Protection and Nourishment of the Brain
advertisement

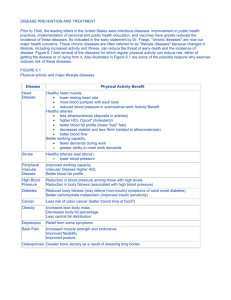
Blood Supply to the Nervous System Objectives 1. Describe the importance of blood circulation to the brain. 2. List major arteries that transport blood to the cerebrum. 3. Describe region supplied by each major artery. 4. Discuss general blood supply for brainstem, cerebellum, and spinal cord. 5. List common points of anastomoses in the vascular system. Objectives 6. Explain significance of potential collateral circulation. 7. Describe venous-sinus system. 8. Discuss mechanism of cerebrovascular accidents. 9. Discuss common cerebrovascular accidents. 10. Describe the mechanism regulating blood flow. 11. Discuss the blood-brain barrier and its clinical significance. Blood Supply Function: Total Dependence of Nerve Cells Oxygen Deprivation Within the Brain Without Adequate Blood Supply Irreversible Damage Site of Lesion Metabolic Needs of the Brain Brain’s Metabolic Needs Blood Flow to the Brain Drainage of Blood from the Brain Veins and Sinuses Vascular Network Blood Circulation to the Brain Vascular Network Large Arteries Small arteries Arterioles with small diameters Capillaries Cerebral Arteries: Lateral Brain and Cerebellar Surface Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.4 Cerebral Arteries: Midsagittal Brain Surface Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.3 Vascular Network Veins Venules Cerebral Venous Sinuses Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.7 Cerebral Veins: Lateral Surface Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.8A Cerebral Veins: Midsagittal Surface Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.8B Cerebrovascular Supply Two Arterial Systems: Cerebral Arteries Love & Webb, 1996, Figure 3-7 Cerebrovascular Supply: Carotid and Vertebral Basilar Systems Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.1A Cerebrovascular Supply: Circle of Willis Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.1B Cerebrovascular Supply: Cerebral Arterial Structure at Base of Brain Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.2 Cerebrovascular Supply: Carotid System Carotid System Cerebral Arteries Love & Webb, 1996, Figure 3-7 Cerebrovascular Supply: Carotid and Vertebral Basilar Systems Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.1A Carotid System External Carotid Artery and its Branches Internal Carotid Artery and its Branches Cerebral Arteries Love & Webb, 1996, Figure 3-7 Carotid System Internal Carotid Cerebrovascular Supply: Carotid and Vertebral Basilar Systems Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.1A Vertebral Basilar System Two Vertebral Arteries Cerebral Arteries Love & Webb, 1996, Figure 3-7 Cerebrovascular Supply: Carotid and Vertebral Basilar Systems Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.1A Cerebrovascular Supply: Circle of Willis Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.1B Cerebrovascular Supply: Cerebral Arterial Structure at Base of Brain Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.2 Vertebral Basilar System Branches Cerebrovascular Supply: Circle of Willis Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.1B Cerebrovascular Supply: Cerebral Arterial Structure at Base of Brain Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.2 Vertebral Basilar System Posterior Spinal Artery Function: Circulatory Disorders Vertebral Basilar System Anterior Spinal Artery Pathway: Function: Circulatory Disorders Corticobulbar Tract Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 14.3A Corticospinal Tract Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 14.3B Vertebral Basilar System Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery Function: Vertebral Basilar System Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Arteries Vertebral Basilar System Pontine Level Cerebrovascular Supply: Circle of Willis Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.1B Vertebral Basilar System Internal Auditory Artery Function: Vertebral Basilar System Superior Cerebellar Arteries Pathway: Function: Circulatory Disorders: Circle of Willis Shape: Location: Connections: Cerebrovascular Supply: Carotid and Vertebral Basilar Systems Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.1A Cerebrovascular Supply: Circle of Willis Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.1B Cerebrovascular Supply: Cerebral Arterial Structure at Base of Brain Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.2 Circle of Willis Components: Communicating Arteries 1. 2. Proximal Portions of the Cortical Arteries 1. 2. 