II. Problembereiche der Wirtschaftspolitik
advertisement
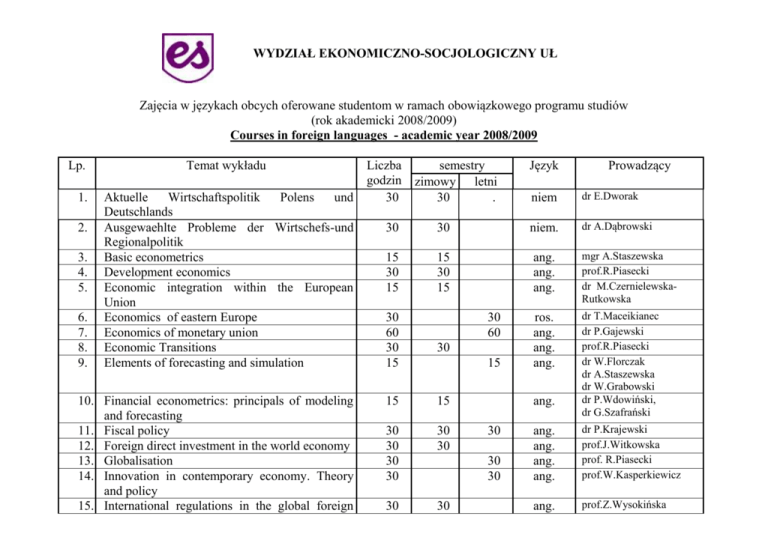
WYDZIAŁ EKONOMICZNO-SOCJOLOGICZNY UŁ Zajęcia w językach obcych oferowane studentom w ramach obowiązkowego programu studiów (rok akademicki 2008/2009) Courses in foreign languages - academic year 2008/2009 Lp. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Temat wykładu Aktuelle Wirtschaftspolitik Polens und Deutschlands Ausgewaehlte Probleme der Wirtschefs-und Regionalpolitik Basic econometrics Development economics Economic integration within the European Union Economics of eastern Europe Economics of monetary union Economic Transitions Elements of forecasting and simulation 10. Financial econometrics: principals of modeling and forecasting 11. Fiscal policy 12. Foreign direct investment in the world economy 13. Globalisation 14. Innovation in contemporary economy. Theory and policy 15. International regulations in the global foreign Liczba godzin 30 semestry zimowy letni 30 . Język Prowadzący niem dr E.Dworak dr A.Dąbrowski 30 30 niem. 15 30 15 15 30 15 ang. ang. ang. mgr A.Staszewska prof.R.Piasecki dr M.CzernielewskaRutkowska ros. ang. ang. ang. dr T.Maceikianec dr P.Gajewski prof.R.Piasecki dr W.Florczak dr A.Staszewska dr W.Grabowski dr P.Wdowiński, dr G.Szafrański 30 60 30 15 30 60 30 15 15 15 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 30 ang. 30 30 30 ang. ang. ang. ang. dr P.Krajewski prof.J.Witkowska prof. R.Piasecki prof.W.Kasperkiewicz ang. prof.Z.Wysokińska 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. trade Introduction to game theory Introduction to game theory and decision making under uncertainty Intermediate microeconomic and macroeconomic Labour market and public policy Linear programming in modelling and solving economic decision problems Macroekonomics Macroeconomics Macroeconomics with elements of economic policy Microeconomics Operations reseach – basic and application Participative management Practical aspects of komputer systems implementation In modern economy Real Estate Markets Regionalpolitic der Europaischen Union (Regional policy of the UE) Sectoral and multisectoral models of the economy 31. Statistics for business and economics 32. Statistical market analysis ang. ang. dr J.Neneman dr I.Konarzewska 30 ang. dr G.Walerysiak 30 15 ang. ang. prof.E.Kwiatkowski dr I.Konarzewska ang. ang. ang. mgr A.Myślińska dr K.Skorupińska dr J.Działo ang. ang. ang. ang. dr M.Kozłowski dr I.Konarzewska prof.St.Rudolf mgr Ł.Murowaniecki ang. ang. dr M.Sopiński dr K.Lewandowski dr hab. M.Plich, dr M.Przybyliński, mgr J.Boratyński Dr E.Roszko-Grzegorek dr A.Jędrzejczak, dr J.Korzeniewski, dr A.Baszczyńska 15 15 15 15 30 30 15 30 30 30 15 30 30 30 30 15 30 15 30 15 30 15 30 30 15 30 15 15 15 ang. 15 15 15 ang. ang. 15 Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: OPERATIONS RESEACH - BASIC THEORY AND APPLICATIONS Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 2 15 1 semesters Lecture Dr Iwona Konarzewska Informatics and Econometrics Written form Mathematics, Statistics Mathematical methods of optimization for decision problems in business and economics with deterministic or probabilistic assumptions. Introduction to linear programming, simplex algorithm, duality and sensitivity analysis. Transportation problem. Description: Decision-Making under uncertainty. Project management - CPM, PERT. Introduction to queueing models. Lawrence J. A., Pasternack B. A. (2002): Applied Management Science, Wiley Literature: Winston W. L., Albright S. Ch.: Practical Management Science, Wandsworth Publ. Co., 1997 Additional information: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: Description: LINEAR PROGRAMMING IN MODELLING AND SOLVING ECONOMIC DECISION PROBLEMS Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 2 15 1 Semester Lecture Dr Iwona Konarzewska Written form Linear Algebra Introduction to linear programming: LP model, graphical solution of two-variable linear problems with sensitivity analysis, modelling special economic problems: blending problem, diet problem, work and production scheduling, multiperiod decision problems and others. Simplex algorithm: Duality and sensitivity analysis. Interpretation of the dual problem and its optimal solution. Transportation problem formulation of the transportation problem – constructing transportation tableau for balanced and unbalanced problems; special situations – prohibited routes, limited capacity, transshipment, methods for developing initial solution. Stepping-Stone and Modified Distribution (MODI) algorithms Anderson D.R., Sweeney D.J., Williams T. A.: Management Science, quantitative approaches to decision making, West Publ. Co.,1994 Hillier F. S., Lieberman G. J.: Introduction to Operations Research, Mc Graw-Hill Publ. Co., 1990 Literature: Winston W. L., Albright S. Ch.: Practical Management Science, Wandsworth Publ. Co, 1997 Winston W., L.: Operations Research: Applications and Algorithms, Duxbury Press, Boston, 1987 Additional information: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: Description: Literature: Additional information: INTRODUCTION TO GAME THEORY AND DECISION MAKING UNDER UNCERTAINTY Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 2 15 1 Semester Lecture Dr Iwona Konarzewska Written form Statistics, Linear Algebra The elements of utility theory. Payoff-table analysis and different decision criteria: without probabilities – max-max, maxmin, Hurwicz criterion, insufficient reason criterion, min-max regret; with probabilities – max expected payoff, min expected regret. Decision trees – solving decision problem using backward induction method. Value of perfect information. Decision making with experimentation – Bayes rule. Estimating value of sample/additional information. Two-person zero-sum and constant-sum games: pure and randomized strategies, domination, solving games – saddle points and solution in randomized strategies, graphical solution procedure, solving games by linear programming. Anderson D.R., Sweeney D.J., Williams T. A.: Management Science, quantitative approaches to decision making, West Publ. Co.,1994 Hillier F. S., Lieberman G. J.: Introduction to Stochastic Models in Operations Research, Mc Graw-Hill Publ. Co., 1990 Winston W. L., Albright S. Ch.: Practical Management Science, Wandsworth Publ. Co, 1997 Winston W., L.: Operations Research: Applications and Algorithms, Duxbury Press, Boston, 1987. Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: STATISTICAL MARKET ANALYSIS Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 2 15 1 Semester Lecture Dr Alina Jędrzejczak, dr Jerzy Korzeniewski, dr Aleksandra Baszczyńska students of the third year of Information and Econometrics Written test General knowledge of English Dr Alina Jędrzejczak, dr Jerzy Korzeniewski, dr Aleksandra Baszczyńska The course consists of 15 hours of classes during which students work on statistical texts written in English. Both understanding Description: and speaking capacities are drilled during the course. The scope of the subject covers characteristics of statistical population, measures of statistical correlation and methods of dynamical phenomena investigation. Literature: Levine D. E., Berenson M. L., Stephan D. (1999), „Statistics for Managers”, Prentice Hall Additional information: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: INTERMEDIATE MICROECONOMIC AND MACROECONOMIC University of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Lecture Dr Grzegorz Walerysiak Two interterm tests Basic math The aims is to make students acquaint with basic micro and macro theories to make them ready to analyze and present basic processes and mechanisms connected with market and economic policy. Content 1 Market: supply and demand side (curves, equations), the market mechanism, elasticities 2. The analysis of competitive markets (evaluating the gains and losses from government policy (minimum prices, quotas, taxes, consumer and producer surplus) Description: 3. Market structure: monopoly (sources of monopoly power, the social costs of monopoly power 4. Price discrimination 5. The goods market (composition of GDP, the determination of equilibrium) 6. Financial market (demand for money, the determination of interest rate) 7. The IS-LM model (government policy in IS-LM model) 8. The AS-AD model (aggregate supply and labor market, the short and medium run, effects of a monetary policy, budget deficit and other factors in short and medium run). a) Pindyck R., Microeconomics, Prentice Hall International, London 2001 Literature: b) Blanchard O., Macroeconomics, Prentice Hall International, Massachutsetts 2003 Hirshleifer J., Price theory and applications, Prentice Hall International, London 1988 Additional information: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: MACROECONOMICS Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Lecture Katarzyna Skorupińska, PhD Students of Economics, III year Final work at the end of the semester, active participation in classes Knowledge of English, basic knowledge of macroeconomics Mr Tadeusz Wejchert, kei@uni.lodz.pl I. Preliminaries 1. Aggregate Output 2. The Other Major Macroeconomics Variables II. The Goods Market 1. The Composition of GDP 2. The Demand for Goods 3. The Determination of Equilibrium Output 4. Conditions for Equilibrium in the Goods Market Description: III. Financial Market 1. The Demand for Money 2. The Determination of the Interest Rate 3. Monetary Policy and Open Market Operations 4. The Supply and the Demand for Central Bank Money IV. Goods and Financial Market: The IS-LM Model 1. The Goods Market and the IS Relation 2. Financial Market and the LM Relation 1. 2. 3. Putting the IS and the LM Relations Together 4. Fiscal Policy 5. Monetary Policy V. The Labor Market 1. Movements in Unemployment 2. Wage Determination 3. Price Determination 4. The Natural Rate of Unemployment VI. Putting All Markets Together: The AS-AD Model 1. Aggregate Supply 2. Aggregate Demand 3. Equilibrium in the Short Run and in the Medium Run 4. The Effects of a Monetary Expansion 5. A Decrease in the Budget Deficit O. Blanchard, 2003, Macroeconomics, (Third Edition), Prentice Hall International Literature: E. Dulio, 1998, Macroeconomics, McGraw-Hill Additional information: - Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: Description: Literature: Additional information: LABOUR MARKET AND PUBLIC POLICY University of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Lecture and Conversation prof. zw. dr hab. Eugeniusz Kwiatkowski Preparation of one paper (essay) on the base of literature, active participation in discussions. none 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 1. 2. 3. Labour market: definitions. Labour market trends in Poland and other countries. Labour market theories: classical, keynesian, natural rate of unemployment, NAIRU. Unemployment in Poland and other countries. Types of unemployment. Unemployment theories. Macroeconomic policy and unemployment. Fiscal policy. Monetary policy. Main controversies. Labour Market Policies: passive and active. Labour Market Policies in Poland. How to beat unemployment: main recommendations. D. Bosworth, P. Dawkins and T. Stromback The Economics of the Labour Market, Longman 1996; R. Dornbusch and S. Fischer Macroeconomics, McGraw – Hill, 1990; E. Kwiatkowski, M.W. Socha, U. Sztanderska, Labour Market Flexibility and Employment Security Poland, “Employment Paper”, 2001/28, ILO, Geneva. Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: FISCAL POLICY Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Lecture Piotr Krajewski students of economics exam Piotr Krajewski 1. The definition of fiscal policy 2. Public sector in Poland 3. The main element sof public sector in Poland 4. Central budget 5. Budget revenues 6. PIT Description: 7. CIT 8. VAT 9. Excise 10. Social security contributions 11. Budget expenditures 12 Budget deficit 13. Public debt Literature: Stiglitz Ekonomia sektora publicznego 2004 PWN, Economics of Public the Sector 2000 Additional information: - Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: ECONOMICS OF EASTERN EUROPE Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Lecture dr Tadeusz Maceikianec Students of economy faculty studying russian language The written test on the end of semester dr Tadeusz Maceikianec Main objective of the course is audience’s familiarization with economy of all Eastern Europe countries(Russia, Belorussia, Ukraine, Moldavia, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Bulgaria, Hungary, Romania, Czech Republic, Slovakia), its condition, mechanisms and institutions of functioning, most important problems and development trends. Relative competitiveness of Polish Description: economy. Main results: knowledge of strengths and weaknesses of the regions economy and knowledge of specialistic russian onomastics. С.