Oct 11, 2007
advertisement

Recitation 5
•
•
•
•
•
IP address
Subnetting
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
IP Forwarding
CIDR
1
IP address
• Goals:
– Identify networks on Internet
– Identify hosts on network
• IP address: 4 bytes
– Each machine in a (IP) network has its own IP address
• Examples: 10000000 0100000 00000001 00000001
128
.
64
.
1
Net id
• IP address contains 2 parts
.
1
host id
– Prefix: network prefix OR net id
– Postfix: host id
• Example: 128.64.1.1/24
, 128.64.1.5/24
All machines in the same network have the same NET ID, and different
2
host ids
Netmask
•
•
How to specify the length of netid in IP address? Solution: Netmask.
Configure IP address for a machine:
– IP Address + Netmask
•
Netmask: 32 bits = 4 bytes
– Prefix of netmask = 111…1
– Postfix of netmask = 00…0
•
Examples: 11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000
255
.
255
.
255
.
0
• NetworkID = IP address “AND” NETMASK
IP address
128. 64.
1.1
Netmask
255.255.255.0
11111111 11111111 11111111 00000000
NetworkID
128. 64.
10000000 01000000 00000001 00000000
1.0
10000000 01000000 00000001 00000001
3
Ways to represent IP address
• For host
– 192.168.1.5
– Combination of IP address and netmask
• IP address: 192.168.1.5
• Netmask:
255.255.255.0
– In binary.
• For network
– 192.168.1.0/24
– Combination of IP address and netmask
• Network ID: 192.168.1.0
• Netmask: 255.255.255.0
4
Range in an IP network
• Assume that we have an IP network:
- 200.100.1.0 /24
Network ID = 200.100.1.0
Netmask = 255.255.255.0
• Broadcast ID ( by filling 1 to all bits for
hostid)
= 200.100.1.255
• Range: (254 host)
– 200.100.1.1 -> 200.100.1.254
5
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol)
• Obtain an IP address/netmask automatically from DHCP server!
• DHCP server may be a machine in network, or
may be integrated in HUB/SWITCH/ROUTER
• Configuration IP address range on DHCP Server
– 128.64.1.2/24 -> 128.64.1.50/24
6
Class A, B, C on Internet
•
•
For INTRANET, we can assign “ANY” IP addresses
For INTERNET, we should follow the RULES
Net ID
•
Host ID
Class A
0xxxxxxx .
xxxxxxxx . xxxxxxxx . xxxxxxxx
Class B
10xxxxxx . xxxxxxxx .
xxxxxxxx . xxxxxxxx
Class C
110xxxxx . xxxxxxxx . xxxxxxxx .
xxxxxxxx
Multicast
111xxxxx . xxxxxxxx . xxxxxxxx . xxxxxxxx
How many hosts are there in a class C network?
2^8 – 2 = 254 hosts
!!! Don’t count the IP address for NetworkID ( host id = 00…0) and broadcast
address (host id = 11..1)
7
Subneting
•
•
Example: You buy a class C network from an ISP, e.g 200.128.1.0/24,
and you want to divide the network into 2 subnets for 2 offices.
Method:
Network ID:
Netmask:
ORIGINAL NETWORK
200
.128
.1
.0
/24
11010000. 10000000. 00000001. 00000000
11111111. 11111111. 11111111. 00000000
SUB NET 1
Netmask: 11111111. 11111111. 11111111. 10000000
Net ID:
11010000. 10000000. 00000001. 00000000
=>
200. 128. 1. 0/25
SUB NET 2
Netmask: 11111111. 11111111. 11111111. 10000000
Net ID:
11010000. 10000000. 00000001. 10000000
=>
200. 128. 1. 128/25
8
Subneting (cont.)
•
Dividing into 4 subnets??
– Divide into 2 subnets, then divide each subnet into 2 other subnets !
•
Dividing into 3 subnets??
– Divide into 2 subnets, then divide one subnet into 2 other subnets !
•
•
Number of hosts in the new subnet?? What is the range???
Broadcast address? Network ID of new subnet??
•
•
Dividing into n subnets?? What is the new subnet mask?
Back to the sample question about subnetting?
9
Sample Question: Subnetting
(6 points) From the address 147.3.0.0, Linda needs to
create 50 subnets, each supporting up to 1000 hosts.
She selects the subnet mask 255.255.252.0. Explain
why this will or will not work.
(4 points) A chain of 80 stores expects to expand by 20
stores per year for the next eight years. Only one
computer connected to a router at each site will be
needed to upload the daily sales figures to corporate
headquarters. The IP address is 165.32.0.0. What
should the subnet mask be?
10
Sample Question: Subnetting
Consider a conventional class B network. A
network administrator decides to give all subnets
in the class B network a sub-net mask of
255.255.248.0.
(5 points) How many sub-nets can the
administrator use if all sub-nets use this mask?
(5 points) How many hosts are possible on each
sub-net?
(5 points) The administrator just heard that she
only needs 16 sub-nets for the class B address.
What sub-net mask maximizes the number of
hosts on each sub-net?
11
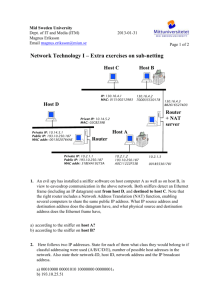
ARP (from IP add. to MAC add.)
•
Application doesn’t know MAC address !!!
