spent their summers with their grandparents in Knoxville, and she graduated
with honors from Fisk University, her grandfather's alma mater, in 1968; after graduating from Fisk, she attended
the University of Pennsylvania and Columbia University. She published her first book of poetry, Black Feeling
Black Talk, in 1968, and within the next year published a second book, thus launching her career as a writer. Early
in her career she was dubbed the "Princess of Black Poetry," and over the course of more than three decades of
publishing and lecturing she has come to be called both a "National Treasure" and, most recently, one of Oprah
Winfrey's twenty-five "Living Legends."
Many of Giovanni's books have received honors and awards. Her autobiography, Gemini, was a finalist for
the National Book Award; Love Poems, Blues: For All the Changes, Quilting the Black-Eyed Pea, Acolytes, and
Hip Hop Speaks to Children: A Celebration of Poetry with a Beat were all honored with NAACP Image Awards.
Blues: For All the Changes reached #4 on the Los Angeles Times Bestseller list, a rare achievement for a book of
poems. Most recently, her children's picture book Rosa, about the civil rights legend Rosa Parks, became a
Caldecott Honors Book, and Bryan Collier, the illustrator, was given the Coretta Scott King award for best
illustration. Rosa also reached #3 on The New York Times Bestseller list. Shortly after its release, Bicycles: Love
Poems reached #1 on Amazon.com for Poetry.
Giovanni's spoken word recordings have also achieved widespread recognition and honors. Her album
Truth Is On Its Way, on which she reads her poetry against a background of gospel music, was a top 100 album
and received the Best Spoken Word Album given by the National Association of Radio and Television
Announcers. Her Nikki Giovanni Poetry Collection, on which she reads and talks about her poetry, was one of five
finalists for a Grammy Award.
Giovanni's honors and awards have been steady and plentiful throughout her career. The recipient of some
twenty-five honorary degrees, she has been named Woman of the Year by Mademoiselle Magazine, The Ladies
Home Journal, and Ebony Magazine. She was tapped for the Ohio Women's Hall of Fame and named an
Outstanding Woman of Tennessee. Giovanni has also received Governor's Awards from both Tennessee and
Virginia. She was the first recipient of the Rosa L. Parks Woman of Courage Award, and she has also been
awarded the Langston Hughes Medal for poetry. She is an honorary member of Delta Sigma Theta Sorority and
has received Life Membership and Scroll from The National Council of Negro Women. A member of PEN, she
was honored for her life and career by The History Makers. She has received the keys to more than two dozen
cities. A scientist who admires her work even named a new species of bat he discovered for her! Black Enterprise
named her a Women of Power Legacy Award winner for work that expands opportunities for other women of
color.
The author of some 30 books for both adults and children, Nikki Giovanni is a University Distinguished Professor
at Virginia Tech in Blacksburg, Virginia.
69
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Nikki Giovanni Interview Transcript
The author Nikki Giovanni was interviewed by Scholastic students in 2002.
How long have you been writing?
Since college, a long time, 30 years.
What inspired you to become a writer? How do you teach children that poetry does not have to rhyme?
I'm fascinated by people, by human beings, and that's what got me interested in writing. I think students already know that
poems don't have to rhyme. You just have to remind them that poems are about beauty and emotion; in other words poems
are about feelings.
Where do you get the inspiration to begin writing your poems? Once you begin writing do you find it easy to finish a
poem?
Yes, I do. Like most writers it's more difficult to begin a poem than to end one. But I have to have the information; it's
information that begins a poem.
Where did you grow up in Ohio?
Lincoln Heights.
What was your childhood like - did you enjoy reading and writing poetry as a kid?
At what age did you write in hopes of being published? I had a really nice childhood; I had great parents. I earned my
allowance by washing dishes, and in the summer I earned my allowance by working in daddy's garden. I'm not good in the
garden; I once pulled up all the peppers - I thought they were weeds. I definitely enjoyed reading, I didn't write much poetry
when I was a little girl, but I've always been a big reader. I did not think about publication until after college.
The information you use to write poems, is it based on personal experience or other things such as facts?
I hope it's based on facts, but I've personally experienced it to some degree. I think it's important to do research, and research
mostly is going to come from books, so all of your reading is potentially helpful to your poetry.
Why do you mix poetry with music?
Poetry and music are very good friends. Like mommies and daddies and strawberries and cream - they go together.
Did you dedicate a poem to Tupac Shakur? What was the name of it? Why?
Yes, the name is "All Eyes on You." I thought it was such a loss to the art community, the black community, and the
American community. I wanted to grieve.