3. Circle of Willis Importance: Anastomotic Point Circle of Willis Two Types of Arteries: 1. Cortical (Circumferential) Arteries 2. Central (Penetrating) Arteries Cortical Arteries 1. Anterior Cerebral Artery Pathway: Cerebral Arteries: Midsagittal Brain Surface Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.3 Cortical Arteries 1. Anterior Cerebral Artery Vascular Supply Regions: Cerebral Arteries of the Lateral and Medial Surfaces of the Left Cerebral Hemisphere Love & Webb, 1996, Figure 3-8 Cortical Arteries 1. Anterior Cerebral Arteries Vascular Supply Interruption of Blood Circulation: Motor Impairment: Cognitive Impairments: Additional Impairments: Decreased spontaneity Motor inaction Impaired judgment Limited concentration Cortical Arteries 2. Middle Cerebral Arteries Pathway: Cerebral Arteries: Lateral Brain and Cerebellar Surface Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.4 Cortical Arteries 2. Middle Cerebral Artery Vascular Supply Important Areas Cerebral Arteries of the Lateral and Medial Surfaces of the Left Cerebral Hemisphere Love & Webb, 1996, Figure 3-8 Cortical Arteries 2. Middle Cerebral Arteries Vascular Supply Cortical Arteries 2. Middle Cerebral Arteries Interruption of Blood Supply Motor Impairment: Sensory Impairment: Other Symptoms: Subcortical damage: Cortical Arteries 3. Posterior Cerebral Artery Pathway: Cortical Arteries 3. Posterior Cerebral Artery Vascular Supply Cerebral Arteries of the Lateral and Medial Surfaces of the Left Cerebral Hemisphere Love & Webb, 1996, Figure 3-8 Cortical Arteries 3. Posterior Cerebral Artery Interruption of Blood Supply Visual Impairment: Central (Penetrating) Arteries Pathway: Central (Penetrating) Arteries Vascular Supply: Supply the subcortical structures that include: Thalamus Hypothalamus Caudate nucleus Putamen Globus pallidus Basal ganglia Internal capsule Choroid plexus Other structures Central (Penetrating) Arteries Interruption of Blood Supply: Anteromedial Arteries Medial Striate Arteries Anterior Choroidal Artery Posteromedial Arteries Posterolateral Arteries Collateral Circulation Alternative Blood Supply: Importance in Recovery: Cerebrovascular Supply: Carotid and Vertebral Basilar Systems Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.1A Cerebrovascular Supply: Circle of Willis Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.1B Collateral Circulation Two Common Points of Collateral Circulation Vascular Pathologies Vascular Diseases of the Brain Vascular Pathologies: Occlusive Vascular Pathologies Atherosclerosis Vascular Pathologies: Occlusive Vascular Pathologies Ischemia Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) Vascular Pathologies: Occlusive Vascular Pathologies Treatment Compensation for Atherosclerosis Cerebrovascular Disorders Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.6A, B, C Vascular Pathologies: Occlusive Vascular Pathologies Embolism Vascular Pathologies: Occlusive Vascular Pathologies Thrombosis Vascular Pathologies: Hemorrhage Hemorrhagic Strokes Vascular Pathologies: Hemorrhage Three Major Types: 1. Intercerebral Hemorrhages 2. Subdural Hematoma 3. Aneurysm Vascular Pathologies: Arteriovenous Malformations Congenital Conditions Venous Sinus System Veins and Sinuses Function: Process: Venous Sinus System: Location of Prominent Dural Sinuses Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 2.42 Dural Sinuses Structure: Function: Major Dural Sinuses: 1. 2. 3. 4. Venous Sinus System Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.7 Cerebral Veins Function: Two Types: 1. Superficial Cerebral Veins Three Large Superficial Veins A. B. C. Cerebral Veins: Lateral Surface Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.8.A Cerebral Veins Two Types: 2. Deep Cerebral Veins Function: Cerebral Veins: Medial Surface Bhatnagar & Andy, 1995, Figure 17.8.B Blood-Brain Barrier Important Clinical Concept Blood-Brain Barrier Selective Membrane Permeability Cortical Pathologies Define the Following Technical Terms: Anastomose Aneurysm Arteriosclerosis Arteriovenous Malformations Atherosclerosis Blood-Brain Barrier Carotid Vascular System Cerebrovascular System Circle of Willis Coagulation Collateral Circulation Embolism Hemorrhage Ischemia Metabolism Paresthesia Sinus Thrombosis Watershed Infarction Review Questions 1. Describe the importance of oxygen to brain cells and how long the brain can sustain blood deprivation. 2. Describe vascular circulation to the brainstem and cerebellum. 3. Describe the difference between cortical (circumferential) and central (penetrating) arteries. 4. Describe the distribution area covered by the anterior, middle, and posterior cerebral arteries. Review Questions 5. What important functional impairments follow interruptions with blood flow in each cortical artery? 6. Discuss the importance and mechanism of collateral circulation. 7. Describe common vascular pathologies. 8. Describe the venous-sinus system. 9. What is the blood-brain barrier and what are its clinical advantages? Blood Supply of the Nervous System Graphics THINGS TO DO BEFORE LECTURE TERMS: Perfusion Act of pouring over or through, especially the passage of a fluid through the vessels of a specific organ Location of Petrous Bone Epicritic sensation Cutaneous nerve fibers that serve the purpose of perceiving fine variations of touch or temperature Watershed region A ridge which directs drainage toward either side Paresthesia Morbid or perverted sensation Abnormal sensation, as burning, prickling, formications, etc.