Biochemistry True and False Nelson / Word 2007
advertisement

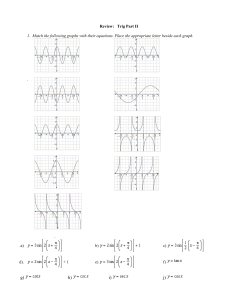
Biochemistry True and False Nelson Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. ____ 1. Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen make up 96 % of the weight of all living organisms. ____________________ ____ 2. Carbon has 6 protons and 7 neutrons. ____________________ ____ 3. The force of attraction between two atoms or ions in a compound is known as a van der Waals force. ____________________ ____ 4. An example of a neutralization reaction is: HCl + NaOH NaCl + H2O ____________________ ____ 5. Water is able to cling to surfaces because of ionic bonds. ____________________ ____ 6. Bases generally have a low pH. ____________________ ____ 7. A buffer maintains your blood pH in the range of 7.3 to 7.5. ____________________ ____ 8. Carbon can only form single and double bonds. ____________________ ____ 9. The hydroxyl group is C–COOH. ____________________ ____ 10. The functional group shown is the carboxyl group. ___________________ ____________________ ____ 11. The functional group shown is the amino group. ___________________ ____________________ ____ 12. Sucrose is made of glucose and galactose. ____________________ ____ 13. An isomer is a molecule with the same formula, but different arrangement of atoms. ____________________ ____ 14. Lipids are hydrophilic. ____________________ ____ 15. A triglyceride is made of glycerol attached to one fatty acid. ____________________ ____ 16. Carbohydrates provide more energy than fats do. ____________________ ____ 17. Lysine is an essential amino acid. ____________________ ____ 18. All proteins are an assembly of various combinations of 20 amino acids. ____________________ ____ 19. In a growing peptide strand, amino acids are added to the –NH2 group. ____________________ ____ 20. The heme group in hemoglobin is an example of an R group. ____________________ ____ 21. A nucleotide consists of a sugar–lipid–nitrogenous base. ____________________ ____ 22. Nucleic acids consist of nucleotides liked together with ionic bonds. ____________________ ____ 23. Linus Pauling was awarded a Nobel Prize in chemistry for his work on the secondary structures of proteins. ____________________ ____ 24. Linus Pauling discovered that atoms that have an equal electronegativity are able to share electrons unequally in a covalent bond. ____________________ ____ 25. Enzymes are destroyed after a reaction. ____________________ ____ 26. Cyanide is a reversible inhibitor that binds to cytochrome oxidase. ____________________ ____ 27. Enzyme inhibitors increase the rate at which an enzyme catalyzes a reaction. ____________________ ____ 28. Competitive inhibition is where an enzymatic reaction is regulated by the product of the reaction. ____________________ ____ 29. The graph shows that the rate of reaction increases and then decreases as the concentration of the substrate increases. _________________ ____ 30. In the production of fruit juices, enzymes break down pectin to extract a larger amount of juice and to produce a clear juice. ____________________ ____ 31. The cell membrane is a dynamic