You said you wanted to grieve for Tupac. Did your poem entitled "The Funeral of Martin Luther King, Jr." come
from the same place of wanting to grieve or was it more of a statement about how so often African-American leaders
are more admired dead than alive?
Those poems come from two different places and the King poem is much more a political poem in my opinion, but I'm not a
critic.
Who or what inspired you to write?
I'm just totally fascinated by people.
What is the most difficult poem you have written? Is it your favorite? Which poem has been your most popular?
My most popular poem is "Ego-Tripping." I've worked on all of them, and just hope they all turn out well.
70
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
What inspired you to write "Cotton Candy on a Rainy Day?"
I think life is cotton candy on a rainy day. For those who grew up with cotton candy the old-fashioned way, it is very delicate.
Pre-made cotton candy that has preservatives is not nearly as good or true. True cotton candy is sugar, color, and air and it
melts very quickly. That was the metaphor - it can't be preserved, it can't be put aside, it can't be banked. It has to be
experienced, like life.
Do you sit down and think about writing, or do you just get sudden inspirations?
I sit down and think about writing specific poems at specific times.
Which of your books is your personal favorite?
I like them all.
What do you like to do in your free time?
I play a little tennis; I like to cook; I like to read, and I love listening to music. I'm also a bird watcher. I spend a lot of time
learning about bird watching.
What books did you read growing up?
I read from my mother's library mostly. So I read a lot of romantic novels, but I've also always been a lover of science fiction
and those are two main areas, science fiction and Victorian novels.
Can you give us some suggestions to increase students' interest in reading and writing?
My main suggestion, and don't laugh, we should read to the students. My students and I in my Introduction to Creative
Writing Class (college level) read Tim O'Brien's In the Lake of the Woods. I had thought they wouldn't want to hear a story
being read, I really did. It turned out to be one of our really wonderful experiences. If you want students to read - read to
them.
Do any of the artists you listen to inspire your poems?
Yes, but looking at my earlier work you will see the Gospel influence; I grew up in the Baptist church. And moving into My
House poems you'd see the jazz influence.
Have you worked with any other choirs after the one with James Cleveland?
I worked with the New York Community Choir under the direction of Bennie Diggs. I had the pleasure of knowing Reverend
Cleveland, and he used to say I stole his song (laughing). James is a great man.
How old were you when you wrote your first poem?
Sixteen? Seventeen? A teenager.
Why did you write "Ego-Tripping?"
Because I wanted to give something to girls. Boys have everything to support their independence and area of wonderfulness;
they have baseball players and astronauts. I wanted the young women to know that we too are wonderful, everything that
happened we did it. I love that poem. I must add if I may, the joy has been that the boys have liked it also. Hearing boys
recite it has been wonderful to me, which means that things that are born of love - bring love. That poem came from a lot of
love.
What do you like about poetry?
I like being able to express my thoughts. That's what I like most about it.
On the average, how long does it take you to write a poem?
I'm a professional writer so I don't want to approach a young writer on that level; it gives them a false sense of possibilities.
71
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
What part of poem writing do you like the most?
The anticipation.
What was your first published poem?
I don't remember the first poem, but the first book was Black Feeling, Black Talk.
How did you go about getting your first poem published?
I think I just submitted it to the magazine or newspaper. I formed a publishing company to publish the first book; it's a
business situation. That's how we did it, and sold the books. You have to separate business and art. I didn't want to go to a
publisher because I didn't want to be rejected. I still don't have an agent. I'm a poet - poets don't need agents.
Do you write a "rough draft" or do you submit your poetry as it first comes to you?
Probably right now, neither, I work on the computer so I make the edits right there. I'm not in school, which makes a
difference. I don't write drafts; I write on the computer.
As an African-American poet, did you face any problems with getting your work published?
As an African-American poet I avoided the problem by creating my own company, so if there was a problem, I didn't know
about it.
Who inspired you to start writing?
I don't believe in role models and inspiration, I just don't believe in it. I never did, but I had a terrific grandmother who was
always very interested in what I was doing. I know my grandmother was a great influence and inspiration in that degree, but I
reject that notion that someone winds you up and starts you on your way.
Why do you write poems for young people?
Because I was once young (laughing). I have a great respect for young people. And I wanted to share what I remembered that
might be interesting or helpful.
Did you read the Harry Potter series? If so what do you think about them?
Every one of them twice. In Quilting: The Black Eyed Pea, there is a review of the Harry Potter movie. I'm a big Harry Potter
fan; the books are great. I wanted the werewolf to come back. In the battle, we knew that Dumbledore was going to make
peace with the giants in the struggle, but I want the werewolves too. I think the werewolves were on our side.
