The Tablet Technology: Practical & Theoretical Applications
advertisement

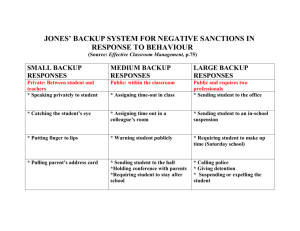
Sustainable MIS Infrastructure BSAD 141 Dave Novak BDIS: 5.1 and 5.2 Lecture Overview MIS Infrastructure Supporting operations Backup plan Disaster recovery plan Business continuity plan Agile MIS Infrastructure EWaste Sustainable IT Infrastructure MIS Infrastructure What is it? Plans for how a firm will build, deploy, use, and share its data, processes, and MIS assets Hardware Software Network Client devices & server devices What is the difference between a client and a server? MIS Infrastructure Data center – A facility used to house management information systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems Cisco projections for data center / cloud traffic to triple over next 3-4 years http://www.zdnet.com/cisco-projects-data-center-cloud-traffic-to-tripleby-2017-7000021985/ Data Centers Why would this matter to you? 1) This is the reality of modern IT / IS operations 2) HUGE $$$ 3) HUGE implications with respect to your organization’s information / data needs and uses Data Centers Design and facilities Infrastructure Power, energy efficiency cooling, site selection, cable infrastructure Legacy hardware, OS integration, rack –vs- blade, virtualization, storage and capacity –vsperformance Operations and best practices Staffing, disaster recovery, capacity planning Data Center Tour Google Data Center • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V9AiN7oJaIM ISWest Green technology Data Center Tour • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AlDWMg49z_U A not-so-impressive Data Center • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LBUYIv1DTYI • Notice the: • • • • Cabling – rat’s nest, clothes line, rainbow of colors Removed floor panels with fans resting on them Tripping hazards ‘sticky notes’ on servers Sustainable Data Centers In addition to cost and performance considerations, may focus on: Reducing carbon emissions Reducing required floor space Choosing a very specific geographic location based on more than just cost minimization strategies Data Center –vs- Cloud Data centers – enterprise IT, organization specific IT resources / assets Public cloud providers (Amazon, Facebook, Google) – provide IT-related resources and services to anyone for a fee Cloud Computing Refers to the use of resources and applications hosted remotely on the Internet Cloud Computing Why would an organization choose this option? Lack of technical expertise Cost savings (capital costs and maintenance) Flexibility Scalability Cloud Computing http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RS 6w5KYlHko&feature=youtu.be http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ae_D KNwK_ms This sounds great! Why would your organization build and maintain their own enterprise IT? Maintaining an enterprise IT system allows the organization complete control – cloud computing does not Data Center –vs- Cloud All storage, security, and service solutions are not equal…. Cloud providers tend to rely on inexpensive, older (not cutting edge) hardware solutions No tier 1 storage vendors in the public cloud (these are largest, most wellknown vendors in the field) Data Center –vs- Cloud Cloud providers tend to rely on Direct Attached Storage (DAS) as opposed to Storage Area Networks (SAN) and do not use Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks (RAID) DAS is inexpensive and simple “Best practices” for fault tolerance and performance utilize some level of RAID – cloud providers tend to replicate complete data to multiple locations Data Center –vs- Cloud Cloud providers tend to rely less on virtualization Virtualization solutions tend to be open source as opposed to commercial Cloud data centers focus on cost minimization and tend to locate where resources are least expensive Supporting Operations 1) Backup plan Strategy for copying and archiving data 2) Disaster recovery/business continuity plan Describes how the organization will deal with any potential disaster • Minimize impact • Prevention • Maximize ability to resume mission critical functions 1) Backup and Recovery Full Backup – An exact copy of a system’s information Differential Backup – Copies only subset of files or parts of files that have changed since last full backup Incremental Backup – Copies all files or parts of files that have changed since previous backup of any type 1) Backup and Recovery Type Pros Cons Full Backup • Restoration is fastest – need only one set of backup data • Backup process is slowest • High storage requirements Differential Backup • Backup process is faster than full • Restoration is faster than incremental • Storage requirements less than full • Restoration is slower than full • Backup process is slower than incremental Incremental Backup • Fastest backup process • Least storage space needed • Restoration is slowest and requires several sets of data Source: http://www.backup.info/difference-between-full-differential-and-incremental-backup 2) Disaster Recovery Plan A detailed process for recovering information or an IT system in the event of natural or man-made disasters Disaster recovery cost curve - Charts (1) the cost to the organization of the unavailability of information and technology and (2) the cost to the organization of recovering from a disaster over time 2) Disaster Recovery Curve 2) Disaster Recovery Plan Hot