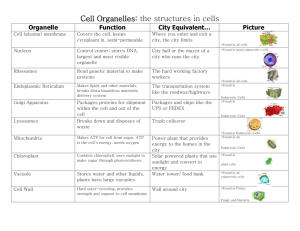
Organelle Structure and Function

CYTOSKELETON
Structure
Network of long protein strands
Located in the cytosol
No membranes
Function
Support
Help with movement of organelles in the cytosol
Cell Type
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant and Animal Cells
CYTOPLASM/CYTOSOL
Structure
Fluid between cell membrane & organelles
Contains water, salts, organic compounds
Function
Aids in movement
Cell Type
Prokaryotic and
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant and Animal Cells
Nucleus
Structure
Double membrane (nuclear envelope)
Function
Control center of the cell
Stores hereditary info (DNA)
Makes RNA and protein
Cell Type
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant and Animal Cells
Nucleolus
Structure
Nonmembrane bound structure
Function
Makes ribosomes
(nucleolus)
Cell Type
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant and Animal Cells
ROUGH ER
Structure
Internal membrane is a system of folded sacs and tunnels
Has ribosomes
Function
Intracellular highway
Molecules move from one part of cell to another to be exported out of cell
Cell Type
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant and Animal Cells
SMOOTH ER
Structure
Internal membrane of systems of folded sacs and tunnels
NO ribosomes
Function
Intracellular highway
Storage area for proteins
Cell Type
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant and Animal Cells
RIBOSOMES
Structure
Made of proteins and RNA
No membrane
Most numerous organelle
Made in nucleus (specifically in nucleolus)
Function
Aids in protein synthesis
Free ribosomes make proteins used by the cell
Ribosomes on rER make proteins for export to other cells
Cell Type
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Plant and Animal Cells
GOLGI APPARATUS
Structure
Stack of membranes or sacs filled with fluid
Function
Processing, packaging, and secreting organelle
Helps with protein synthesis
Cell Type
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant and Animal Cells
Vesicles
Structure
Small membrane-bound sacs
Function
Divide some materials from the rest of the cytoplasm
Transport these materials from place to place within the cell
Cell Type
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant and Animal Cells
Examples of Vesicles include:
- Lysosomes
- Vacuoles
- Transport vesicles
- Secretory vesicles
MITOCHONDRIA
Structure
Double membrane
Have own DNA
Very numerous in high requirement cells (muscles)
Function
Powerhouse of the cell
(energy)
Transfers energy into ATP to be used as energy for life functions
Cell Type
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant and Animal Cells
VACUOLES
Structure
Fluid filled organelles
Very large
Function
Stores enzymes
Stores waste
Cell Type
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant Cells (large)
Animal Cells (small)
LYSOSOMES
Structure
Spherical organelles
Contain enzymes
Function
Digestion
Organic molecules
Old organelles
Foreign substances
Cell Type
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant and Animal Cells
CENTRIOLE
Structure
Made of microtubules
Occur in pairs
Function
Aid in cell division
Cell Type
Eukaryotic Cells
Animal Cells
CILIA
Structure
Short hair-like projections
numerous
Function
Movement
Cell Type
Eukaryotic Cells
Animal cells
FLAGELLA
Structure
long projections that
move in whip like fashion
Function
Movement
Cell Type
Eukaryotic and
Prokaryotic Cells
Animal cells
CELL WALL
Structure
Wall outside membrane
Made of cellulose
Has pores
Function
Protect
Support
Cell Type
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant Cells
CHLOROPLASTS
Structure
Double membrane
Contains DNA
Contains green pigment
(chlorophyll)
Function
Responsible for photosynthesis
Cell Type
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant Cells
Chromatin
Structure
Strands of genetic material
Function
Genetic information of the cell
Cell Type
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic
Cells
Plant and Animal Cells
PLASTIDS
Structure
Membrane bound organelle
Function
Storage (starches, lipids, pigments)
Cell Type
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant Cells
CELL MEMBRANE
Structure
Lipid bilayer
Proteins
Function
Selectively permeable
Boundary for cell
(protection)
Cell Type
Prokaryotic and
Eukaryotic Cells
Plant and Animal Cells
Cell Analogy - Factory
Cell membrane
The doors to the factory
Ribosomes
The room where the item is made
Vacuoles
Storage room
Mitochondria
Generator room
Lysosome
Garbage cans
ER
Hallways
Nucleus
Main office
Golgi Apparatus
Assembly area
Cell Wall
The outer walls