Роузфилд, Сравнительная экономика стран мира. Культура, богатство и власть в XXI веке, Московский Literature: государственный институт международных отношений , Москва 2004 Н.В.Захарова, Экономика стран Европейского союза. Учебное пособие, Гардарики, Москва 2008 Additional information: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: Description: ECONOMICS OF MONETARY UNION Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 8 60 2 Semesters Seminar Pawel Gajewski Short presentations, discussion, semester tests. Macroeconomics, basic knowledge of international economics The course aims at discussing vital macroeconomic issues through the prism of participating in a monetary union. The course is composed of two parts (one part per one semester): (i) Theoretical aspects of economics in a monetary union and the performance of eurozone (issues: history of economic and monetary integration, OCA theory, macroeconomic policy under monetary union, common monetary policy, economic track of the eurozone, fiscal policies and the SGP, impact of EMU on prices, reasons not to join) (ii) Poland and EMU (issues: Polish economy now, Poland and OCA criteria, costs and benefits of a monetary union, mechanisms of absorbing shocks, areas of reforms) The course starts and ends with a “join or not to join” debate. Each topic is introduced in a short presentation prepared by the students. The group is then encouraged to ask questions and express opinions on the presentation and the topic itself. The lecturer is responsible for moderating the discussion and ensuring that all the key problems related to the topic are covered in the discussion. Students obtain points for presentations and active participation in discussions. They are graded based on the amount of points gathered during the semester. Textbook: Paul de Grauwe, “Economics of Monetary Union”, Oxford University Press. Literature: Additional papers and reports (or relevant links) are distributed through email. Additional information: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: MICROECONOMICS Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Lecture Maciej Kozłowski 1 Exams English & Basic Microeconomics Knowledge Mr. Maciej Kozłowski The purpose of a course in Microeconomics is to provide a thorough understanding of the principles of economics that apply to the functions of individual decision makers, both consumers and producers, within the larger economic system. It Description: places primary emphasis on the nature and functions of product markets, and includes the study of factor markets and of the role of government in promoting greater efficiency and equity in the economy. C.R.McConnell, S.L.Brue, W.H.Pope, Microeconomics, 1990, McGraw-HillRyerson Limited, Toronto Bradley R. Schiller, The Economy Today, 1989, Random House, Business Division, New York Frank Robert H., Bernanke Ben S., Principles of Microeconomics, 2006 Literature: Frank Robert H., Microeconomics and Behavior, 2005 W. Nicholson, Intermediate Microeconomics, SouthWest Thomson Learning, 2006 Additional: W.J.Ethier, 1988, Modern International Economics, W.W. Norton and Company, New York-London: Additional information: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: REGIONALPOLITIK DER EUROPÄISCHEN UNION ( REGIONAL POLICY OF THE UE) Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Lecture Krzysztof Lewandowski, PhD Polish students of Economics, 3rd year test Good knowledge of German History of the EU, Institutions of the EU, Budget of the European Community, determinants of regional growth, regional policy in new theories, evolution of the regional policy in the EC; instruments of the regional policy; objectives of the regional policy; forms of intervention; EU structural policy in period 2007 – 2013; Interaction of Community`s and national regional policy in Description: Poland and Germany. A. Hoppe, Europäische Regionalpolitik und ihre national Implementation, Leske & Budrich, Opladen 2001. W. Weidenfeld, W. Wessels (Hrsg.), Europa von A bis Z, Nomos, Berlin 2006. Literature: K. Toepel, Zusammenwirken von nationaler und europäischer Regionalpolitik in den neuen Bundesländern, Peter Lang, Frankfurt am Main. R. Bieber, A. Epinay, M. Haag, Die Europäische Union, Nomos, Baden – Baden 2008. Additional information: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: MACROECONOMICS Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 8 60 2 semesters Conversatory Anna Myślińska Full time students, second cycle (both Polish and foreign) Attendance, activity, essays I would prefer basic economic courses but as not all of my students have taken it - none Anna Myślińska Mostly lecture, with some questions to students. Description: Literature: Additional information: J. Sachs, F. Larrain, Macroeconomics In The Global Economy, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, 1993 David Romer, Advanced Macroeconomics, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., New York, St. Louis et al., 1996 Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: INTERNATIONAL REGULATIONS IN THE GLOBAL FOREIGN TRADE Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Lecture Prof. dr hab. Zofia Wysokinska Master degree IV year Economics Lecture with the active participation of students Students is obliged to have basic knowledge concerning the International Economics or International Economic Relations Zofia Wysokinska; e-mail: zofwys@uni.lodz.pl 1. Liberalization of foreign trade in the world economy 