Ch. 1 - Cell Organelles Worksheet
advertisement

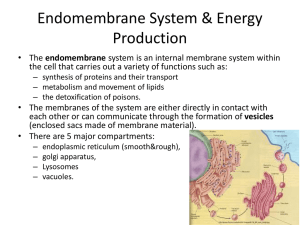
Biology 2201 – Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 – Cell Organelles and their Functions -Cell membrane -Endoplasmic reticulum -Vacuole -Microtubules/filaments -Cytoplasm -Ribosome -Vesicle -Lysosome -Nucleus -Mitochondria -Golgi apparatus -Flagella -Nucleolus -Chloroplast -Cilia -Cell wall Tiny two-part structure found throughout the cytoplasm that helps put together proteins. Structure that separates the cell interior from the outside world and controls the movement of materials into and out of the cell. Helps the cell maintain homeostasis. It has a lipid bi-layer. Command centre of the cell that contains the DNA blueprints for making proteins and is surrounded by a double-membrane to protect the DNA from potentially damaging by-products of biochemical reactions. Small membrane bound transport sac. Some special types of vesicles have different jobs in the cell (such as lysosomes that contains digestive enzymes that break down old cell parts or material brought into cells and peroxisomes that break down lipids and toxic waste products). Fluidic gel made up mostly of water and dissolved nutrients and waste. Provides a fluidic environment organelles to carry out chemical reactions. Powerhouse of the cell where organic molecules (usually carbohydrates) are broken down inside a double membrane to release and transfer energy. Large, membrane bound fluid filled sac for the temporary storage of food, water or waste products. Network of three kinds of interconnected fibres that maintain cell shape and allow for movement of cell parts (includes the cytoskeleton). Stack of flattened membrane-bound sacs that receive vesicles from the ER, contain enzymes for modifying proteins and lipids, package finished products into vesicles for transport to the cell membrane (for secretion out of the cell) and within the cell as lysosomes. System of flattened membrane-bound sacs and tubes continuous with the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope that has two types of membrane. The rough __ has ribosomes and synthesizes proteins and the smooth __ which has canals which help transport the proteins throughout the cell. Hair-like structures extending from the cell membrane that beat in a coordinated rhythm to produce movement. Many microscopic, onecelled organisms have ___, allowing them to move through water Contains digestive enzymes that break down old cell parts or material brought into cells. Plant cells have an outer ___ made of cellulose; animal cells do not have this. It provides rigidity and protection. Plastid that gives green plants their colour and transfers energy in sunlight into stored energy in carbohydrates during photosynthesis. Specialized area of chromatin (uncoiled DNA) inside the nucleus where ribosomal RNA is produced to make ribosomes. Long hair-like projections extending from the cell membrane that use a whip-like motion to move the cell. Ex. Sperm cells have a ___ which allow them to swim in the in seminal fluid.