Political Geography
advertisement

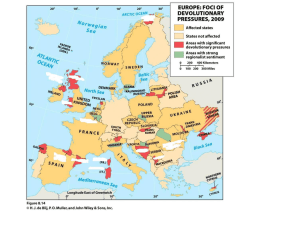
Political Geography: State Shapes and Borders AP Human Geography Territorial Morphology: The Shape of States • • • • • • Compact Prorupted Elongated Fragmented Perforated Micro Compact • Ease of communication; distance from capital to everything else easy • Example: Switzerland; Hungary Prorupted • Compact with a large projecting extension • Issues with “devolution” sometimes • Example: DR Congo; Thailand Fragmented • States with several discontinuous pieces of territory; like islands. Devolution an issue • Example: Indonesia Perforated • A state the completely surrounds another one • Example: South Africa and Lesotho Elongated • Long narrow shape due to geography or other political or economic reasons • Examples: Chile and Gambia Microstates • Tiny, usually homogenous, states • Example: Andorra, Liechtenstein, Luxembourg, Singapore Exclaves and Enclaves • Exclaves: small bits of territory that lie separate from the rest of the state by another state; not land locked • Example: Russia and Kaliningrad Enclaves • Enclaves: landlocked pieces of a state surrounded by another state • Example: Armenia, Azerbaijan and NagornoKarabakh Boundaries • Physical: easy to see and use; water (lakes, rivers, etc..) use the median-line principle • Oceans use: Law of the Sea (1983)- territory goes out to 12 nautical miles • Cultural: harder to define; language? Religion? Ethnicity? “Balkanization” and “shatter belts”(Caucasus Mts.) • Geometric: straight and imaginary Physical and Geometric Balkanization and “Shatter Belts” Boundary Disputes • Positional(definitional): Where is the border? India and China over Assam/Himalayas • Territorial: Who should own what? Pakistan vs. India over Kashmir • Resource(allocation): Who gets to use the stuff? Ex: Kuwait vs. Iraq (oil); GA VS FLA. Over water • Functional(operational): What rules should we use at the border? Ex: USA/Mexico border control and NAFTA India and China