Why did you pick Ashley Bryan to illustrate "The Sun Is So Quiet?" Is he your favorite illustrator? How do you work
together if he lives in Maine and you live in Virginia?
Ashley and I share a mutual friend; her name is Connie Harris and she was formerly the head of the Children's Library
Section in Cincinnati. It's probably fair to say that Connie brought us together. And I do love his work. I've worked with a lot
of people, but Ashley is one of my favorites. Distance doesn't matter. There is no distance - long distance - especially with
the Internet.
How do your children influence your poetry?
I only have one child. His name is Thomas, and I think my relationship with Thomas encouraged me to look again at the
needs or interests of children.
What are some of your goals for the future?
I hope to travel more. I enjoy traveling, that is a goal. I'm interested in retracing Darwin's steps - the naturalist, that's a goal.
Everything else is a hope. I would hope to go to Mars, but it's not likely.
Do you prefer teaching poetry or writing it yourself?
That's like asking if I prefer cooking or eating, they are part of the same process.
72
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
Do you sometimes get frustrated when you are writing?
Yes. I think everybody does, it's not something to be unhappy with yourself about either.
Was there anything else you wanted to be besides a poet?
Not actually, maybe if I'd been a little better I could have been a professional tennis player, like Venus Williams. That
would've been a dream. I also liked to paint, but I had to recognize that I would never be a professional painter. You have to
recognize these things and move on. But if I were 12 years old today, I'd want to be an astronaut.
What are your favorite movies, poems, and books?
My favorite movie is one that your parents probably won't let you see - The Godfather; it's a terrific film. One of my favorite
books is The Lies of the Cell by Louis Thomas. But I also like Sula, by Tony Morrison, a lot.
Do you get nervous when your poems are about to go out to the public?
No (laughing). By the time they are about to go out, I know they are ready.
About how much time a day do you spend writing your poems?
Quite a bit lately because I'm working on a book, but once the book is finished less because I'll be working on my research. I
don't write every day.
Did you go to college for this? Or did you plan on doing something else?
I went to college as a history major, liberal arts. I made preparations, not plans. I still think that's important.
Do you think you will continue writing throughout the years?
I hope so.
Who is one of your favorite poets?
I like a lot of poets. I loved the work of Robert Louis Stevenson when I was growing up because I love children's literature,
but now, I don't even know who I DON'T like. I read a lot and enjoy it.
What advice do you have for young people who want to be poets today?
The most important thing is to pay attention. The next would probably be to read; it's so important to pay attention. It keeps
you from being bored, and I might add it keeps you from being boorish.
How would you encourage middle-school students to feel comfortable writing poetry as a form of creative expression?
I'd be sure to praise the creativity because even on the college level, which I teach, praise is going to get you better work. Its
not that you don't want better skills, like spelling, but it can't be the divining decision. Try to look into what the children are
sharing. Start every sentence with, "That's really good. Now tell me . . ." Kids are very nervous about being criticized, start
them off from a very positive point. I'm pleased that you all asked questions today - that's not easy to do. I'm glad we had an
opportunity to interact closer.
This article was updated in March 2008.
73
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
speak up
speak up for love
speak up for life
speak up for me
this is your life
speak out
speak up
speak loud
speak strong
speak clear
so someone can hear
this is your life
speak to the people
speak to be equal
speak to save
speak to the grave
speak to the living
speak to the dead
speak to the start
speak to the hills
this is your life
that only you can live
jamaya ewing
74
Grade: 6
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
“Eleven”
by: Sandra Cisneros
What they don't understand about birthdays and what they never tell you is that when you're eleven, you're
also ten, and nine, and eight, and seven, and six, and five, and four, and three, and two, and one. And when you
wake up on your eleventh birthday you expect to feel eleven, but you don't. You open your eyes and everything's
just like yesterday, only it's today. And you don't feel eleven at all. You feel like you're still ten. And you are-underneath the year that makes you eleven.
Like some days you might say something stupid, and that's the part of you that's still ten. Or maybe some
days you might need to sit on your mama's lap because you're scared, and that's the part of you that's five. And
maybe one day when you're all grown up maybe you will need to cry like if you're three, and that's okay. That's
what I tell Mama when she's sad and needs to cry. Maybe she's feeling three.
Because the way you grow old is kind of like an onion or like the rings inside a tree trunk or like my little
wooden dolls that fit one inside the other, each year inside the next one. That's how being eleven years old is.
You don't feel eleven. Not right away. It takes a few days, weeks even, sometimes even months before you
say Eleven when they ask you. And you don't feel smart eleven, not until you're almost twelve. that's the way it is.
