Food Chain and Food Web Activity: Name: Directions: Every living
advertisement

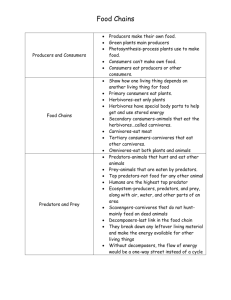
Food Chain and Food Web Activity: Name:________________________ Directions: Every living thing plays a role in one or more food chains. Your task today is to learn how organisms depend on another for food and energy. For this activity, you will be designing both food chains and food webs. Follow the directions below to get started: What Habitat is your group focused on? _____________________________________ Procedure: Acquire a set of organism cards that includes a sun card, a sheet of large poster paper, and a marker. Put out your cards on the sheet of paper and familiarize yourself with the living creatures. Try to organize your cards into the following groups: producers, herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and possibility detritivores. Put the sun card at the bottom of your poster paper. Organize one food chain of a primary producer, a primary consumer, a secondary consumer, and (if possible) a tertiary consumer. Draw an energy arrow from the sun to each level of your chain. Raise your hand and have your food chain checked by your teacher. After your teacher checks your work, draw your food chain here: Next, you are going to take the rest of your cards and design a food web. Start by organizing your cards into several food chains and making connections between those chains to each other. Think about how the diets of your living creatures can contain more than one food source. Ask your teacher for help if you are stuck on a card. When you are done, all your cards should be on your poster sheet with arrows connecting them. Have your teacher check your food web. After your teacher checks your work, draw your food web here: When you are done drawing your food web, add the following terms to your picture: autotrophs, heterotrophs, herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, and detritivores (if you have them). Label your trophic levels of Primary Producers, Primary Consumers, Secondary Consumers, Tertiary Consumers, and Quaternary Consumers or Apex Predators. Show your work to your teacher when you are done and make sure these terms are labeled in your food web drawing on the previous page. Answer the following questions: 1. What is the difference between a food chain and a food web? 2. Food chains are isolated relationships between consumers and producers and cannot intersect with each other. In other words, any given consumer can only eat one type of producer. True or False? a) True b) False 3. Food chains and food webs represent the pathways that energy and matter move through an ecosystem. True or False? a) True b) False 4. What is NOT an example of a primary consumer? a) A mouse that eats mostly seeds b) A deer that eats mostly grass c) An osprey that eats mostly fish d) A squirrel that eats mostly acorns 5. Primary consumers are all carnivores. True or False? a) True b) False 6. A _______________ has a disproportionately large role in structuring its ecosystem relative to its abundance and size. a) keystone species b) heterotroph c) tell-tale species d) primary species 7. In a kelp forest ecosystem, sea otters are the only animals that eat spiny sea urchins. Urchins eat kelp. An animal that is not typically a part of this ecosystem—the orca—began eating sea otters because its usual population of prey—seals—had declined. When the orcas began eating sea otters, the sea urchin population increased drastically and decimated the kelp population. In this scenario, which is the keystone species? a) The orca b) The sea otter c) The kelp d) The seal 8. Why doesn’t all of the energy available in primary producers transfer up the food chain? a) Some organic material cannot be digested b) Some energy is consumed at each level by cellular metabolic processes c) Some energy is stored in fat d) A and B 9. Energy is recycled in a food chain. True or False? a) True b) False 10) What is the advantage of a food web diagram as compared to a food chain diagram? 11) Things such as sunlight and air aren’t food. Why were they included in the food webs that we looked at in this lesson? 12) Throughout the world, species of plants and animals are becoming extinct every day. What effect do you think the extinction of a species would have on the food web in that ecosystem? 13) John Muir wrote that “When we try to pick out anything by itself, we find it hitched to everything else in the universe.” a) What does that mean? b) How are you “hitched” to: a. Oil spills in the Gulf of Mexico? b. Air pollution in Denver? c. Coal mining in Appalachia?