–
Application works with IP address:
ssh 128.6.171.162
ping 192.168.1.1
•
Recall: Ethernet Frame Structure
MAC Dest. address
•
(ssh cereal.rutgers.edu)
MAC Source
address
Type
DATA ….
CRC
“A” knows IP X of “C”, how can A send an ethernet frame to C? How does A know MAC
of C??
HUB
Send
broadcast
MAC A -> FF: …FF, Type=ARP
Who has IP X ????
MAC C -> MAC A, type=ARP
Hey guy, I have IP X !!!
MAC A-> MAC C, type=IP
A
B
C
IP packet
D
12
Multi-Hop Forwarding Example
X sends an IP packet to Y??
1.X-> R1a
a
N1
3. R2b->Y
2. R1b->R2a
R1
b
a
R2
b
N2
x
N3
Y
1. X sends to its gateway (IP of R1a)
MAC X -> MAC R1a
IP X -> IP Y
DATA
IP X -> IP Y
DATA
IP X -> IP Y
DATA
2. R1 forwards the packet to R2
MAC R1b -> MAC R2a
3. R2 forwards the packet to Y
MAC R2b -> MAC Y
13
Multi-Hop Forwarding Example
R1
N1
R2
R3
N2
N3
N4
Dest Next hop
Routing table @ R2
N1
N2
N3
N4
R1
Deliver directly (ARP)
Deliver directly (ARP)
R3
Actual routing table contains IP addresses, Flags
indicating type of entries, net mask etc.
14
IP forwarding
ROUTING TABLE AT A ROUTER:
Destination Gateway
Genmask
Flags Metric Ref
128.6.5.0
A
255.255.255.128
U 0
128.6.5.128 B
255.255.255.128
U 0
0
127.0.0.0
0.0.0.0
255.0.0.0
U 0
0.0.0.0
128.6.5.1
0.0.0.0
UG 0
Use Iface
0
0
0
eth1
0
0
0
0
(default)
0
128.6.5.1
0.0.0.0
UG
0
0
eth0
lo
eth0
eth0
Question1: Packet with dest IP = 128.6.5.200, what is the next-hop (gateway)?
For each entry:
if ( <dest IP> AND <netmask> == <destination field>)
{
choose the next hop = the corresponding gateway;
break;
}
Question2: How many networks does the router connect to?
15
Network programming in Java
TCP/IP stack
Host A
Host B
Application Protocol
Application
Layer
Transport Protocols (UDP and TCP)
Transport
Layer
IP
IP
Data
Application
Layer
Transport
Layer
TCP/UDP
header
Data
TCP/UDP
header
Data
IP
Network
Layer
Network
Layer
Network
Layer
Network
Layer
Host-toNet Layer
Host-toNet Layer
Host-toNet Layer
Host-toNet Layer
IP
header
16
Sample Question: IP Forwarding
The following table is a routing table using
CIDR. Address bytes are in
hexadecimal. The notation “/12”
defines the length of the mask in bits.
For example, for C4.50.0.0/12, the
mask is 12 bits, or FF.F0.0.0 in
hexadecimal notation.
For each of the following destination IP
addresses (in hexadecimal), state
what the next hop will be by using the
routing table above (2 points each):
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
C4.4B.31.2E :
C4.5E.05.09 :
C4.4D.31.2E :
C4.5E.03.87 :
C4.5E.7E.12 :
C4.5E.D1.02 :
Dest.
Next Hop
C4.5E.2.0/23
A
C4.5E.4.0/22
B
C4.5E.C0.0/19
C
C4.5E.40.0/18
D
C4.4C.0.0/14
E
C0.0.0.0/2
F
80.0.0.0/1
G
default
H
17
Reducing Routing Table Size
Without CIDR:
200.71.0.0
200.71.1.0
200.71.2.0
…..
200.71.255.0
service
provider
200.71.0.0
200.71.1.0
200.71.2.0
…..
200.71.255.0
Routing
table
With CIDR:
200.71.0.0
200.71.1.0
200.71.2.0
…..
200.71.255.0
service
provider
200.71.0.0/16
Routing
table
18
Sample Question: CIDR
• The company X has 4 offices, each office has one
subnet. All subnets connect to a router (Router 1 in the
figure). This router connects to the ISP router. The
subnets are described in the figure.
139.200.1.0/26
Subnet A
139.200.1.1
139.200.1.64/26
Subnet B
139.200.1.65
192.168.1.2/24
192.168.1.3/24
Internet
139.200.1.128/26
Subnet C
139.200.1.129
Router 1
ISP Router
139.200.1.192/26
Subnet D
139.200.1.193
19
Sample Question: CIDR (cont.)
A. Fill out the routing table for the router 1:
Destination
Netmask
Nexthop
Interface
Eth1
Eth2
Eth3
Eth4
192.168.1.0
255.255.255.0
192.168.1.2
Eth0
0.0.0.0
0.0.0.0
192.168.1.3
Eth0
20
Sample Question: CIDR (cont.)
B. Assume that the ISP router forwards to the router 1 an
IP packet that has the destination address
139.200.1.135. Which subnet will the packet be
forwarded to? Based on the routing table in (1), what is
the interface that the router 1 will forward the packet
through?
C. Assume that the ISP router implement CIDR. What is
the routing entry for all subnets of the company X in the
routing table of the ISP router?
Destination
Netmask
Nexthop
Interface
Eth1
21