Cell Theory: All living things are made of one or more cells The cell
advertisement

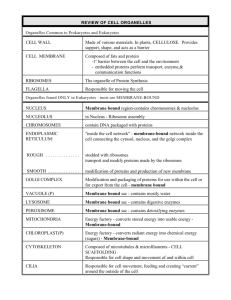
Cell Theory: All living things are made of one or more cells The cell is the basic, functional, structural unit of life Cells come from preexisting cells Nucleus: Description: double membrane bound sphere with pores Function: protect genetic information from fluctuations in the cytoplasm Nucleolus: Description: dense dark stained region in the nucleus Function: ribosome synthesis Nucleoid: Area in a prokaryotic cell where the chromosome is found Ribosome: Description: a structure made of RNA and protein, has twp parts Function: protein synthesis Rough ER: Description: portion of the endoplasmic reticulum having ribosome attached attached to the nuclear membrane Function: production and transport of protein that leaves the cell Smooth ER: Description: portion of the endoplasmic reticulum that lack ribosomes Function: transport proteins made at the rough ER, fatty acid synthesis, neutralize toxins Golgi complex: Description: stack of membrane bound flat sacs Function: storage, modification, transport of proteins Lysosome: Description: membrane bound sac containing hydrolytic enzymes Function: intracellular digestion Mitochondria: Description: double membrane bound, contains its own DNA, has two internal compartments Function: cellular respiration, makes ATP Cytoskeleton: Description: made of microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules Function: cellular structure and shape, intracellular transport Microfilaments: Description: made of actin protein units, solid rod Function: muscle contraction, amoeboid movement Microtubules: Description: made of tubulin protein units, hollow rod Function: main support and structure of animal cells, chromosome movement during Cell division, found in cilia, flagella, and centriole Centriole, centrosome, MTOC: Description: Centriole: two cylindrical structures found outside the animal cell nucleus 9 microtubule triplets arranged in a cylinder, 9+0 Centrosome: region outside the animal cell nucleus where the centrioles found Function: organize microtubules into the spindle apparatus for cell division Cilia: Description: nine microtubule doubles arranged in a cylinder, with two single microtubules down the center, 9+2 hair like extension from cell surrounded by the plasma membrane shorter than the cell’s diameter and numerous Function: movement from point “a” to point “b”, movement of fluid (Protista) over the surface of the cell, movement of material out of your lungs. Flagella: Description: nine microtubule doubles arranged in a cylinder, with two single microtubules down the center, 9+2 whip like extension from the cell surrounded by the plasma membrane much longer than the cell’s diameter, one or two per cell Function: movement from point “a” to point “b” only Chloroplast: Description: double membrane bound, contains its own DNA, has two internal compartments, contains the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll chlorophyll is green Function: photosynthesis Chromoplast: Description: membrane bound sac Function: synthesis of other plant accessory pigments that help photosynthesis, serve as antioxidants for the plant as well as for you Amyloplast: (leucoplast) Description: membrane bound sac Function: starch synthesis and storage Sap vacuole: Description: membrane bound sac, when full it can occupy up to 90% of the cell Function: storage of water and products of photosynthesis Food vacuole: Description: membrane bound sac formed by phagocytosis Function: contain cell food, will join with a lysosome for digestion inside the cell Contractile vacuole: Description: membrane bound sac that has a star shape Function: collect and excrete excess water, protect against osmotic lysis found in cells which lack a cell wall that live in a water environment. (Ptotista) Cell wall: Description: most external boundary of the cell, found in plants, fungi, Archaea, Bacteria Function: protect the cell from osmotic lysis, gives the cell its shape