barrier surrounding the cytosol. ____________________ ____ 32. Subunits of ribosomes are assembled in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. ____________________ ____ 33. Lysosomes are involved in protein synthesis. ____________________ ____ 34. Polypeptide chains are assembled in the ribosomes and enter the smooth endoplasmic reticulum where they are modified into final form. ____________________ ____ 35. Cells that have a low requirement for energy generally have many mitochondria. ____________________ ____ 36. The endomembrane system includes the plasma membrane, nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, vesicles, and mitochondria. ____________________ ____ 37. A vacuole takes up 50 to 90 % of an animal cell’s interior. ____________________ ____ 38. The enzyme catalase found in vacuoles is used to convert hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen. ____________________ ____ 39. Cilia are hairlike structures that create movement. ____________________ ____ 40. Pseudopods are used in some eukaryotic cells to move the cell and engulf prey. ____________________ ____ 41. The phospholipid bilayer is very solid. ____________________ ____ 42. Phospholipid molecules in a membrane are arranged with their non-polar fatty acid tails facing the exterior. ____________________ ____ 43. Cholesterol is only found in the membranes of plant cells. ____________________ ____ 44. Cholesterol has a hydrophilic OH group at one end and a hydrophobic region at the other end. ____________________ ____ 45. Proteins that are embedded in the lipid bilayer are called peripheral membrane proteins. ____________________ ____ 46. Membrane proteins have four functions: transport, enzymatic activity, triggering signals, and communication. ____________________ ____ 47. Peripheral membrane proteins are held to membrane surfaces by covalent bonds. ____________________ ____ 48. The R groups of non-polar amino acids are hydrophilic. ____________________ ____ 49. The diagram shows a peripheral membrane protein. ____________________ ____ 50. Most peripheral proteins are found on the cytoskeleton side of the membrane. ____________________ ____ 51. Scientists are researching the use of nanobots to diagnose and treat cancer. ____________________ ____ 52. The transmembrane exchange of materials involves the plasma membrane only. ____________________ ____ 53. Osmosis is a form of active membrane transport. ____________________ ____ 54. The transport of ions is facilitated by carrier proteins. ____________________ ____ 55. Water diffuses from an area of high solute concentration to an area of low water concentration. ____________________ ____ 56. Molecules that are best able to move across a membrane unassisted are small polar molecules. ____________________ ____ 57. A red blood cell that is placed in a hypertonic solution will expand. ____________________ ____ 58. If a red blood cell is placed in an isotonic solution, there will be no net movement of water. ____________________ ____ 59. A cell is placed in a hypertonic solution. This means that the concentration of water is higher in the solution. ____________________ ____ 