Routine Data Systems - Carolina Population Center
advertisement

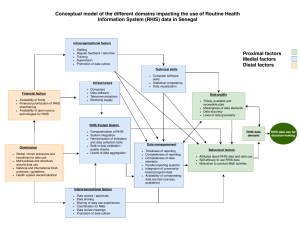
Routine Data Systems Data Use for Program Monitoring Learning Objectives Differentiate between routine and non-routine data Understand parameters and influences of HIS via the PRISM framework Recognize & use tools available to improve RHIS function Session Overview General concepts of an RHIS Health information systems PRISM framework for understanding factors that influence RHIS PRISM Toolset for RHIS1 RHIS Performance Diagnostic Tool RHIS Overview & Facility/Office Checklist Organizational & Behavioral Questionnaire RHIS Management Assessment Tool Activity – Applying the PRISM Tools 1MEASURE Evaluation, Data demand and information use in the health sector: strategies and tools Definitions Health information system A system providing specific information support to decision-making process at each level of an organization1 Health system All resources—people, institutions & other— arranged according to established policies to protect, promote and improve the health of the served population2 2 WHO, 1Hurtubise R (1984). Managing Information Systems. Kumarian Press, West Hartford. http://www.euro.who.int/observatory/Glossary/To pPage?phrase=H Definitions: Routine vs. Non-routine Data Routine data Are collected continuously at various times periods (daily, patient by patient, monthly etc.) Come from the HIS and its subsystems that are collected as part of an ongoing system Non-routine data Are collected at certain periods of time, or over a specific period of time Come from special studies or surveys carried out for specific purposes Are we talking about this? Or this? Or do we mean this? All of these, but this is where we really want to get Why do programs need information? Programs Need Information to Understand entire context of program status Enhance program performance through evidence-based decision making All major functions service delivery, resource mobilization, financing, stewardship All levels Community to national level Health Information Systems (HIS) HIS is an integral part of the health system Just like a health system, an HIS is not static Health systems in continuous process of change due to pressure from both outside and within the system HIS must amend itself to these changes HIS Sub-systems: Frequency of Data Collection Routine or continuous data collection Health facility-based (pt. info. & service stats) Community based (service statistics) Vital registration Sentinel reporting Program reporting systems Non-routine or periodic data collection Household or facility-based surveys Population census Rapid assessment procedures (RAP) Research HIS and HIV Programs A subset of the comprehensive health system Data sources can be routine or non-routine Contribute to data collection of various HIS subsystems Need harmonization and integration in data collection & utilization within context of national HIS (the Third One) PRISM* Framework for HIS Performance1 Inputs information system assessment, strategies & interventions Technical Determinants • system design • data collection forms • Skills/knowledge of personnel Behavioral determinants Attitudes, motivation, values Desired Outcomes = information system performance • good quality information • appropriate use of information Improved Health System Performance Systemic/Environmental Determinants: leadership, structure, culture, roles/responsibilities, resources *Performance of Routine Information System Management 1MEASURE Evaluation. 2006. Data demand and information use in the health sector: Strategies and Tools Improved Health Status RHIS Performance Diagnostic Tool HIS Quality & Use Influences Standard indicators Data collection forms Appropriate IT Data presentation Trained people Technical Determinants Technical Determinants RHIS Overview & Facility/Office Checklist HIS Quality & Use Influences Motivation Attitudes & values Confidence Sense of responsibility Behavioral Determinants Behavioral Determinants Organizational and Behavioral Questionnaire HIS Quality & Use Influences Resources Health sys. structure Roles & responsibilities Organizational culture System & Environment Determinants System & Environmental Determinants RHIS Management Assessment Tool PRISM Tools - Rationale RHIS often not produce good information for health sector decision-making Data quality may low No processes in place for using data Managers/staff not understand importance of role in information process & have little incentive Traditional Assessments of RHIS narrow in focus Answer only part of why RHIS not high quality Typical focus is on data collection or information technology alone PRISM Tools - Rationale Well designed interventions to improve RHIS should address these questions Is the organization committed to information-using culture? Do people responsible for data collection have necessary skills? Do they understand & care about importance of their work? Do managers support them with training, supervision & needed resources? Description of PRISM Tools Systematically provide answers, using an ordered process of gathering information about RHIS Objectively measure performance & identify factors hindering performance Assess performance of RHIS Identify technical, behavioral & organizational factors affect RHIS performance Aid in designing/prioritizing interventions to improve performance Support ongoing efforts for M&E of data quality & use in decision-making. PRISM Tools - Implementation Apply all four Tools for systematic assessment Implement Tools in this order: RHIS Performance Diagnostic Tool RHIS Overview & Facility/Office Checklist Organizational & Behavioral Questionnaire RHIS Management Assessment Tool PRISM Tools: RHIS Performance Diagnostic Tool Primary component in the set Determines overall RHIS performance (like MESS for whole M&E system) Examines data quality & information use to identify gaps Identifies overall strengths and weaknesses PRISM Tools: RHIS Overview & Facility/Office Checklist Addresses technical determinants of RHIS such as Structure & design of existing information systems Information flows Interaction between different information systems Use to understand availability & status of RHIS resources & practices PRISM Tools: Organizational & Behavioral Questionnaire Addresses behavioral and organizational determinants to RHIS, examines Staff capacity Knowledge, skills, confidence and motivation Organizational culture Promote value of information quality & use? Compares these factors with RHIS performance to identify related gaps PRISM Tools: RHIS Management Assessment Tool Allows a rapid assessment of management and supportive RHIS practices Results in recommendations for stronger RHIS management PRISM Tools – Guiding Principles Holistic approach that recognizes RHIS performance depends on combination of technical, organizational & behavioral factors Each of these components contributes to whole system, whole is more than the sum of its parts Causal influence of all determinants in 3 areas must be understood to improve performance PRISM Tools Guiding Principles When data collectors understand importance of their contributions, they will be more committed When decision-makers believe they have high quality data, more likely to use it for evidencebased decisions When people empowered to make decisions, become champions for accountability and transparency PRISM Tools Tools are administered, based on Observations, document review, information technology review Triangulation of multiple data sources increases validity of findings Self-assessment aspect creates sense of ownership for results & atmosphere of collaboration Steps to use PRISM Tools Identify a potential opportunity Determine how Tools would be used for the presenting need Perform pre-assessment planning Determine organization’s readiness to improve RHIS Assemble core team stakeholders Identify key informants to interview Modify Tool to fit application Assess & analyze current RHIS performance Use the Tools in order (Diagnostic, overview, organizational/behavioral, management assessment) Define plan for reaching desired level of RHIS performance Implement plan and monitor progress Goal of RHIS Produce meaningful insights about performance of health system Is our HIV program working? Increasing people willing to be counseled & tested Decreasing HIV incidence Reaching more pregnant, HIV + women More effective information systems lead to better health status for more of the population MEASURE Evaluation is a MEASURE project funded by the U.S. Agency for International Development and implemented by the Carolina Population Center at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partnership with Futures Group International, ICF Macro, John Snow, Inc., Management Sciences for Health, and Tulane University. Views expressed in this presentation do not necessarily reflect the views of USAID or the U.S. Government. MEASURE Evaluation is the USAID Global Health Bureau's primary vehicle for supporting improvements in monitoring and evaluation in population, health and nutrition worldwide.