site - A separate and fully equipped facility where the company can move immediately after a disaster and resume business Cold site - A separate facility that does not have any computer equipment, but is a place where employees can move after a disaster Agile MIS Infrastructure Characteristics of an agile (clever, coordinated) MIS infrastructure 1) Accessibility 2) Availability 3) Maintainability 4) Portability 5) Reliability 6) Scalability 7) Usability 1) Accessibility Refers to the ease of accomplishing objectives: defines different “levels” or categories of user in terms of what each user can access, view, or create/delete when using a system Administrator access – Unrestricted access to the entire system 2) Availability Availability – Refers to the time when the system is operational or ready for use Unavailable – Time frames when a system is not operating and cannot be used High availability – System is continuously operational at all times 3) Maintainability Refers to how quickly, or the ease a system can transform to support changes as well as the time/effort to repair or upgrade Organizations must watch today’s business, as well as tomorrow’s, when designing and building systems Systems must be flexible enough to meet all types of business changes 4) Portability Refers to the ability of an application to operate on different devices or software platforms: how quickly/easily an application be moved from one environment to another 5) Reliability Refers to the proportion of time a system is functioning correctly and the accuracy of the information being provided Reliability is another term for accuracy when discussing the correctness of systems within the context of efficiency IT metrics 6) Scalability Refers to how well a system can adapt to the increased demands of growth Performance - Measures how quickly a system performs a process or transaction Capacity planning - Determines future environmental infrastructure requirements to ensure high-quality system performance 7) Usability Refers to the degree to which a system is easy to learn and efficient and satisfying to use How would you measure this? E-Waste Discarded, obsolete, or broken electronic devices CDs, DVDs, thumb drives, printer cartridges, cell phones, TVs, DVD players, etc… http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h_Zq Sige34c E-Waste Americans discard 30 Million computers each year Europeans discards 100 Million phones each year Only 15-20% of all E-waste is recycled E-Waste is 2% of the physical waste produced in the US This 2% is the source of 50-70% of the toxins released from our waste stream Source: Green IT, Velte, Velte and Elsenpeter. Mcgraw Hill. 2008 Why is E-waste different from other waste streams? Anticipated increase, decrease or leveling off of this material? Lifespan of Electronics compared to other appliances? Up-cycling parts or components? Ease of assembly and modularization of parts? Same materials? Sustainable IT Infrastructure What does this even mean? Pursuing goals such as: Improving “efficiency” Reduce green house gas emissions Reduce electricity usage Reduce e-waste Educate the public and users Sustainable IT Infrastructure The book focuses on “technological” solutions, but in reality usage policies are the most cost effective approaches to sustainability Energy star purchases Exchanges for outdated equipment Turning off monitors – putting computers in sleep mode Using smart power strips Sustainable IT Infrastructure The components of a sustainable MIS infrastructure can include Grid computing Cloud computing Virtualized computing Grid Computing A collection of computers, often geographically dispersed, that are coordinated to solve a common problem Applying resources from many computers to share processing power, memory, and data storage Virtualization Creating a software-based representation of something (rather than the actual thing) Making one resource appear as many (one physical file server appear as multiple file servers) or making many resources appear as one Mimicking the behavior of another system using simulation http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=V9AiN7oJ aIM Virtualization For example, a virtual OS is the concept of having more than one OS (more than the native OS) on a single computer • • • • Parallels VMWare VirtualBox Virtual Win Windows OS can be run in a virtual environment on a MAC Linux on a PC Virtualization Virtualization technology fundamentally strives for the same thing regardless of vendor.. Reducing the technological footprint by enabling more virtual machines (VM’s) to run on a single hardware device. Virtualized server architecture Traditional Standalone Server. May be Intel or RISC P to V process Virtualization Physical World Virtualized World Hardwar e Traditional x86 Architecture • Single OS image per machine • Software and hardware tightly coupled • Multiple applications often conflict • Underutilized resources Virtualization: • Separation of OS and hardware • OS and application contained in single file • Applications are isolated from one another • Hardware independence & flexibility Driving Reasons for Virtual Infrastructure Economic Environmental Less power consumed Less toxic electronic devices System Portability Enhanced Management Summary MIS Infrastructure Supporting operations components Agile MIS Infrastructure components EWaste Sustainable IT Infrastructure components