60. A Na+/K+ pump simultaneously pushes three Na+ ions out of a cell and pumps three K+ ions into the cell. ____________________ Biochemistry True and False Nelson Answer Section MODIFIED TRUE/FALSE 1. ANS: OBJ: MSC: 2. ANS: T PTS: 1 1.1 The Fundamental Chemistry of Life Knowledge F, 6 REF: K/U LOC: B2.1 PTS: 1 REF: K/U LOC: B2.1 MSC: Knowledge 3. ANS: F, chemical bond OBJ: 1.1 The Fundamental Chemistry of Life PTS: LOC: 4. ANS: OBJ: 5. ANS: OBJ: 1.1 The Fundamental Chemistry of Life 1 REF: K/U B2.1 MSC: Knowledge T 1.2 Water: Life's Solvent F, hydrogen bonds PTS: 1 LOC: B2.1 6. ANS: F, high PTS: LOC: 7. ANS: OBJ: 8. ANS: PTS: 1 LOC: B2.1 REF: A MSC: Knowledge REF: K/U MSC: Knowledge OBJ: 1.2 Water: Life's Solvent 1 REF: K/U B2.1 MSC: Knowledge T 1.2 Water: Life's Solvent F, double, and triple OBJ: 1.2 Water: Life's Solvent PTS: 1 LOC: B2.1 REF: A MSC: Understanding PTS: 1 LOC: B2.1 9. ANS: F, C–OH REF: K/U MSC: Knowledge OBJ: 1.3 The Carbon Chemistry of Life PTS: 1 LOC: B2.1 10. ANS: F, carbonyl REF: C MSC: Knowledge OBJ: 1.3 The Carbon Chemistry of Life PTS: LOC: 11. ANS: OBJ: 12. ANS: 1 REF: T/I OBJ: 1.3 The Carbon Chemistry of Life B3.3 MSC: Analysis and Application T PTS: 1 REF: T/I 1.3 The Carbon Chemistry of Life LOC: B3.3 MSC: Analysis and Application F, fructose PTS: LOC: 13. ANS: OBJ: 1 REF: A B3.2 MSC: Knowledge T 1.4 Carbohydrates and Lipids OBJ: 1.4 Carbohydrates and Lipids PTS: 1 LOC: B2.1 REF: K/U MSC: Knowledge 14. ANS: F, hydrophobic PTS: 1 LOC: B3.2 15. ANS: F, three REF: K/U OBJ: 1.4 Carbohydrates and Lipids MSC: Understanding PTS: 1 LOC: B3.2 16. ANS: F, less REF: K/U MSC: Knowledge OBJ: 1.4 Carbohydrates and Lipids 1 REF: A B3.2 MSC: Evaluation T 1.5 Proteins and Nucleic Acids T 1.5 Proteins and Nucleic Acids F, –COOH OBJ: 1.4 Carbohydrates and Lipids PTS: LOC: 17. ANS: OBJ: 18. ANS: OBJ: 19. ANS: PTS: 1 LOC: B3.2 20. ANS: F, prosthetic PTS: LOC: PTS: LOC: 1 B3.2 1 B3.2 REF: MSC: REF: MSC: K/U Knowledge K/U Understanding REF: K/U OBJ: 1.5 Proteins and Nucleic Acids MSC: Understanding PTS: 1 REF: A OBJ: 1.5 Proteins and Nucleic Acids LOC: B3.2 MSC: Understanding 21. ANS: F, sugar–phosphate PTS: 1 REF: K/U OBJ: 1.5 Proteins and Nucleic Acids LOC: B3.2 MSC: Understanding 22. ANS: F, phosphodiester PTS: 1 REF: T/I OBJ: 1.5 Proteins and Nucleic Acids LOC: B3.2 MSC: Understanding 23. ANS: F, chemical bonding PTS: OBJ: LOC: 24. ANS: 1 REF: K/U 1.6 Biology Journal: Linus Pauling: Creativity and Controversy in Science and Society B3.2 MSC: Understanding F, equally PTS: OBJ: LOC: 25. ANS: 1 REF: K/U 1.6 Biology Journal: Linus Pauling: Creativity and Controversy in Science and Society B3.2 MSC: Understanding F, unchanged PTS: 1 REF: K/U MSC: Understanding 26. ANS: F, an irreversible PTS: 1 REF: A MSC: Understanding OBJ: 1.7 Enzymes LOC: B3.4 OBJ: 1.7 Enzymes LOC: B3.4 27. ANS: F, decrease PTS: 1 REF: K/U MSC: Understanding 28. ANS: F, feedback OBJ: 1.7 Enzymes LOC: B3.4 PTS: 1 REF: K/U MSC: Understanding 29. ANS: F, levels off OBJ: 1.7 Enzymes LOC: B3.4 PTS: MSC: 30. ANS: OBJ: 31. ANS: OBJ: 1.7 Enzymes LOC: B3.4 1 REF: T/I Understanding T 1.7 Enzymes LOC: B3.4 F, plasma membrane PTS: 1 LOC: B3.1 32. ANS: F, nucleolus