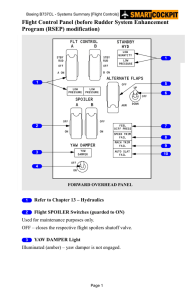
6.03 Secondary Controls and Secondary Effects of Controls
advertisement
Theory of Flight 6.03 Secondary Controls and Secondary Effects of Controls References: FTGU pages 15, 28, 29 Review 1. What control surface causes roll? 2. What movement does the elevator create? 3. Which axis does yaw act around? 4. Name the 2 types of fuselage construction. 6.03 Secondary Controls and Secondary Effects of Controls • MTPs: – Trim – Spoilers and Dive Breaks – Flaps – Secondary Effects of Controls – Coordination Trim • Trim tab: adjustable device located on the trailing edge of control surfaces • Purpose – alleviates pressure on the controls • Other types of trim are bungees connected to the control column • Most often only on the elevator Trim The trim tab moves in the opposite direction as the control surface Trim • Trim in a glider – No trim tabs • Types - side trim (bungee) - stick trim (ratchet) Bungee Trim Spoilers & Dive Brakes • Primarily used in glider flying • Spoilers – are hinged plates on top of the wing – disrupt the airflow over the wing to “spoil” the lift (Top) • Dive Brakes – increase drag (Bottom) NASA applet - http://www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/k-12/airplane/spoil.html Spoilers & Dive Brakes Purpose – allows the pilot to control the rate of decent during final approach and landing - Spoilers and dive breaks increase drag and decrease lift Flaps • • • • Increases the camber of the wing This increases the lift and the drag Known as a high lift device Allows the aircraft to have a steeper approach path with a decreased stall speed • Allows glider pilot to fly slower in a thermal Flaps • Types of flaps Secondary Effects • The air movement over control surfaces when they are moved causes adverse effects • When you yaw you get Roll • When you roll you get Adverse yaw Roll from Yaw Roll from yaw • When rudder is applied, the wing on the outside of the turn moves faster, which causes it to experience more lift Faster = more lift Roll from Yaw MORE LIFT CAUSES ROLL TO THE LEFT FASTER YAW LEFT Adverse Yaw from Roll • When ailerons are applied the plane has a tendency to yaw away from the lower wing because of aileron drag. • The wing that rises experiences more lift, but also more induced drag. Adverse Yaw from Roll Right aileron UP MORE LIFT MORE DRAG ROLL CAUSES ADVERSE YAW Left aileron DOWN LESS LIFT LESS DRAG Coordination • To turn the aircraft without causing unnecessary drag, aileron and rudder must be used. • Using too much rudder will cause a “skidding turn”. • Using too little (or opposite) rudder will cause a “slipping turn”. Coordination You slip in and skid out. Think of driving and skidding around a corner. Confirmation 1. How is adverse yaw created? 2. Why is there roll when an airplane is yawed? 3. What is the purpose of flaps? 4. Name 2 types of trim. 5. What is trim used for? 6. What is the difference between slipping and skidding? Confirmation Draw on the airplane where the following go: • • • • Flaps Spoilers Elevator Trim tab Aileron Trim tab C-130 Deploying Flares