2. The role of the WTO in the world economy 3. Transnational regulations within the WTO (provisions and clauses) 4. The role of General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) 5. The role of General Agreement on Trade in Services (GATS) 6. Trade Related Investment Measures (TRIMs) and Trade Related Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPs)- Agreements within the WTO regulations Description: 7. Multilateral Environmental Agreements (MEA) 8. Cooperation of the WTO with International Standardization Organization (ISO) 9. Common Trade Policy (CTP) of the EU and its instruments 10. Reform of CTP in the context of the WTO provisions 11. Competition policy in the EU and provisions of the WTO 12. Anti-dumping Agreement 13. The Agreement on Clothing and Textiles (ACT) 14. Adaptation to WTO and EU rules in Poland 1) WTO Annual Report, http://www.wto.org/english/res_e/reser_e/annual_report_e.htm 2) Zofia Wysokinska, Foreign Trade in Environmental Products; The WTO Regulations and Environmental Programs, Global Literature: Economy Journal , 2005 3) Documents and Reports from the WTO Web-side, www.wto.org Additional information: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: MACROECONOMICS WITH ELEMENTS OF ECONOMIC POLICY Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Lecture Joanna Dzialo 3-rd year students Written exam Basic knowledge of economics Joanna Działo 1/The goods market: composition of GDP, demand for goods, determination of equilibrium output, investment equal saving 2/Financial markets: demand for money, supply of money, determination of interest rate 3/ Goods and financial markets: the IS-LM model: using a policy mix, how does the IS-LM model fit the facts? 4/ The labour market: movements in unemployment, wage determination, price determination, the natural rate of unemployment Description: 5/Putting all markets together: the AS-AD model: aggregate supply, aggregate demand, equilibrium in the short run and the medium run, the effects of a monetary expansion, an increase in the budget deficit 6/The natural rate of unemployment and the Phillips curve: inflation, expected inflation and unemployment Phillips curve 7/ Openness in goods and financial markets: exports and imports, the choice between domestic goods and foreign goods, nominal exchange rate, from nominal to real exchange rate 8/ The goods market in an open economy: the IS relation in an open economy, equilibrium output and the trade balance R.S. Pindyck, D.L. Rubensfeld, 2001, Microeconomics, 5th Edition, Prentice Hall International. Inc. The Economists, different issues J. Sachs, F. Larrain, Macroeconomics In The Global Economy, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, 1993 Additional information: W. E. Griffiths, R. Carter Hill, G. G. Judge, Learning and practising econometrics, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1993 Literature: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: FINANCIAL ECONOMETRICS: PRINCIPLES OF MODELLING AND FORECASTING Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 2 15 1 Semester Lecture dr Grzegorz Szafrański, dr Piotr Wdowinski Econometrics, Finance students final test and econometric project on financial series modelling / forecasting basic econometrics (preferably in English) dr Grzegorz Szafrański, dr Piotr Wdowiński The course is focused on modelling and forecasting financial markets. Students do research with financial data (e.g. stock returns, interest rate, exchange rates). Single-equation econometric models with low and high frequency data are used in forecasting. New Description: econometric methods are applied, like GARCH modelling framework, vector autoregression models, cointegration and error correction models. Students present both theoretical and empirical research on modelling financial time series. The research is done with econometric software GRETL Literature: Additional information: 1. Brooks (2002), Introductory Econometrics for Finance, CUP, with slides available online at www.cambridge.org 2. Campbell, Lo and MacKinley (1997), The econometrics of financial markets, Princeton University Press. 3. Fama, French (2004), The Capital Asset Pricing Model: Theory and Evidence, Journal of Economic Perspective, 18, 2546. 4. Osińska M. (2006), Ekonometria finansowa, PWE, Warszawa. 5. Szafrański (2008), The Interest Rate Pass-through in Poland 1997-2005, Findecon Monograph Series: Advances in Financial Market Analysis Number 4: Financial Markets: Principles of Modelling, Forecasting, and Decision-Making, WUŁ. 6. Wdowiński P. (2004), Determinants of Country Beta Risk in Poland, CESifo Working Paper Series No. 1120. Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: SECTORAL AND MULTISECTORAL MODELS OF THE ECONOMY Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 2 15 1 Semester Seminar Dr hab. Mariusz Plich Dr Michał Przybyliński Dr Jakub Boratyński Students with background in quantitative economics Presentations and written test Econometrics, Macroeconomics, Microeconomics Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: Dr hab. Mariusz Plich During the course students are introduced into sectoral and multisectoral modelling. They learn the principles of building and application of integrated models and applied general equilibrium models. Course contents: 1. Multisectoral modelling – basic concepts. Applications of multisectoral models of the economy. 2. General outline of an INFORUM-type model. Blocks of the INFORUM model: foreign trade, consumption, investment, wages, labour productivity, employment. Description: 3. Basic assumptions and structure of a typical applied general equilibrium (AGE) model. 4. Parameter calibration in AGE models. Simulation and comparative static analysis. Extensions to the basic specification. 5. Demand systems. 