USA
advertisement

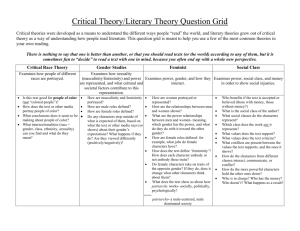
USA - country profile Team: Alexandra Gogalova - Slovakia Radoslaw Stepnik - Poland Roger Schmitt - Germany 1 USA - country profile Agenda Structure 1. About the USA 1.1 Intro 1.2 History 1.3 Some facts and backgrounds 2. The US-culture 2.1 Hofstede´s dimensions 2.2 Gesteland - The pattern of business behavior 3. To negotiate in the USA 4. Class opinion 5. Conclusion 2 Born in the USA 3 USA - country profile History • Original inhabitants Indians • 1492 Christopher Columbus discovered America • Since 16th century settling through European immigrants • Colonial time (France, Spain and England) • Independence fight (Independence Day 4th July 1776) • Civil war (North against South 1861 – 1865) • Abolition of the slavery 1865 • Rose slowly to the economic giant (19th – 20th century) • Market Crash New York (25.10.1929) and world economic crisis • Different wars (First and Second World War, Vietnam, Iraq, etc.) • Attack on the World Trade Center (11.09.2001) Afghanistan, Iraq 4 USA - country profile Some facts and backgrounds Today • Federal States: 50 Seal of the USA • Population figure: 295,734,134 (July 2005) • Density: 30 inhabitants per km² • Capital: Washington D.C. • Language: No official language but mostly American English 5 USA - country profile Some facts and backgrounds Today • Languages: 82.1 % English, 10.7 % Spanish, 3.8 % Indo-European, 2.7 % Asian and Pacific island, 0.7 % others (2000) • Biggest town: New York (8,108,000 inhabitants) • Form of government: Democratic federal republic • President: George W. Bush • Currency: US-Dollar • National anthem: The Star-Spangled Banner • Religion: 54 % Protestants, 25 % Catholics, 10 % no religious conviction, 3 % orthodox, 3 % Jewish, 2 % Mormons (2004) • Economy: Biggest political economy of the world - GPD 11,728 $ bn (2004) 73 % tertiary, 23 % secondary, 4 % primary sector • National sports: American Football, Baseball, Basketball, Ice hockey 6 USA - country profile Power Distance Index (PDI) Power Distance Index • In USA with a ranking of 40, compared with a world average of 55 • Hierarchy in organizations means an inequality of roles, established for convenience • Decentralization is popular • Narrow salary range between top and bottom of organization • The middle class is large • Power is based on formal position, expertise • The ideal boss is a resourceful democrat 7 USA - country profile Individualism (IDV) Individualism • In USA with a ranking of 91, compared with a world average of 43 • The highest level of IDV among listed countries • Individualistic attitude • Loose bonds with others • Relationship employer-employee is a contract supposed to be based on mutual advantage • Hiring and promotion decisions are supposed to be based on skills and rules only • Everyone has a right to privacy • Everyone is expected to have a private opinion • Laws and rights are supposed to be the same for all 8 USA - country profile Masculinity vs. Femininity Masculinity vs. Femininity • In USA with a ranking of 62, compared with a world average of 50 • This indicates the country experiences a higher degree of gender differentiation of roles • The male dominates a significant portion of the society and power structure • Masculine societies tend to see men as assertive and women as nurturing • Competitive behavior • Strong are admired Italy 42 days France 37 days Germany 35 days • Material values are important Brazil 34 days • Work is sense of living United Kingdom 28 days Canada 26 days Korea 25 days Japan 25 days U.S. 13 days Source: www.infoplease.com 9 USA - country profile Masculinity vs. Femininity Masculinity vs. Femininity • Not so many women in management position • Resolving international conflicts by fighting • Positive correlation between masculinity and Defense spending as a percentage of GNP • Big and fast are beautiful • Men don't show their emotions • Sexual harassment is a big issue • Sex and violence in newspapers and on TV • Advertising is part of lives of Americans • Maintenance of economic growth should have highest priority 10 USA - country profile Uncertainty Avoidance Uncertainty Avoidance • With a ranking of 46, compared to the world average of 64 • Fewer rules • Open to innovations, risk, etc. • Students prefer open-ended learning situations and discussions • Tolerance, moderation • Citizen protest acceptable 11 USA - country profile Uncertainty Avoidance Uncertainty Avoidance • Tend to accept competition and conflict, tolerate dissent and deviance. • Many nurses, few doctors • Human rights: nobody should be persecuted for their beliefs • Positive attitudes towards young people • Scientific opponents can be personal friends • Tolerant political ideologies • Employees tend to change jobs more frequently 12 USA - country profile Long term orientation Long term orientation • The lowest dimension for the US at 29, compared to the world average of 45 • This low LTO ranking is indicative of the societies' belief in meeting its obligations and tends to reflect an appreciation for cultural traditions. • Change can occur more rapidly as long-term traditions and commitments do not become impediments to change. • A sense of security and stability, a protection of one’s reputation, a respect for tradition, and a reciprocation of greetings; favors and gifts. 13 USA - country profile The pattern of business behavior The pattern of business behavior (R. Gesteland) • Deal focused culture (task-oriented) contact with prospective buyer without any previous relationship or connection getting down to business rely on written agreements direct language and low-context communication • Rigid-time culture (monochronic) punctuality fixed agendas schedules meetings are rarely interrupted 14 USA - country profile The pattern of business behavior The pattern of business behavior (R. Gesteland) • Informal culture supposed to value status equality • Variably expressive culture verbal (clear way) paraverbal (loudly, avoid silence) nonverbal (distance behavior 40 to 60 cm , variable touch behavior, firm eye contact) 15 USA - country profile To negotiate in the USA To negotiate in the USA • “Time is money” • American dream • Communication • Meals and Business • Lawyers • Regional subcultures • Money is key priority 16 USA - country profile To negotiate in the USA To negotiate in the USA • FUN, FUN, FUN! • Women in management • Language • Opportunity • Work time • Give and take • Knowledge of other cultures • Protection of rights by law in the workplace 17 USA - country profile To negotiate in the USA To negotiate in the USA • Punctuality • Business dress • Smoking • Informality • Flexibility • Addressing • The way of greeting • Small talk 18 USA - country profile To negotiate in the USA To negotiate in the USA Welcome Topics • Sports • Food • Music Topics to avoid • Religion • Politics • Controversial subjects (racism, sexism...) • Personal matters 19 USA - country profile Class opinion Class opinion Questions: • Do you like the Americans and American culture? • Would you like to adopt the American lifestyle? • What you like and don’t like about the Americans? Results: • The majority answered YES to the first questions. Some respondents added that they do not think there is a notion of the American culture. • Only ONE person would like to adopt the American lifestyle • Positive and negative feelings about the Americans 20 USA - country profile Conclusion Conclusion 21 USA - country profile Sources Sources: Gesteland, R. (1999) Patterns of Cross-Cultural Business Behavior Hofstede, G. (1991) Cultures and Organizations – Software of the mind Hofstede, G. (1998) Masculinity and Femininity Financial Times (18th July, 2nd and 15th August, 2000) www.executiveplanet.com wikipedia.org www.cia.gov www.geert-hofstede.com www.usa.de www.cnn.com www.infoplease.com 22 USA - country profile Thanks Thank you for your attention! And… 23