Book 7: Geometry, Measurement & Algebra: ( Describe and relate
advertisement

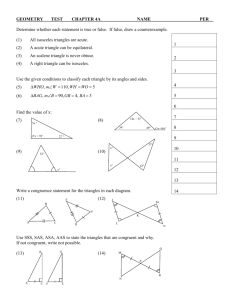
Teachers: To assure that the above standards are understood, always remind, ask and show your students: 5.3.1 How can you determine the two names of a triangle? BRIDGES CORRELATION to 5.3.1 Unit 3, Sessions 7, 12–14, 16 October Calendar Grid Set C1 Geometry: Triangles & Quadrilaterals, Activity 1 and Ind. Worksheets 1 & 2 Bridges Practice Book, pages 43, 44, 97, 140 Informal Bridges Practice Book, pages 43, 44, 97, 140 5.3.2 If the area of a parallelogram is A=bh, why would the formula for the are of a triangle be. bh? BRIDGES CORRELATION to 5.3.2 Unit 3, Sessions 1, 4, 16 Unit 3, page 336 (Challenge) Home Connections, Vol. 1: HC’s 23, 28, 34 September Problem Solving October Calendar Grid January Problem Solving March Problem Solving Number Corner Student Book pages 8, 14, 27, 34, 86, 94, 139–141 Set C1 Geometry: Triangles & Quadrilaterals, Activities 3 & 4 and Independent Worksheets 5 & 6 Bridges Practice Book, pages 45, 47, 51, 53, 54, 58, 72, 85, 91 Grade 5 MATH: Oregon Department of Education Standards for Practice or Progress Monitoring. Current Standard: 5.3 Geometry, Measurement, and Algebra: Describe and relate twodimensional shapes to three-dimensional shapes and analyze their properties, including volume and surface area. Book #7 This booklet will focus ONLY on the items in Bold Black [5.3.1 and 5.3.2] in the table below. 5.3.1 Identify and classify triangles by their angles (acute, right, obtuse) and sides (scalene, isosceles, equilateral). 5.3.2 Find and justify relationships among the formulas for the areas of triangles and parallelograms. 5.3.3 Describe three-dimensional shapes (triangular and- rectangular prisms, cube, triangular- and square-based pyramids, cylinder, cone, and sphere) by the number of edges, faces, and/or vertices as well as types of faces.. 5.3.4 Recognize volume as an attribute of three-dimensional space. 5.3.5 Determine volume by finding the total number of same-sized units of volume that fill a three dimensional shape without gaps or overlaps. 5.3.6 Recognize a cube that is one unit on an edge as the standard unit for measuring volume. 5.3.7 Determine the appropriate units, strategies, and tools for solving problems that involve estimating or measuring volume. 5.3.8 Decompose three-dimensional shapes and find surface areas and volumes of triangular and rectangular prisms. Informal Bridges Practice Book, pages 45, 47, 51, 53, 54, 58, 72, 85, 91 Formal Unit 3, Session 22 (Unit Post-Assessment and Student Reflection Sheet) Number Corner Teacher’s Guide, pages 110–114, 232–236, 320–324, 400–404 (Checkups 1, 2, 3, and 4) 5.3.9 Identify and measure necessary attributes of shapes to use area, surface area, and volume formulas to solve problems (e.g., to find which of two gift boxes needs the most wrapping paper or has the greater volume?). The test samples and strand data for this booklet can be found on the Oregon State Departments of Education web site. The use of this booklet was designed for the Hillsboro School District based on HSD Power Standards along with the ODE strand categories. This booklet is paid for and furnished to teachers for instruction by the HSD. The concept of this booklet was created by Rick & Susan Richmond © Rick & Susan Richmond 2010 Revision: Original 03-2010 Revision 10-2011 These problems are presented in an OAKS testing format. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, without written permission from Rick & Susan Richmond and the Oregon State Department of Education and the Hillsboro School District. Page 11 5.3.1 Identify and classify triangles by their angles (acute, right, obtuse) and sides (scalene, isosceles, equilateral). 1. In which triangle is there a right angle? A. A B. B C. C D. D 5.3.1 Identify and classify triangles by their angles (acute, right, obtuse) and sides (scalene, isosceles, equilateral). 10. This triangle fits in which classification? A. Right Triangle B. Scalene Triangle C. Isosceles Triangle D. Equilateral Triangle Do your work here: Do your work here: Mathematics Test Specifications and Test Blueprints 2010-2011 Rick and Susan Richmond 2011 - 2012 Page 1 Page 10 5.3.1 Identify and classify triangles by their angles (acute, right, obtuse) and sides (scalene, isosceles, equilateral). 9. Which of the following shows an equilateral triangle? 5.3.1 Identify and classify triangles by their angles (acute, right, obtuse) and sides (scalene, isosceles, equilateral). 2. What kind of triangle is this? A. right triangle B. Equilateral triangle A. A C. Isosceles but not equilateral B. B D. scalene C. C D. D Do your work here: Do your work here: Rick and Susan Richmond 2011 - 2012 2004-2008 ODE Sample Tests Page 9 Page 2 5.3.1 Identify and classify triangles by their angles (acute, right, obtuse) and sides (scalene, isosceles, equilateral). 3. Each angle in this triangle is? A. Acute B. Obtuse C. Right D. Equilateral 5.3.2 Find and justify relationships among the formulas for the areas of triangles and parallelograms. 8. What is the area of this parallelogram? Do your work here: A. 30 cm2 B. 26 cm2 C. 60 cm2 D. 17 cm2 Do your work here: 2004-2008 ODE Sample Tests Rick and Susan Richmond 2011 - 2012 Page 3 Page 8 5.3.2 Find and justify relationships among the formulas for the areas of triangles and parallelograms. 5.3.2 Find and justify relationships among the formulas for the areas of triangles and parallelograms. 7. Which would be used to find the Area of parallelogram WXYZ? A. Area = 12 x 7 B. Area = 2 x 12 x 6 C. Area = 12 x 6 D. Area = 12 x 6 2 4. In the figure below, WXYZ is a parallelogram. If the area of triangle WXY is 22 square inches, what is the area of WXYZ? A. 11 square inches B. 22 square inches C. 33 square inches D. 44 square inches Do your work here: Do your work here: Oregon Mathematics Test Specifications Blueprints 2011-2012 Rick and Susan Richmond 2011 - 2012 Page 7 Page 4 5.3.2 Find and justify relationships among the formulas for the areas of triangles and parallelograms. 5. A parallelogram is shown below with an Area of 120 inches and a height h of 8 inches. 5.3.2 Find and justify relationships among the formulas for the areas of triangles and parallelograms. 6. A parallelogram is shown on the grid. h What is the dimension of base? Which expression represents the area of this parallelogram? A. 30 B. 20 C. 15 D. 60 A. 6+6+4+4 B. 8+8+4+4 C. 6x4 D. 8x4 Do your work here: Do your work here: Rick and Susan Richmond 2011 - 2012 Rick and Susan Richmond 2011 - 2012 Page 5 Page 6