Strategic Analysis of J&J Electrical Contractors, Inc.
advertisement

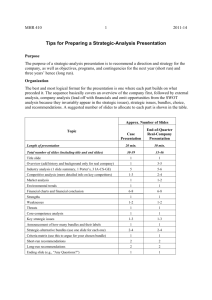
STRATEGIC ANALYSIS OF J&J ELECTRICAL CONTRACTORS, INC. Group 1 Spring 2010 OVERVIEW Founded in 1987, by John Abernathy, current CEO - Wife Jean is current CFO Does electrical contracting for heavy industrial installations, commercial and office buildings, educational institutions, public works, and many specialized systems including maintenance services Competes in the Southern California electrical-contracting industry Well established company known for excellent customer service NIAT declined from 2002 to 2005 THE SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA ELECTRICALCONTRACTING INDUSTRY Growing industry Regulated by local cities and states Moderate technological innovation Change in contracting industry due to economy Fragmented PORTER‘S FIVE-FORCES MODEL Intensity of Rivalry Very high New Entrants Geothermic Energy Bargaining Power Of buyers: High Of suppliers: Medium Suppliers Rivals Buyers Electrical Wholesalers J & J, Buck Electric, Power Plus!, Daniel’s Electrical Construction Co., McBride Electric, and Champion Electric, Inc. Commercial/indus trial clients, public sector and private homeowners Threat of Substitutes Substitutes Barriers to Entry None Non-licenced electrical contractors Low INDUSTRY ATTRACTIVENESS Factors Weight Rating Product Degree of Regulation 5 0.5 2.5 Degree of technological innovation 15 0.6 9.0 Intensity of competition 30 0.1 3.0 Industry growth rate 30 0.7 21.0 Size of potential market 20 0.8 16.0 100 - 51.5 Totals COMPETITIVE STRENGTH Success Factors Weight Rating Product Financial Strength 15 10 0.7 0.4 10.5 4.0 Customer Service 25 1.0 25.0 Brand Image 35 20 0.7 0.5 24.5 10.0 100 - 74.0 Management Marketing Totals G.E. MATRIX COMPETITIVE ANALYSIS Intense competition - Low barriers to entry - Many competitors Basis of competition - Price [esp. public sector] - Quality - Reputation COMPETITIVE ANALYSIS (CONT.) A few very large national competitors But they go after large contracts More direct competitors include Buck Electric, Power Plus!, Daniel’s Electrical Construction Co., McBride Electric, and Champion Electric Buck Electric specializes in solar photovoltaic Most competitors are doing residential construction field, whereas J & J Electric is focused more on commercial and public sector [classrooms] MARKET ANALYSIS • • • • • The target market is all residential, commercial, industrial, and public-sector electrical-contracting work in the Inland Empire Price-sensitivity is high, especially in public-sector bidding Growth rate was high in residential construction in mid-2000s Current customer needs are: quality, price, on-time completion, initial installation, bringing public buildings up to code, and energy conservation incentives Future customer needs are renovations and addons ENVIRONMENTAL TRENDS Declining of commercial and industrial construction, due to recession of early 2000s Energy Policy Act of 2005 was passed and, as a result, State and local government legislation increasingly addressed code updates for older buildings Population growth was increasing, creating more potential jobs Greater affordability and demand for alternative-energy installations such as solar photovoltaic, fuel cells, and microturbine-power plants Greater demand for networked installations and security systems REVENUES ($M) 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 NIAT ($K) 500 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 CURRENT RATIO 5 4 3 2 1 0 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 DEBT-TO-EQUITY RATIO 1.1 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 CASH ($K) 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 -50 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 AVERAGE COLLECTION PERIOD (DAYS) 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 Z2-SCORE Safe Zone FINANCIAL CONCLUSION The company is in strong financial condition, but NIAT is declining and ACP is too high In 2005… • Revenues increased 2.62% • Current ratio is 2.82—good working capital • Debt-to-equity ratio is 55%—good financial leverage • Cash is $108M—good for future investment • Z2-Score is 8.57—well in the safe region However… • NIAT declined 20% to $136.9K • ACP is 63.3 days STRENGTHS Strong reputation for integrity, responsibility, and reliability Strong working relationships in the private sector Additional estimator/project manager enabled J&J to bid on larger projects Master Builder software allowed for more precise bidding Ahead in the experience curve Revenues increased 2.62% Cash is $108 Million Z2-Score is 8.6 CORE-COMPETENCE ANALYSIS Criteria for Sustainable Competitive Advantage Capability Is this capability valuable? Is this capability rare? Is this capability costly to imitate? Is this capability nonsubstitutable? Competitive