CEO-CIO Relationship Review - Society for Information Management
advertisement

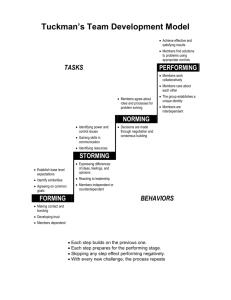
CEO-CIO Relationship Review High Speed Business and IT Transformation Takes Off at the Auto Industry’s Premium Transportation Manager SIM Detroit August 31, 2010 1 Introductions • Chris Healy • President and Chief Executive Officer, AAG – 35 years experience in business operations, planning, logistics management, and customer service – Sr. VP and GM North America FedEx Global Logistics – Executive leadership positions Caliber Systems, Boyd Brothers, Roberts Express, & Emery Air Freight – Member of the Council of Logistics Management • Greg Davidson • Chief Information Officer & Chief Marketing Officer – 27 years of software development, product marketing, IT consulting, and senior management – Recently CIO and Vice President of Professional Services Delivery, Accretive Solutions – Vice President Enterprise Systems Development, Sage Software, Irvine, CA – Vice President Systems Development, Platinum Software (now Epicor), Irvine, CA 2 Introduction to Active Aero Group Active Aero Group • Essentially two business units • • • Active On-Demand – specialty 3PL USA Jet Airlines – cargo and passenger airline Active On-Demand • Expedited freight services • • • • • • • 7 by 24 by 365 call centers Expedited culture! USA Jet Airlines • • • • • • • Air Charter Ground Express Air Freight Full Truckload MD-83s DC-9s Falcon 20s Began as air charter Added charter passenger services 7 by 24 by 365 flight operations Heavy dependency upon IT systems to operate AOD 3 AOD BUSINESS MODEL 4 Key Customers 5 Agenda • Initial state of IT-Business relationship • Initial state of IT • CEO-CIO relationship evolution over last 3 years • • • • Stages of IT-Business relationship development Forming: aligning people, process and technology Storming and Norming: process development for IT and the Business Performing: IT driving Business innovation & competitive stance • Questions and Answers 6 Initial State of IT-Business Relationship • CEO and CIO worked closely for 6 months prior to CIO beginning work • IT leadership role did not exist on a peer level with business leadership • Business viewed IT as: • • • • Unable to meet delivery dates Systems deliveries were of poor quality Dictating software feature and functionality Not as a partner • IT viewed the Business as: • • • Unable to provide functional requirements Unrealistic relative to delivery and timing expectations Not as a partner 7 Initial State of IT • People • • • • Organization lacked structure Initially “we know more about the business…” attitude was present Some personnel were not a good fit Administrative management of resources was not evident • Process • • • IT organization lacked a defined process Business roles and responsibilities relative to working with IT were never defined Business process was largely undefined and lightly documented • Technology • • • • Older technology was in place in production – relatively stable New technology had performance and quality challenges Some infrastructure was in need of replacement Telecom vendors were not managed well 8 FORMING 9 Forming: Aligning People, Process and Technology • People • • • Got “the right people on the bus” (From Good to Great by Jim Collins) Developed and institutionalized a few documented policies, procedures and processes – involved educating both IT and the Business Built a culture around quality and working “harder and smarter” • Firefighting was initially the name of the game • Crisis management was continual during the Forming phase • Process • • • Selected best practices from ITIL and CMMI process sets Prioritized implementation of best practices due to existing challenges Implemented Change Management and Release Management first • • • • Policies and procedures were formally documented and trained Needed a way to implement Change Requests quickly with a high level of quality Change Management gave us a way to define unique changes and assess impact Release Management provided a controlled means to bundle sets of Change Requests through the development, testing, and deployment phases 10 Forming: Aligning People, Process and Technology • Technology • Tactical: triage of new applications and existing infrastructure was then a daily event • Strategic: completed Single Point Of Failure (SPOF) analysis • SPOF then drove significant infrastructure projects • New corporate email system (Exchange) • New network switches, routers and firewalls • New SAN, web servers and database servers • Built out Disaster Recovery data center • Virtualization (VMWare) kept costs down • DoubleTake served as single technology for Exchange and SQL Server data synchronization 11 Forming: The CEO’s Take on This Phase • General comments on the state of the IT-Business relationship at this time • Crisis situations decreased significantly over this short period of time • Many small, incremental, tactical systems changes went into place (e.g. limit of 5 Change Requests per department) • Business noticed the increased professionalism throughout the IT Release Management cycle – they were now heavily involved! • State of CEO-CIO relationship at this time • IT Portfolio Management increased Business’ awareness that they were dealing with a finite set of resources • Trust was quickly earned via relatively large IT infrastructure investments in a very short period of time • Time working together was spent addressing tactical issues, hoping for a time when strategic issues could be addressed soon 12 Forming: The CEO’s Take on This Phase • Ultimately what I wanted from IT • Fast • Bulletproof • Scalable 13 STORMING AND NORMING 14 Storming and Norming: Process Development for IT and the Business • People • Moved from no structure to an effective, 3-part IT organization • Business Analysis and Quality Assurance (the alpha and omega) • Systems Architecture, Project Management, and Development • IT Operations • Instilled a culture of personal responsibility and accountability • Project postmortem Lessons Learned sessions proved invaluable • Mistakes became learning opportunities • Honesty and openness became woven into the IT team fabric • On the other hand, repeating mistakes became intolerable • Working with the Business was something new for key IT staff • Initial resistance and concerns raised • Immediate value was realized by doubters 15 Storming and Norming: Process Development for IT and the Business • Process • Implemented IT Service Continuity Management (ITSCM) for BC/DR • Business had a high level of incentive to make this happen • Provided a ranking of applications in terms of Business importance • ITSCM then became the backbone of the Business Continuity framework • Completed ITSCM buildout, quarterly testing, … Yankee Air Museum Fire, Oct. 2004 Willow Run Airport 16 Storming and Norming: Process Development for IT and the Business • Process continued, also implemented: • • • • • • • • IT Portfolio Management* Project Management* Configuration Management Incident Management Problem Management Requirements Management* Quality Management* Vast majority of projects were on time and achieved quality objectives * Significant Business involvement 17 Storming and Norming: Process Development for IT and the Business • Technology • Implemented a Service Management mentality within IT Operations • • • • Renegotiated telecom contracts • • • • • ServiceDesk software was a key acquisition Established ITIL Service Desk processes for serving the Business Began proactively monitoring key systems and servers Voice services provider changed Network circuit providers rationalized and BGP implemented Costs significant reduced Software tools and versions updated Additional new software tools were acquired and implemented • • • HP Mercury LoadRunner HP Mercury Quality Center HP Mercury QTP 18 Storming and Norming: The CEO’s Take on This Phase • General comments on the state of the IT-Business relationship at this time • • • • Systems stabilized giving IT and the Business more time to collaborate IT gained a deeper knowledge of the Business Business gained an insight into what a disciplined IT team could deliver With IT Portfolio Management in place, and with Change Management/Release Management running well for several months, IT earned a place at the leadership table; the Business and IT were aligned • State of CEO-CIO relationship at this time • • • • • This relationship became more strategic in nature Tactical efforts lessened as crises became rare events CIO’s knowledge of the Business increased rapidly, earning the respect of peers CEO began to see CIO as a strategic partner Tactically, CEO brought CIO into an increasing number of sales pursuits 19 PERFORMING 20 Performing: IT Driving Business Innovation & Competitive Stance • People • Performance Management implemented • First goals and objectives defined for team • For many, first performance reviews (manager and self-evaluation) • First Performance Improvement Plan efforts • Educational opportunities arose – investing in our people • The people in turn responded with greater throughput and enthusiasm 21 Performing: IT Driving Business Innovation & Competitive Stance • People: as CIO, took on additional roles • Informally as “Chief Process Officer” per ISO certification efforts • Formally as Chief Marketing Officer • Began leveraging past marketing experience to assist driving new sales • Began executing upon a number of marketing efforts • Developed detailed marketing plan and strategy • Delivered set of collaterals that leverage technology and services • Began rebranding efforts • Rebuilt marketing websites • Conducted first customer focus group • Conducted first marketing webinar • Initiated direct marketing and telemarketing campaigns • Now poised to build marketing team to expand upon driving quality leads 22 Performing: IT Driving Business Innovation & Competitive Stance • Process • Workflow development was completed for all Business units • Identified several Business bottlenecks and rework loops • Graduated to running ISO certification effort for entire AOD division • Sales • Operations • Accounting 23 Performing: IT Driving Business Innovation & Competitive Stance • Technology • Implemented competitive features into mission critical applications • Key selling points for large enterprise customers • Competitive barriers to entry • IT began playing a more active role in team sales efforts • • • • • • Team of equal partners: Sales, Operations, and IT Defining technology solutions for new customers Demonstrating new product features Collaborating with customer IT organizations on joint projects Delivered new functionality for customers where required IT took proactive technology stance • • • • Increased systems monitoring efforts Instituted monthly reviews Availability now averages 99.98% per month Built out Performance Testing Lab to stay ahead of Sales team and company growth 24 Performing: IT Driving Business Innovation & Competitive Stance • Technology case study • Customer: Celestica • Contract Manufacturer of Blackberry and other devices • High value theft issues • Defined new functionality for mapping and truck movement alerting • EDI-to-XML interfaces with their truckload carriers • Alerts for truck not moving in addition to existing alerts • Detailed mapping app for Celestica and RIM • Became key marketing case study 25 Performing: The CEO’s Take on This Phase • General comments on the state of the IT-Business relationship at this time • IT grew beyond alignment with the Business, now a growth catalyst • Landing and delighting Customers is our focus and IT plays a key role • IT automation and streamlining of Business processes serves as a catalyst to Business scalability • IT has an interwoven, symbiotic relationship now within: • Business operations planning • Business strategy definition • Sales pursuits and proposal development • Ultimately, IT delivered what I wanted • Fast • Bulletproof • Scalable 26 Performing: The CEO’s Take on This Phase • State of CEO-CIO relationship at this time • The CIO role has helped move the company into a technology leadership role within our industry • CIO role is vital to continuing company’s growth • CIOs must have the following attributes to become a trusted CEO partner • • • • • • • • Vision Business knowledge and perspective Leadership Innovation Communication Teamwork Alignment Business and customer relationships 27 QUESTIONS & ANSWERS SIM Detroit August 31, 2010 28