Session 1 0620 1 211.50KB 2015-09
advertisement

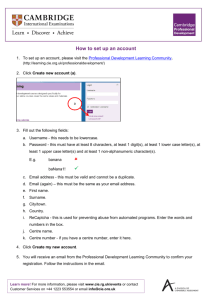
In-Service Teacher Training Assessment in IGCSE Chemistry 0620 Session 1: Introduction to the Syllabus www.cie.org.uk Welcome • Introductions • Background • Aim of training www.cie.org.uk Session 1 looks at: • Syllabus aims • The structure of the syllabus • Assessment objectives • The development of different skills • The difference between formative and summative assessment www.cie.org.uk Aims of the syllabus (1): Relevance and application • Relevance of chemistry to everyday life • The social and economic aspects of chemistry • The application of chemistry in solving problems • Ethical and cultural influences www.cie.org.uk Aims of the syllabus (2): Practical skills • • • • Carrying out experiments Inventiveness Following instructions Accuracy and precision www.cie.org.uk Aims of the syllabus (3): Communication and objectivity • Communication skills are important in everyday life • Objectivity is an important part of science • Science has some limitations and does not always provide answers www.cie.org.uk Structure of the syllabus (1): Overall structure • There are 14 sections covering physical, inorganic and organic chemistry • Some sections are divided into subsections www.cie.org.uk Structure of the syllabus (2): Overall structure • The Core curriculum is applicable to all students • The Extended curriculum builds on the core material and the relevant sections are placed next to each other www.cie.org.uk Structure of the syllabus (3): Overview of curriculum content • • • • 1 Particles (C + S)) 2 Experimental techniques (C + S)) 3 Atomic structure and bonding (C + S) 4 Stoichiometry (formulae and equations) (C+ S) • 5 Electricity and chemistry (C + S) • 6 Chemical changes (energetics) (C + S) • 7 Chemical reactions (rates and equilibrium) (C + S) www.cie.org.uk Structure of the syllabus (4): Overview of curriculum content (2) • • • • 8 Acids, bases and salts (C + S) 9 The periodic table (C + S) 10 Metals (reactivity, metal extraction) (C+S) 11 Air and water (including gaseous pollutants) (C + S) • 12 Sulphur (S) • 13 Carbonates (C) • 14 Organic chemistry (alkanes, alkenes, alcohols, acids & macromolecules) (C + S) www.cie.org.uk Structure of the syllabus (5): Core and Supplement • What extra knowledge is required for the Supplement? • What extra skills are required for the Supplement? • Are there any parts of the Supplement and Core which overlap? • Do certain topics appear in more than one of the sections 1-14? www.cie.org.uk Assessment objectives (1): General assessment objectives Assessment objective Weighting • Knowledge with understanding 50% • Handling information and problem solving 30% • Experimental skills 20% www.cie.org.uk Assessment objectives (2): The scheme of assessment Paper • Paper 1 (multiple choice) • Paper 2 (theory) Weighting 30% Discriminating Core or grades Extension C-G C 50% C-G C 50% 20% A-D * C + E (theory) C OR • Paper 3 • Papers 4 or 5 or 6 (practical) www.cie.org.uk Assessment objectives (3): Paper 2 or Paper 3? • Paper 2 is based on the Core curriculum (80 marks) Paper 2 targets C-G candidates • Paper 3 is based on the Extended curriculum (60 marks) plus 20 marks targeted at the Core curriculum Paper 3 targets A-C candidates • Which paper should be chosen? www.cie.org.uk Assessment objectives (4): Practical assessment • Paper 4 Coursework • Paper 5 Practical Test • Paper 6 Alternative to Practical www.cie.org.uk Assessment objectives (5): The importance of practical work Candidates need to be able to: • Understand how to carry out practical procedures • Record readings and construct tables of data www.cie.org.uk Assessment objectives (6): The importance of practical work Candidates need to be able to: • Undertake tests for gases and ions • Identify sources of error • Suggest suitable techniques and apparatus for an investigation www.cie.org.uk Assessment objectives (7): Coursework (Paper 4) • There are 4 strands: • C1 Using and organizing techniques, apparatus and materials • C2 Observing, measuring and recording • C3 Handling experimental observations and data • C4 Planning investigations www.cie.org.uk Assessment objectives (8): The role of teachers in practical work • Provide students with opportunities to develop their practical skills • Produce and assist with subjects for investigations • Sources of information • Advise students in the practicality of schemes they have chosen • Suggest length of time and general treatment of the problem • Exercise continuing supervision of the assessment www.cie.org.uk Formative assessment (1): Formative and summative assessment • Summative assessment involves terminal testing and interim testing • There is no individual feedback on summative assessments that involve public examinations • Formative assessment involves assessing student progress on a regular basis • There is always feedback to the student in formative assessment • The feedback from formative assessments are used by the students to improve their performance www.cie.org.uk Formative assessment (2): The nature of formative assessment • Formative assessment involves an interaction between the student and teacher • The teacher is able to assess progress, for example by feedback on tests etc. • True formative assessment encourages improvement in performance www.cie.org.uk Formative assessment (3): Ways of assessing progress • • • • • Marking Feedback on tests Answers given to verbal questions Target setting Student self evaluation Closing comments