Earth Science
advertisement

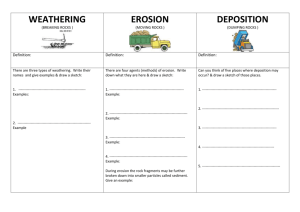
What are the different types of weathering and how do they affect the earth’s surface? Password Review Describe the word below using only one word. constructive Password Review Describe the word below using only one word. crust Password Review Describe the word below using only one word. erosion Password Review Describe the word below using only one word. earthquake Password Review Describe the word below using only one word. divergent Password Review Describe the word below using only one word. destructive Password Review Describe the word below using only one word. mantle Password Review Describe the word below using only one word. volcano Password Review Describe the word below using only one word. Weathering What are the different types of weathering and how do they affect the earth’s surface? Weathering is a general term used to describe processes that break down rocks at or near the surface of the earth. Weathering Biological Physical Chemical Physical Weathering Water Seeps inside crack and pores of rock and freezes and wedges rocks apart Rivers tumble rocks making them smooth Examples Potholes, sidewalk cracks, smooth river rocks. Physical Weathering Air: Changes in temperature from hot to cold, making rocks expand and contract, weakens and cracks them. Examples: Cracks on surfaces of rocks. Wind Blows sand and small rocks against large rocks, chipping them away and smoothing them (like sandpaper) Examples: Smooth rocks in the deserts What are the different types of weathering and how do they affect the earth’s surface? Chemical Weathering Water Enters cracks and pores or rock, the chemicals in the water react with minerals in rock and dissolve or change them. Examples: Caves, statues, and buildings dissolving Chemical Weathering Air Air contains oxygen which interacts with minerals such as iron, aluminum, silicon and copper Examples: Iron rusting Copper turning green Biological Weathering Plants Animals People -tree roots that grow in cracks of rocks -burrowing animals dig and scrape on rocks -excavating, digging, mining, construction Ex. Ex. - Lichen grows on rocks and makes an acid that dissolves them Ex. Weeds in sidewalks, tree roots cracking side walks Animal homes or burrows Rock steps worn down around rocks from people walking, mines With a Partner… Do the mini quiz You have about 5 minutes to complete this task. Check! Cave formation After a cold winter, more cracks appear in the sidewalk Scratches on a rock that appear to be from raccoon The Statue of Liberty was once bronze, but now green. Shiny rocks made in a rock tumbler Tree roots that have cracked a sidewalk What is erosion, and what are the three main agents of erosion? WARM UP….DECIDE WHAT EACH FORCE IS, CONSTRUCTIVE OR DESTRUCTIVE. Constructive Earthquakes Volcanic Eruptions Weathering Erosion Deposition Floods Destructive Let’s take a trip to the GRAND CANYON! Gravity Wind Erosion Water Ice Water Erosion Water is the most powerful agent of erosion. Rain water picks up soil and sand as it runs off. Rivers carry away rocks and soil. Over many years, rivers move enough materials to create valleys and canyons. Along the coast, the waves of the oceans move sand and rocks. Wind Erosion Wind erosion happens mostly along the ground surface. Wind carries off soil and small rocks. Wrap it up. Elbow partners…. Is erosion a destructive or constructive force? Explain your thinking. On Your Own…. Put your notes in the binder. 2. Complete the vocabulary activity (turn it in number order). 3. Read a science book from the front. 1. Constructive Earthquakes Volcanic Eruptions Weathering Erosion Deposition Floods Destructive What is erosion, and what are the four main agents of erosion? MATERIALS…. BINDER NOTES PENCIL Ice Erosion Snow and ice can form glaciers in the mountains These glaciers move down the mountainside acting as bulldozers, picking up rocks. Gravity Erosion Gravity is the force that causes object to fall to Earth. Rivers and glaciers flow downhill because of gravity. Landslides and rock falls are a result of gravity. Wrap it Up… ODD MAN OUT…. Which one doesn’t belong, and why? Glaciers Landslides Earthquakes Volcanoes Wrap it Up… ODD MAN OUT…. Which one doesn’t belong, and why? Water Wind Fire Ice Gravity On Your Own…. Put your notes in the binder. 2. Complete the text book activity….(Chapter 1, Lesson 2). 3. Read a science book from the front. 1. Gravity Wind Wind erosion happens mostly along the_______surface. Wind _______ off soil and small rocks. Erosion Water Water is the __________ agent of erosion. Rain water picks up soil and sand as it _________. Rivers __________ rocks and soil. Over many years, rivers move enough materials to create ______________ Along the coast, the ________of the oceans move sand and rocks. Gravity is the force that causes object to ______ to Earth. Rivers and glaciers ______________ because of gravity. _______________ _________ are a result of gravity Ice Snow and ice can form _______in the mountains These glaciers move down the mountainside acting as bulldozers, ___________. What is deposition? How does this relate to erosion and weathering? MATERIALS…. BINDER PENCIL Erosion Weathering Deposition With your neighbors, take two minutes to come up with a definition of weathering and erosion. Erosion The carrying away of sediments by moving water, wind, moving ice, or gravity. Weathering A destructive force that breaks down earth’s surface mechanically or chemically. What do you think Deposition is? Deposition What is deposition? What are examples of deposition? What is deposition? What are examples of deposition? Mississippi River Delta What is deposition? What are examples of deposition? Sand Dunes Erosion The carrying away of sediments by moving water, wind, moving ice, or gravity. Weathering A destructive force that breaks down earth’s surface mechanically or chemically. Deposition The dropping, or releasing of sediments that have been moved from one place to another. How do weathering, erosion, and deposition relate? Wrap it Up…. Odd Man Out… Himalayan Mountains San Andreas Fault Hawaiian Islands Delta On your own… Complete the Weathering, Erosion, Deposition Sort. 2. Complete your work from yesterday. 3. Read a science book from the front. 1.