6. Estimation problems in sectoral models. Compulsory Almon, C. (1979) A System of Consumption Functions and its Estimation for Belgium, Southern Economic Journal, vol. 46, No. 1, July, pp. 85‐106. Almon, C. (1996) A Perhaps Adequate Demand System. Inforum Working Papers or: Modeling Consumer Demand. In: Craft of Economic Literature: Modeling. Part 3. Chapter 18. Almon, C. (1996) Regression with just the facts. Inforum Working Papers. Grassini, M. (2005), CGE Versus Inforum Modelling Approach, 15th International Conference on Input-Output Techniques, http://inforumweb.umd.edu/papers/ioconferences/2005/GrassiniPeking.pdf. Kehoe, P. J., Kehoe, T. J. (1994), A Primer on Static Applied General Equilibrium Models, Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Quarterly Review, Vol. 18, No. 1. Meade, D. S. (2001), The LIFT Model, Inforum Working Papers (WP#01-002). Pan, S., Yu, S., 2003, Introduction to MUDAN Model (CUFE Version), http://www.inforum.umd.edu/papers/conferences/2003/s_pan01.pdf. Supplementary Almon, C., Craft of Economic Modeling (parts 1-3). Deaton, A. and Muellbauer, J. (1980) An almost ideal demand system, American Economic Review, Vol. 70, No. 3, June, pp. 312‐326. Deaton, A. (1986) Demand Analysis. In: Griliches Z., M. D. Intriligator (eds.) Handbook of Econometrics. Elsevier Science Publisher. Chapter 30. McKitrick, R. R. (1998), The Econometric Critique of Computable General Equilibrium Modeling: The Role of Functional Forms, Economic Modelling, Vol. 15. Plich, M. (2000) System of Demand Functions for Poland – New Estimates. In: Proceedings of AMFET'99 Conference – Modelling Economies in Transition, Absolwent, Łódź: 161–185. Ponewczyński M. (2005), Consumption in the IMPEC Model with Application of the Perhaps Adequate Demand System – New Results. In: Modelling Economies In Transition 2004. AMFET, Łódź. Shoven, J. B., Whalley, J. (1984), Applied General-Equilibrium Models of Taxation and International Trade: An Introduction and Survey, Journal of Economic Literature, Vol. 22. Additional information: Course title: STATISTICS FOR BUSINESS AND ECONOMICS School, city: Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Faculty: Economics and Sociology ERASMUS Subject code: 2 15 1 Semester Tutorials Elżbieta Roszko-Grzegorek Course participants both national and international students. Attendance, active participation and submission of assignment will be grounds to pass the course. During this course students will learn how to apply statistical terminology in English. Due to this knowledge of descriptive Prerequisites: statistics methods supported by the ability of making calculations is a must. Deadline of application: Contact person: 1. Data, measurement, and statistics 2. Descriptive statistics I: Qualitative data Quantitative data Frequency distribution Class and class width Graphs 3. Descriptive statistics II: Description: Mean Median Mode Percentiles Quartiles Measures of dispersion 4. Simple linear regression and correlation: 5. Index numbers 1. T. Walczak, Słownik terminów statystycznych, GUS, Warszawa 1997 2. A. Welfe, J. Brzeszczyński, M. Majsterek, Angielsko-polski i polsko-angielski słownik terminów metod ilościowych, PWE, Warszawa 2002 Literature: 3. D.Z. Anderson, D.J. Sweeney, T.A. Williams, Statistics for Business and Economics, West Publishing Company 1990 4. BLS Handbook of Methods, US, Department of Labour Bureau of Labour Statistics, April 1997 ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Additional information: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF COMPUTER SYSTEMS IMPLEMENTATION IN MODERN ECONOMY Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Faculty of Economics and Sociology 2 15 1 Semester Conversatory Dr Łukasz Murowaniecki Preparation of the paper by every student and presentation of this paper to other students None A teaching objectives is preparation to work with documents in English, introduction to rules of topic presentation in English, introduction to basic terms in computer science. Contents: 1. Selection of proper English sources. 2. Preparation of chosen topic by each student. 3. Presentation of prepared topic. 4. After presentation: discussion, q&a, teacher’s comments and summary. Exemplary list of topics: 1. Computer crimes 2. History of digital communication Description: 3. Information technology and computers in modern economy 4. Digital wallet (e-money) 5. Computing file formats 6. Key features of on-line banking 7. Voice over Internet Protocol 8. Artificial intelligence 9. Cryptography 10. EAN and bar codes 11. Enterprise Resource Planning 12. Digital photography 13. Software engineering 14. System analysis and design Literature: Bibliography depends on the topic selected by student. For every topic lecturer suggests list of materials and literature. Additional information: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: REAL ESTATE MARKETS Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Faculty of Economics and Sociology 2 15 1 Semester Lecture Dr Michał Sopiński Test, getting credit Dr Michał Sopiński, misopi@uni.lodz.pl 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Description: 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. Literature: Real Estate as an economic good Legal basis Physical characteristic features Economic characteristic features Legal and institutional characteristic features Functions of real estate Definitions of real estate market Real estate market characteristics Property market diversification Demand and supply analysis Property market balance Functions of real estate market Property market subjects Real estate market fluctuations Real estate and capital markets Property and portfolio theory Value vs. price Real estate European markets Global property markets Polish vs. foreign real estate markets Kodeks cywilny E. Kucharska-Stasiak: Nieruchomość w gospodarce rynkowej, Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN Warszawa 2006 r. E. Kucharska-Stasiak - red.: Inwestowanie w nieruchomości, Valor Łódź 1999 r. Additional information: --- E. Kucharska-Stasiak - red.: Zarządzanie nieruchomościami, Valor Łódź 2000 r. J. Brzeski - red.: Vademecum zarządcy nieruchomości, Krakowski Instytut Nieruchomości Kraków 2001 r. Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: ECONOMIC INTEGRATION WITHIN THE EUROPEAN UNION Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Faculty of Economics and Sociology 2 15 1 Semester Lecture Dr Małgorzata Czernielewska - Rutkowska Test, getting credit Dr Małgorzata Czernielewska – Rutkowska, mczernielewska@interia.pl 1.Institutional and legal rchitecture of the European Union. The process of widening and deepening of the European integration 2.Financial system of the European Union: general budget - statement of revenues and expenditure, principles of budgetary law, budgetary procedure, financial control by Court of Auditors and OLAF, Delors I, Delors II, Agenda 2000 packages, towards new financial perspective, main dilemmas of EU public finances. 3.Budgetary and monetary policies as two main centres of policy-making. Exchange rate policy 4.Is the Single Market really single? Internal Market - an area without internal borders where free movements of goods, freedom to provide sendces, free movement of capital Description: and free movement of workers and people is ensured as a cornerstone of the European economic integration. A tentative assessment 5.Labour market as a challenge for employment policy: main employment indicators, the Luxembourg process, the European Social Fund as a main tool of social policy 6.Why and what policy of socio-economic cohesion in the European Union?. Status quo, outcome, towards a new (?) policy 7.The European Union in the world - international comparisons. The most dynamic and knowledge-based economy? The Lisbon process: strategy, outcome, policy challenges, mid-term review, strengthening Artis, M., Nixon, F. (1997), The Economics ofthe European Union, Oxford University Press Literature: El-Agraa, A et al. (2000), The European Union: History, Institutions, Economics and Policies, Prentice Hali Grauwe, P. de (2000), Economics ofMonetary Union, Oxford University Press, 2000 Hitiris, T. (1998), The European Union Economics, Prentice Hali Pelkmans, J. (2001), European Integration. Methods and Economic Analysis, Longman Swann, D. (2000), The Economics of Europę: from Common Market to the European Union, Penguin Additional information: ---- Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: AUSGEWAEHLTE PROBLEME DER WIRTSCHAFTS- UND REGIONALPOLITIK Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Lecture Dr Adam Dąbrowski Grundlagen der Makro- und Mikrooekonomie Deadline of application: Contact person: Dr Adam Dąbrowski, adamd@uni.lodz.pl I. Das Wesen der Wirtschaftspolitik Zum Begriff und Inhalt der Wirtschaftspolitik Rahmenbedingungen der Wirtschaftspolitik Disziplinaere Verknupfung Theoretische Konzeptionen der Wirtschaftspolitik /Dogmengeschichtliche Grundlagen/ II. Problembereiche der Wirtschaftspolitik Theorie der Wirtschaftspolitik – Elemente des wirtschaftspolitischen Entscheidungsprozesses, Elemente der Wirtschaftspolitik /Ziele, Mittel Traeger/ Strukturpolitik Geldpolitik Fiskalpolitik Arbeitsmarktpolitik Aussenwirtschaftspolitik Regionalpolitik in Praxis Begruendung einer Regionalpolitik Ziele der Regionalpolitik Instrumente Regionale Strategien UE-Regionalpolitik Fallbeispiele : /Deutschland, Polen/ Description: III. Literature: Vahlens Kompendium der Wirtschaftstheorie und Wirtschaftspolitik, Verlag Vahlen, neuste Auflage. Hans-Rudolf Paters, Grundlagen der Mesooekonomie und Strukturpolitik, Verlag Paul Haupt, Bern und Stuttgart, neuste Auflage. L.Schaetzl, Wirtschaftsgeographie, /3 Baende/,Schoeningh, Muenchen, Wien, Zuerich 1998. F. Buttler, K.Gerlach, P.Liepmann, Grundlagen der Regionalpolitik, Reinbek bei Hamburg, neuste Auflage. P.Winiarski (red.), Polityka gospodarcza, PWN, Warszawa 2000. Additional information: --- Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: INTORDUCTION TO GAME THEORY Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 2 15 1 Semester Lecture Jarosław Neneman Written exam Introduction to Microeconomics Non-technical introduction to Game Theory. First the tools of Game Theory are presented, then its applications. The lecture is full of games played among and with students. CONTENT Basic ideas and terminology Description: Games with sequential moves, extend form of game Games with simultaneous moves, normal form of game Prisoners’ dilemma Strategic moves Literature: A. Dixit, S. Skeath, Games of Strategy, 2nd ed., W.W. Norton, 2004 Additional information: Course title: PARTICIPATIVE MANAGEMENT School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Seminar Professor Stanisław Rudolf 20 students Tests Essay and presentation on one of the issues 30th of September or 15th of February Tadeusz Wejchert +48426355363, kei@uni.lodz.pl Issues: Main forms of participative management, The role of creativity in business , The concept of total quality management, Communication in company, Group forms of work organisation, Brain storming, Team building, Search conferences, Changes Description: management, Quality circles, The stages of problem solving process, European Works Councils, Workers participation in the supervisory board of companies, Privatisation and participative management , Participative management as an important aspect of globalisation , The concept of company marketing orientation , Knowledge management, Compulsory: E. Poustma, Recent Trends in Employee Financial Participation in the European Union, Luxembourg, 2002 P.M Senge, The dance of Change: The Challenges to Sustaining Momentum in Learning Organizations, 2001 Literature: Supplementary: E. Bono, Serious Creativity, New York, 1992 K. Sisson (editor), New Forms of Work Organisation. Can Europe realise its potential?, Dublin 1997 D.K.Carry, K.J.Hard, W.J.Trahant, Managing in the Change Process, McGraw-Hill 1996 P.F.Drucker, Managing in Turbulent Times, Oxford, 1990 Additional information: Course title: ELEMENTS OF FORECASTING AND SIMULATIONS School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Sociology and Economics 2 15 1 semester Lecture Dr Waldemar Florczak, dr Anna Staszewska, mgr Wojciech Grabowski Written examination 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Description: Literature: Additional information: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Basic concepts and notions. Forecasting in the regression model. Forecasting in the simultaneous equations