Only today I wish I didn't have only eleven years rattling inside me like pennies in a tin Band-Aid box. Today I
wish I was one hundred and two instead of eleven because if I was one hundred and two I'd have known what to
say when Mrs. Price put the red sweater on my desk. I would've known how to tell her it wasn't mine instead of
just sitting there with that look on my face and nothing coming out of my mouth.
"Whose is this?" Mrs. Price says, and she holds the red sweater up in the air for all the class to see.
"Whose? It's been sitting in the coatroom for a month."
"Not mine," says everybody. "Not mine."
"It has to belong to somebody," Mrs. Price keeps saying, but nobody can remember. It's an ugly sweater
with red plastic buttons and a collar and sleeves all stretched out like you could use it for a jump rope. It's maybe a
thousand years old and even if it belonged to me I wouldn't say so.
Maybe because I'm skinny, maybe because she doesn't like me, that stupid Sylvia Saldivar says, "I think it
belongs to Rachel." An ugly sweater like that, all raggedy and old, but Mrs. Price believes her. Mrs. Price takes the
sweater and puts it right on my desk, but when I open my mouth nothing comes out.
"That's not, I don't, you're not...Not mine," I finally say in a little voice that was maybe me when I was four.
"Of course it's yours," Mrs. Price says. "I remember you wearing it once." Because she's old and the
teacher, she's right and I'm not.
Not mine, not mine, not mine, but Mrs. Price is already turning to page thirty-two, and math problem
number four. I don't know why but all of a sudden I'm feeling sick inside, like the part of me that's three wants
come out of my eyes,only I squeeze them shut tight and bite down on my teeth really hard and try to remember
today when I am eleven, eleven. Mama is making a cake for me tonight, and when Papa comes home everybody
will sing Happy Birthday, Happy Birthday to you.
But when the sick feeling goes away and I open my eyes, the red sweater's still sitting there like a big red
mountain. I move the red sweater to the corner of my desk with y ruler. I move my pencil and books and eraser as
far from it as possible. I even move my chair a little to the right. Not mine, not mine, not mine.
In my head I'm thinking how long till lunchtime, how long till I can take the red sweater and throw over the
schoolyard fence, or leave it hanging on a parking meter, or bunch it up into a little ball and toss it in the alley.
Except when math period ends Mrs. Price says loud and in front of everybody, "Now, Rachel, that's enough,"
because she sees I've shoved the red sweater to the tippy-tip corner of my desk and it's hanging all over the edge
like a waterfall, but I don't care.
"Rachel," Mrs. Price says. She says it like she's getting mad. "you put that sweater on right now and no
more nonsense."
"But it's not-"
75
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Grade: 6
"Now!" Mrs. Price says. This is when I wish I wasn't eleven, because all the years inside of me--ten, nine,
eight, seven, six five, four, three, two one--are pushing at the back of my eyes when I put one arm through one
sleeve of the sweater that smells like cottage cheese, and then the other arm through the other and stand there with
my arms apart like if the sweater hurts me and it does, all itchy and full of germs that aren't even mine.
That's when everything I've been holding in since this morning, since when Mrs. Price put the sweater on
my desk, finally lest go, and all of a sudden I'm crying in front of everybody. I wish I was invisible but I'm not. I'm
eleven and it's my birthday today and I'm crying like I'm three in front of everybody. I put my head down on the
desk and bury my stupid clown-sweater arms. My face all hot and spit coming out of me, until there aren't any
more tears left in my eyes, and it's just my body shaking like when you have the hiccups, and my whole head hurts
like when you drink milk too fast.
But the worst part is right before the bell rings for lunch. That stupid Phyllis Lopez, who is even dumber
than Sylvia Saldivar, says she remembers the red sweater is hers! I take it off right away and give it to her, only
Mrs. Price pretends like everything's okay.
Today I'm eleven. There's a cake Mama's making for tonight, and when Papa comes home from work we'll eat it.
There'll be candles and presents and everybody will sing Happy Birthday, Happy Birthday to you, Rachel, only it's
too late.
I'm eleven today. I'm eleven, ten, nine, eight, seven, six, five, four, three, two, and one, but I wish I was one
hundred and two. I wish I was anything but eleven, because I want today to be far away already, far away like a
runaway balloon, like a tiny o in the sky, so tiny-tiny you have to close your eyes to see it.
76
Language Arts Unit:
Changes
Timeframe: 8 weeks
Nothing Gold Can Stay
Nature's first green is gold,
Her hardest hue to hold.
Her early leaf's a flower;
But only so an hour.
Then leaf subsides to leaf,
So Eden sank to grief,
So dawn goes down to day
Nothing gold can stay.
Robert Frost
Retrieved from: http://www.poemhunter.com/poem/nothing-gold-can-stay/
77
Grade: 6