PTS: 1 REF: A MSC: Understanding REF: K/U MSC: Knowledge OBJ: 2.1 Cell Structures PTS: 1 REF: K/U LOC: B3.1 MSC: Knowledge 33. ANS: F, The endoplasmic reticulum OBJ: 2.1 Cell Structures PTS: 1 REF: K/U LOC: B3.1 MSC: Knowledge 34. ANS: F, rough endoplasmic reticulum OBJ: 2.1 Cell Structures PTS: 1 LOC: B3.1 35. ANS: F, high OBJ: 2.1 Cell Structures REF: K/U MSC: Knowledge PTS: 1 REF: T/I OBJ: 2.1 Cell Structures LOC: B3.1 MSC: Understanding 36. ANS: F, Golgi bodies PTS: 1 REF: K/U LOC: B3.1 MSC: Knowledge 37. ANS: F, plant cell’s OBJ: 2.1 Cell Structures PTS: 1 REF: K/U LOC: B3.1 MSC: Knowledge 38. ANS: F, peroxisomes OBJ: 2.1 Cell Structures PTS: LOC: 39. ANS: OBJ: 40. ANS: OBJ: 1 REF: K/U OBJ: B3.1 MSC: Understanding T PTS: 2.1 Cell Structures LOC: T PTS: 2.1 Cell Structures LOC: 2.1 Cell Structures 1 B3.1 1 B3.1 REF: MSC: REF: MSC: K/U Knowledge K/U Knowledge 41. ANS: F, fluid PTS: 1 REF: K/U LOC: B3.6 MSC: Knowledge 42. ANS: F, polar phosphate heads OBJ: 2.2 Membrane Structure and Functions PTS: 1 REF: K/U LOC: B3.6 MSC: Knowledge 43. ANS: F, animal cells OBJ: 2.2 Membrane Structure and Functions PTS: LOC: 44. ANS: OBJ: MSC: 45. ANS: 1 REF: K/U OBJ: 2.2 Membrane Structure and Functions B3.6 MSC: Knowledge T PTS: 1 REF: K/U 2.2 Membrane Structure and Functions LOC: B3.6 Knowledge F, integral membrane proteins PTS: 1 REF: K/U OBJ: 2.2 Membrane Structure and Functions LOC: B3.6 MSC: Knowledge 46. ANS: F, attachment and recognition of molecules PTS: 1 REF: K/U LOC: B3.6 MSC: Knowledge 47. ANS: F, non-covalent bonds OBJ: 2.2 Membrane Structure and Functions PTS: 1 REF: K/U LOC: B3.6 MSC: Knowledge 48. ANS: F, hydrophobic OBJ: 2.2 Membrane Structure and Functions PTS: 1 REF: K/U OBJ: 2.2 Membrane Structure and Functions LOC: B3.6 MSC: Knowledge 49. ANS: F transmembrane protein (integral membrane protein) transmembrane protein integral membrane protein PTS: LOC: 50. ANS: OBJ: MSC: 51. ANS: OBJ: LOC: 52. ANS: 1 REF: C OBJ: 2.2 Membrane Structure and Functions B3.6 MSC: Understanding T PTS: 1 REF: K/U 2.2 Membrane Structure and Functions LOC: B3.6 Understanding T PTS: 1 REF: A 2.3 Explore Applications of Cell Biology: Nanotechnology in Medicine B1.2 MSC: Knowledge F, and the organelle membranes PTS: 1 REF: K/U LOC: B3.6 MSC: Knowledge 53. ANS: F, passive membrane transport OBJ: 2.4 Transport across Membranes PTS: 1 REF: K/U LOC: B3.6 MSC: Knowledge 54. ANS: F, channel proteins OBJ: 2.4 Transport across Membranes PTS: 1 REF: K/U LOC: B3.6 MSC: Knowledge 55. ANS: F area of high water concentration low solute concentration OBJ: 2.4 Transport across Membranes PTS: 1 LOC: B3.6 56. ANS: F, non-polar REF: T/I OBJ: 2.4 Transport across Membranes MSC: Understanding PTS: 1 LOC: B3.6 57. ANS: F, shrink REF: T/I OBJ: 2.4 Transport across Membranes MSC: Understanding PTS: LOC: 58. ANS: OBJ: 59. ANS: 1 REF: T/I OBJ: 2.4 Transport across Membranes B3.6 MSC: Understanding T PTS: 1 REF: T/I 2.4 Transport across Membranes LOC: B3.6 MSC: Understanding F, in the cell PTS: 1 REF: T/I OBJ: 2.4 Transport across Membranes LOC: B3.6 MSC: Understanding 60. ANS: F, two K+ ions PTS: 1 LOC: B3.6 REF: K/U MSC: Knowledge OBJ: 2.4 Transport across Membranes