model and in the VAR. Forecasting in qualitative variables models. Forecasting in count data models. Forecasting currency and financial crises. Combined forecasts. Simulation analyses. Goldberger A. S., Econometric Theory, John Wiley & Sons Inc., New York, 1964 Maddala G. S., Introduction to Econometrics, John Wiley & Sons Inc., Chichester, 2002 Maddala G. S., Limited-Dependent and Qualitative Variables in Econometrics, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1994 Makridakis S., Wheelwright S. C., Hyndman R. J., Forecasting. Methods and Application, John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1998 Whitley J. D., A Course in Macroeconomic Modelling and Forecasting, Harvester Wheatsheaf, New York, 1994 Welfe A., Brzeszczyński J., Majsterek M., Angielsko-polski, polsko-angielski słownik terminów metod ilościowych, PWE, Warszawa, 2002 Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: BASIC ECONOMETRICS Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 2 15 1 Semester Lecture dr Anna Staszewska 3rd year of Informatics and Econometrics Written exam Introductory course in Econometrics dr Anna Staszewska This unit aims to familiarise the students with econometrics as it is presented in the English language. It should enable the students to apply statistical techniques to the estimation and testing of economic models and thereby provide them with skills necessary both to undertake their own empirical studies and to evaluate empirical work in the published literature. Description: Course contents: regression inference, specification analysis and model selection, simultaneous equations models, Monte Carlo experiments and the bootstrap. 1/ compulsory: 1. A.Welfe, J.Brzeszczyński, M.Majsterek, Słownik terminów metod ilościowych. Angielsko–polski. Polsko-angielski, PWE Warszawa, 2002. 2. Greene W. H., Econometric Analysis, Prentice Hall, 2008 Literature: 2/ supplementary: 1. 2. 3. 4. W.Charemza, D.F.Deadman, New Directions in Econometric Practice, London, 1997 Davidson R., MacKinnon J.G., Econometric Theory and Methods, Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2004 G.S.Maddala, Introduction to Econometrics, Wiley, 2001 Pindyck R.S., Rubinfeld D.L., Econometric Models and Economic Forecasts, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1991 Additional information: COURSE TITLE: ECONOMIC TRANSITION School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: University of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 hours 1 Semester Lecture Prof. dr Ryszard Piasecki 60% final test, 10% participation, 30% two essays Microeconomics, macroeconomics End of February Prof.. Dr Ryszard Piasecki CONTENT: I. Recent economic trends and prospects II. Macroeconomic policies a) monetary management b) fiscal stance c) assessment of macroeconomic policies III. Progress in structural reform a) the labour market b) pension reform c) privatisation and enterprise restructuring d) the banking system IV. The health care a) reforming the system b) problems that need to be addressed by the reform c) achieving equity objectives d) assessment and recommendations V. The tax system reform a) the economic and social context influencing the design of the tax system b) taxation and economic performance c) scope for further reform Description: Literature: Additional information: VI. Poland in the European Union VII. Poland and globalisation Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: INNOVATION IN CONTEMPORARY ECONOMY. THEORY AND POLICY. University of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Lecture dr hab. Witold Kasperkiewicz, professor 3 year Written exam 30.06.2009 Description: Theories of innovation, national system of innovation, innovation policy, knowledge-based economy, intellectual capital in firm 1. Ch. Freeman, The Economics of Industrial Innovation, F. Pinter, London, 1982. Literature: 2. J. A. Schumpeter, Business Cycles, New York - London, 1939. 3. M. M. Fischer, Innovation, Networks and Knowledge Spillovers, Springer, Berlin 2006. Additional information: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT IN THE WORLD ECONOMY Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Lecture Prof. Janina Witkowska Students of Economics Assessment Method: Presentation of papers (50%) and active participation in classes (50%). Prerequisites: Basic knowledge of international economics Deadline of application: October 1st Contact person: Ms Daria Fidos 1. Transnational corporations and foreign direct investment. Main definitions. Types of foreign direct investment. 2. Recent trends in foreign direct investment in the world economy. Geographical patterns of global foreign direct investment. Sector/branch structure of foreign direct investment. 3. Motives for and barriers to foreign direct investment in Central and Eastern Europe. 4. Policy towards foreign investors. Definition and main types of foreign direct investment incentives. 5. Incentives competition among countries. Consequences for host countries. Description: 6. Trade–related investment measures. GATT/WTO Agreement on TRIMs. Prohibited TRIMs according to the Agreement. 7. Foreign direct investment and development – effects on development through trade. 8. Foreign direct investment and development of host countries: savings and investment, Technology transfer and innovation. 9. Foreign direct investment and development of host countries: entrepreneurship and linkages employment and skill development 10. Foreign direct investment, trade and development: policy issues. 11. Social responsibility of transnational corporations. UN Global Compact. 12. Foreign direct investment theories: the traditional view, the ‘oligopolistic’ advantages theory, the product life-cycle theory, the internalisation theory, the eclectic theory of international production. 13. Foreign direct investment inflows into Poland: selected aspects. Characteristics of foreign direct investment according to country of origin, sector/ branch structure and regional structure. 14. Consequences of foreign direct investment inflows for the economy of Poland. 