Peripheral Devies
advertisement

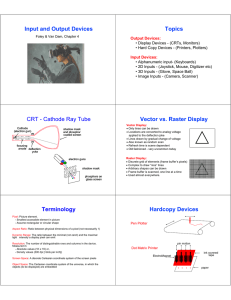
Peripheral Devices Device Drivers A program to tell the system software how to work with that piece of hardware Some common device drivers are built in the system software (Operating System) e.g. keyboard and mouse drives Plug-n-Play Devices Devices designed such that Windows can detect them, install and configure the device driver automatically For non plug-n-play devices, we have to install and configure the device driver manually. Input Devices (1) Keyboard – – – P/S2 keyboard USB keyboard Wireless keyboard Input Devices (2) Pointing Devices – – Mouse, trackball, touch pad, light pen, digitizer Touch screen Input Devices (3) Scanning devices – – – – – – Image scanner Fax machine – scan image to bitmap Bar code scanner – scan Universal Product Code (UPC) Magnetic ink character scanner (MICR) Optical character scanner (OCR) Optical mark scanner (OMR) Input Devices (4) Voice Input Device – – – Microphone – to receive the sound signal Sound card – to convert the sound signal to digital form Use speech recognition software to recognize human speech Input Devices (5) Handwriting Recognition Device – – – Need handwriting recognition software Called natural input Slow inputting speed Output Devices (1) Visual Display Unit (VDU) – Commonly called monitor 2 common types of monitor – CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) monitor – High radiation and bulky LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) monitor No radiation and slim Output Devices (2) Printer – to produce hard copy Laser printer – – – to produce high quality output resolution up to 2400 dpi (dot per inch) use carbon toner, usually for black and white printout, colour is very expensive Output Devices (3) Inkjet printer – – – – produce good quality colour output resolution up to 1440 dpi use ink droplets to compose the image The printer is much cheaper than laser printer but the ink is very expensive Output Devices (4) Dot matrix printer – – – – Use impact principle Can print multiple (carbon) copies at a time, usually use in printing invoices The ink ribbon is cheap Poor quality of printout Output Devices (5) Plotter – – – – Drawing high quality image, use colour pens, can draw smooth curves Can print on large paper size, use roll of paper To draw posters and maps Use in CAD (Computer Aided Design) Output Device (6) Voice output devices – – Sound card, to convert computer signals to sound Speakers, to amplify the sound output Storage Devices (1) Floppy Disk (Diskette) – – – – – – – – A flexible plastic circular disc Packed in a plastic square jacket Formatted to 1.44MB Divided to many circular tracks Each track is divided to many sectors Use magnetic technology to store data ‘0’ or ‘1’ Random access Slow accessing speed Storage Devices (2) Hard Disk – – – – – – – High storage capacity, over 100 GB Hard metallic surface Consists of several metallic disks Data are stored in cylinder (a deck of tracks) (see p.86) Use magnetic technology Very high access speed Random access Storage Device (3) Optical disk – – – – – – CDROM, DVDROM, CDRW, DVDRW Use optical technology, laser reflection on pits ‘1’ will reflect the laser beam while ‘0’ does not High storage capacity, 700 MB for a CDROM, 17GB for a DVDROM Random access High access speed Storage Device (4) Tape – – – – – – – – Cheap Sequential access Use magnetic technology Ideal for backup data, we need to backup and restore all data High storage capacity Slow access speed Group of records are stored in a block Inter-block gaps are needed for stopping and starting the read/write head. Storage Device (5) Other Storage devices – can be read/write Removable disks -Zip disk(100/250MB), superdisk(120MB), Jazz disk(1GB) MO disk Flash memory cards – compact flash, smart media and memory stick, commonly used in digital camera Network Devices (1) Network Interface Card (NIC) (LAN card) – – – Connection between the network and the computer bus Have built-in transceiver, for data transmitting and receiving Usually 100 MB/s Wireless LAN card – – Usually 11 MB/s Work within the distance range, and no blocking in between. Network Devices (2) Connectors RJ-45 telephone jack connector – For connecting twisted pairs LAN cable BNC connector – For connecting coaxial cables Network Device (3) Terminators – Use in bus network, to prevent signal rebounce and echo at the ends of bus. Network Device (4) Hub – Switch – To connect the workstations within a room on same floor To connect the workstations for different floors in a building, it is faster and more efficient than a Hub. Router – To connect different LANs together to form a Wide Area Network (WAN) Network Device (5) Repeater – When a network spans a long distance, the signal weaken, repeater is used to reproduce the signal. Exchange – To boost the signals along the network path for a Wide Area Network. Network Device (6) Computer – Server – Different computers play different roles on a network Provide services to other computers connected to the network, usually have higher processing power and larger storage capacity. Workstation – The computers connected to the network but not act as a server. Network Device (7) - Servers File server – Print server – To host a web site and publish web pages on the web, support HTML, Java script, CGI, PHP and ASP web languages Email server – Manage the print jobs from different computers to different network printers, and manage the print queues. Web server – control the sharing and access of files over the network, must have a huge storage capacity. To store, send and receive emails over the Internet Internet server – To provide Internet access Communication Device Modem - Modulator-demodulator – – It transforms digital signals of computer to analog signals to be transmitted through telephone lines. (Modulation) It also transforms analog signals back to digital signals for the computer that receives the signals. (Demodulation) Data/Signal Rate Data Rate – Signaling Rate (Baud Rate) – – Refer to the no. of bits per second sent Refer to the no. of signals per second sent Each signal may consists of several bits e.g. 101 Bandwidth – – The frequency range of a particular media is directly proportional to the data rate Types of network Client-Server Network – – – Some computers act as server to provide services to clients on the network Server programs are running on the server Client programs are running on client computers Peer-to-peer Network – – – Every computer plays the same role in the network. They form a workgroup, no server and no client The security in a peer-to-peer network is low. It is easy to set up, since no server programs or client programs need to be run.