consequences Performance implications Master Builder Software Yes Yes Yes No Sustainable competitive advantage Above-average returns PublicSector Projects Yes No No No Competitive parity Average returns Customer Service Yes Yes No Yes Temporary competitive advantage Above-average returns WEAKNESSES Not competitive with price wars in private sector Limited geographic expansion into different markets Low “hit rate” in public-sector bidding (1 in 15) Declining NIAT Very high ACP because of high A/R in public-sector projects High ratio (9:1) of public- to private-sector projects No technical expertise in low-voltage applications, alternativeenergy-source installations, or system wiring Principals have differing visions for the company THREATS Low barriers to entry Increased price of raw materials Supply shortages KEY STRATEGIC ISSUES How can J&J… … expand into private projects? … expand into other sectors and other geographic areas? … keep up with its competitors? KEY STRATEGIC ISSUES Should J&J… … reduce its ratio of public to private projects? … pursue more community-college and university bond projects? … become a general contractor? … broaden its services offered to include home-audio or security systems, low-voltage installations, or installation of alternative-energy-power sources … expand into other high-growth areas in California and neighboring states? J & J ELECTRICAL CONTRACTORS HAS THREE STRATEGIC ALTERNATIVES 1. Reduce ratio of public/private jobs 2. Expand geographically 3. Offer advanced technical services 1. REDUCE RATIO OF PUBLIC/PRIVATE JOBS Become more selective in pursuing public projects But pursue the lucrative community-college and university bond projects Get more residential-remodeling and commercial work Do more market research within the growth areas Form strategic alliances with corporate developments Hire a marketing consultant to help promote the company’s name in the private sector Continue working closely with other general contractors Continue the company’s culture of outstanding service and ethical operations Continue current programs Increase market share Finance through cash and debt 2. EXPAND GEOGRAPHICALLY Expand to other high growth areas in Southern California Expand into Northern California Increase market share Open new locations—one at a time—in developing parts of the Inland Empire Acquire small 1–3 person firms in the right locations that have the right skill sets Continue bidding on school and community-college projects—but now in an expanded area Improve the hit ratio through better estimation of future costs Continue the company’s culture of outstanding service and ethical operations Continue current programs Finance through cash and debt 3. OFFER ADVANCED TECHNICAL SERVICES Begin offering high-tech services such as home-audio or security systems, low-voltage installations, or alternative-energy-power sources Increase market share Seek and hire individuals (not all at once) with the experience and expertise to install both systems and alternative-energy-power sources Form strategic alliances with manufacturers of alternative-energy-power sources and telecom/network systems Cross-train employees in these new areas Continue current programs Continue the company’s culture of outstanding service and ethical operations Finance with cash and debt CRITERIA MATRIX Criteria 1. Reduce ratio of private/public jobs 2. Expand geographicaly 3. Offer advanced technical services Profitability P 5 7 9 Growth in revenues P 5 8 7 Competitive Advantage P 5 7 9 Investment required N -3 -7 -7 Overall riskiness N -6 -7 -4 6 8 14 Overall Score 2006 RECOMMENDATIONS Increase revenues 15% and NIAT 10% Increase market share Aquire resources necessary to advance technology Raw materials and operation equipment Hire individuals who are experienced in both new and current systems Implement training and development programs Market to new and existing customers Continue the company’s culture of outstanding service and ethical operations Maintain customer loyalty Continue current programs 2006 RECOMMENDATIONS (CONT.) If competition is severe in offering new advanced technical services, causing revenues to lag projections by 15%, then J&J should intensify its marketing efforts 2008 RECOMMENDATIONS Increase revenues 20%/yr and NIAT 15%/yr Increase market share Offer price incentives for first-time customers Maintain customer loyalty Form strategic alliances with manufacturers of alternativeenergy-power sources and telecom/network systems Cross-train employees in these new areas Stay current with the latest technological advances Continue the company’s culture of outstanding service and ethical operations Continue current programs 2008 RECOMMENDATIONS (CONT.) If copper-wire costs increase, causing NIAT to lag projections by 15%, then J&J should use R. F. Romex wire instead of electrical conduit ANY QUESTIONS?