1/ Compulsory: 1. World Investment Report 2008. Transnational Corporations, and the Infrastructure Challenge (Overview), UN, N. York and Geneva, 2008 2. M. Du Pont, Foreign Direct Investment in Transitional Economies. A Case Study of China and Poland, Houndsmills, London, N. York 2000 3. Foreign Direct Investment and Development, UN, N. York and Geneva,1999 Literature: 2/ Optional: 1. J. Witkowska , Foreign Direct Investment in the Changing Business Environment of the European Union's New Member States, http://www.bepress.com/gej/vol7/iss4/2 2. Incentives and Foreign Direct Investment, UN, N. York and Geneva, 1997 3. Implementing the Global Compact. A Booklet for Inspiration, UNDP, Copenhagen June 2005. Additional information: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: DEVELOPMENT ECONOMICS Univeristy of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Lecture Prof.zw.dr hab. Ryszard Piasecki 40% essays (3), 10% participation, 50% final test Microeconomics, macroeconomics End of October Prof. Ryszard Piasecki AIMS To provide students with knowledge of development economics ( theory and practise) in the context of globalisation processes. To make them analyse development problems connected with the global economy. The accent is put on recognition of the crisis of economic development, poverty, the Washington Consensus limits, institutional and cultural aspects of development, strategies of development, new development paradigms. CONTENT 1. Defining, measuring, and analysing economic development Description: 2. Theories of economic development – general framework 3. Import-substitution and export-oriented strategies (country case studies of South-East Asian, Latin American and African countries) 4. New country-specific strategy (India, China) 5. The Washington Consensus (its limits) and Post-Washington Consensus 6. Institutional and cultural factors of development 7. The Dilemmas of Development LEARNING OUTCOMES On completion of this module a student should be able to: Identify, define, and analyse main factors of economic development and globalisation Describe and know how to measure the level of economic development To describe, and compare main development models To understand main globalisation challenges TEXTBOOK Ha-Joon Chang (ed), Rethinking development economics, Anthem, Press 2002 RECCOMMENDED READING Ash Narain Roy, The Third World in the Age of Globalisation: Requiem or New Agenda ?, Zed Books, London and New York, 1999 Ben Fine, Costas Lapavitsas i Jonathan Pincus (ed), Development Policy in the Twenty.first Century (beyond the post-Washington consensus), Routledge, London 2001 Literature: Oswaldo de Rivero, The Myth of Development: The non-viable economies of the XXI century, Zed Book Ltd, New York 2001 Piasecki R., Wolnicki M., “The Evolution of Development Economics and Globalization”, International Journal of Social Economics, London – New York, March 2004 Severine Rugumamu, Globalization and Africa’s Future: Towards Structural Stability, Integration and Sustainable Development, AAPS Occas.pap. ser ISSN 1561-9478, vol. 5, no 2, 2001 Stiglitz J.E., Knowledge for Development: Economic Science. Economic Policy and Economic Advice, The World Bank 1999 Streeten P., Globalisation: Threat or Opportunity, Copenhagen Business School Press, Copenhagen 2001 Additional information: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: GLOBALISATION University of Lodz, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Lecture Prof.zw.dr hab. Ryszard Piasecki 40% essays (3), 10% participation, 50% final test Microeconmics, macroeconomics End of October, 2008 Prof.zw. dr hab. Ryszard Piasecki AIMS To provide students with knowledge of globalisation processes in today’s world ( theory and practise).To make them analyse globalisation challenges, main actors, potential threats and opportunities. The accent is put on liberalisation of movements of goods, capital and services as well as the development of communication and telecommunication techniques, the Washington Consensus limits, institutional and cultural aspects of globalisation, multinational corporations and new development paradigms. Description: CONTENT 8. Defining, measuring, and analysing globalisation 9. Theories of globalisation – general framework 10. The role of the USA 11. National state in the globalisation era 12. Developed and underdeveloped world 13. The Washington Consensus (its limits) and Post-Washington Consensus 14. Institutional and cultural aspects of globalisation Globalisation, Global Governance and the Dilemmas of Development TEXTBOOK Literature: J. E. Stiglitz, The Roaring Nineties, W.W. Norton Company, New York 2003 RECCOMMENDED READING Bhagwati J, In Defense of Globalization, Oxford University Press, 2004 Posner R.A., Frontiers of Legal Theory, Harvard University Press, 2001 Piasecki R., Wolnicki M., “The Evolution of Development Economics and Globalization”, International Journal of Social Economics, London – New York, March 2004 Rugumamu S., Globalization and Africa’s Future: Towards Structural Stability, Integration and Sustainable Development, AAPS Occas.pap. ser ISSN 1561-9478, vol. 5, no 2, 2001 Stiglitz J.E., Knowledge for Development: Economic Science. Economic Policy and Economic Advice, The World Bank 1999 Streeten P., Globalisation: Threat or Opportunity, Copenhagen Business School Press, Copenhagen 2001 Additional information: Course title: School, city: Faculty: ERASMUS Subject code: ECTS points: Number of hours: Duration: Type: Lecturer: Target group: Assessment Method: Prerequisites: Deadline of application: Contact person: AKTUELLE WIRTSCHAFTSPOLITIK POLENS UND DEUTSCHLANDS Lodzer Univeristät, PL LODZ 01 Economics and Sociology 4 30 1 Semester Der Vortrag Dr Edyta Dworak Das 4. Jahr Die műndliche und schriftliche Prüfung 7.03.09 edyta.dworak0@neostrada.pl Probleme der Wirtschaftspolitik in Polen und Deutschland Description: 1.G. Mankiw, Volkswirtschaftslehre, Schaeffer, Poeschel, Stuttgart 2004 2.P. Samuelson, W. Nordhaus, Volkswirtschaftslehre, Bund-Verlag, Koeln 1985 3.Franfurter Allgemeine Zeitung, 4.Der Spiegel Literature: Additional information:





