6.2 Properties of Parallelograms
advertisement
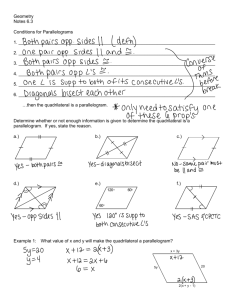
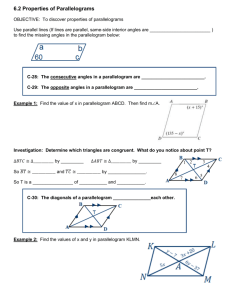
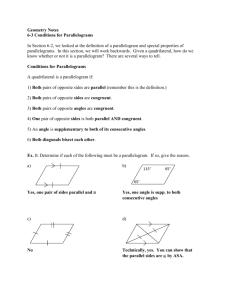
6.2 Properties of Parallelograms Geometry Mrs. Spitz Spring 2005 Objectives: • Use some properties of parallelograms. • Use properties of parallelograms in real-lie situations such as the drafting table shown in example 6. Assignment: • pp. 333-335 #2-37 and 39 In this lesson . . . And the rest of the chapter, you will study special quadrilaterals. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs of opposite sides parallel. When you mark diagrams of quadrilaterals, use matching arrowheads to indicate which sides are parallel. For example, in the diagram to the right, PQ║RS and QR║SP. The symbol PQRS is read “parallelogram PQRS.” Theorems about parallelograms Q • 6.2—If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then its opposite sides are congruent. ►PQ≅RS and SP≅QR P R S Theorems about parallelograms Q R • 6.3—If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then its opposite angles are congruent. P ≅ R and Q ≅ S P S Theorems about parallelograms Q • 6.4—If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then its consecutive angles are supplementary (add up to 180°). mP +mQ = 180°, mQ +mR = 180°, mR + mS = 180°, mS + mP = 180° P R S Theorems about parallelograms Q R • 6.5—If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then its diagonals bisect each other. QM ≅ SM and PM ≅ RM P S Ex. 1: Using properties of Parallelograms • FGHJ is a parallelogram. Find the unknown length. Explain your reasoning. a. JH b. JK 5 F G K J b. 3 H Ex. 1: Using properties of Parallelograms • FGHJ is a parallelogram. Find the unknown length. Explain your reasoning. a. b. 5 F G K 3 JH JK SOLUTION: a. JH = FG Opposite sides of a are ≅. JH = 5 Substitute 5 for FG. J b. H Ex. 1: Using properties of Parallelograms • FGHJ is a parallelogram. Find the unknown length. Explain your reasoning. a. b. 5 F G K 3 JH JK SOLUTION: a. JH = FG Opposite sides of a are ≅. JH = 5 Substitute 5 for FG. J b. b. JK = GK Diagonals of a bisect each other. JK = 3 Substitute 3 for GK H Ex. 2: Using properties of parallelograms Q PQRS is a parallelogram. Find the angle measure. a. mR b. mQ P R 70° S Ex. 2: Using properties of parallelograms Q PQRS is a parallelogram. Find the angle measure. a. mR b. mQ P a. mR = mP mR = 70° R 70° Opposite angles of a are ≅. Substitute 70° for mP. S Ex. 2: Using properties of parallelograms Q PQRS is a parallelogram. Find the angle measure. a. mR b. mQ P a. mR = mP R 70° S Opposite angles of a are ≅. mR = 70° Substitute 70° for mP. b. mQ + mP = 180° Consecutive s of a are supplementary. mQ + 70° = 180° Substitute 70° for mP. mQ = 110° Subtract 70° from each side. Ex. 3: Using Algebra with Parallelograms P PQRS is a parallelogram. Find the value of x. mS + mR = 180° 3x + 120 = 180 3x = 60 x = 20 S 3x° 120° R Consecutive s of a □ are supplementary. Substitute 3x for mS and 120 for mR. Subtract 120 from each side. Divide each side by 3. Q Ex. 4: Proving Facts about Parallelograms A E B 2 Given: ABCD and AEFG are parallelograms. Prove 1 ≅ 3. D 1 C G 3 F 1. ABCD is a □. AEFG is a ▭. 2. 3. 1 ≅ 2, 2 ≅ 3 1 ≅ 3 1. Given Ex. 4: Proving Facts about Parallelograms A E B 2 Given: ABCD and AEFG are parallelograms. Prove 1 ≅ 3. D 1 C G 3 F 1. 2. 3. ABCD is a □. AEFG is a □. 1 ≅ 2, 2 ≅ 3 1 ≅ 3 1. Given 2. Opposite s of a ▭ are ≅ Ex. 4: Proving Facts about Parallelograms A E B 2 Given: ABCD and AEFG are parallelograms. Prove 1 ≅ 3. D 1 C G 3 F 1. 2. 3. ABCD is a □. AEFG is a □. 1 ≅ 2, 2 ≅ 3 1 ≅ 3 1. Given ▭ are ≅ 2. Opposite s of a 3. Transitive prop. of congruence. Ex. 5: Proving Theorem 6.2 A B Given: ABCD is a parallelogram. Prove AB ≅ CD, AD ≅ CB. D 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. ABCD is a . Draw BD. AB ║CD, AD ║ CB. ABD ≅ CDB, ADB ≅ CBD DB ≅ DB ∆ADB ≅ ∆CBD AB ≅ CD, AD ≅ CB 1. Given C Ex. 5: Proving Theorem 6.2 A Given: ABCD is a parallelogram. Prove AB ≅ CD, AD ≅ CB. 1. 2. ABCD is a . Draw BD. 3. 4. AB ║CD, AD ║ CB. ABD ≅ CDB, ADB ≅ CBD DB ≅ DB 5. 6. 7. ∆ADB ≅ ∆CBD AB ≅ CD, AD ≅ CB B D 1. 2. Given Through any two points, there exists exactly one line. C Ex. 5: Proving Theorem 6.2 A Given: ABCD is a parallelogram. Prove AB ≅ CD, AD ≅ CB. D 1. 2. ABCD is a . Draw BD. 1. 2. 3. 4. AB ║CD, AD ║ CB. ABD ≅ CDB, ADB ≅ CBD DB ≅ DB 3. 5. 6. 7. ∆ADB ≅ ∆CBD AB ≅ CD, AD ≅ CB B Given Through any two points, there exists exactly one line. Definition of a parallelogram C Ex. 5: Proving Theorem 6.2 A Given: ABCD is a parallelogram. Prove AB ≅ CD, AD ≅ CB. D 1. 2. ABCD is a . Draw BD. 1. 2. 3. 4. AB ║CD, AD ║ CB. ABD ≅ CDB, ADB ≅ CBD DB ≅ DB 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. ∆ADB ≅ ∆CBD AB ≅ CD, AD ≅ CB B Given Through any two points, there exists exactly one line. Definition of a parallelogram Alternate Interior s Thm. C Ex. 5: Proving Theorem 6.2 A Given: ABCD is a parallelogram. Prove AB ≅ CD, AD ≅ CB. B D C 1. 2. ABCD is a . Draw BD. 1. 2. 3. 4. AB ║CD, AD ║ CB. ABD ≅ CDB, ADB ≅ CBD DB ≅ DB 3. 4. Given Through any two points, there exists exactly one line. Definition of a parallelogram Alternate Interior s Thm. 5. Reflexive property of congruence 5. 6. 7. ∆ADB ≅ ∆CBD AB ≅ CD, AD ≅ CB Ex. 5: Proving Theorem 6.2 A Given: ABCD is a parallelogram. Prove AB ≅ CD, AD ≅ CB. B D C 1. 2. ABCD is a . Draw BD. 1. 2. 3. 4. AB ║CD, AD ║ CB. ABD ≅ CDB, ADB ≅ CBD DB ≅ DB 3. 4. Given Through any two points, there exists exactly one line. Definition of a parallelogram Alternate Interior s Thm. 5. 6. Reflexive property of congruence ASA Congruence Postulate 5. 6. 7. ∆ADB ≅ ∆CBD AB ≅ CD, AD ≅ CB Ex. 5: Proving Theorem 6.2 A Given: ABCD is a parallelogram. Prove AB ≅ CD, AD ≅ CB. B D C 1. 2. ABCD is a . Draw BD. 1. 2. 3. 4. AB ║CD, AD ║ CB. ABD ≅ CDB, ADB ≅ CBD DB ≅ DB 3. 4. Given Through any two points, there exists exactly one line. Definition of a parallelogram Alternate Interior s Thm. 5. 6. 7. Reflexive property of congruence ASA Congruence Postulate CPCTC 5. 6. 7. ∆ADB ≅ ∆CBD AB ≅ CD, AD ≅ CB Ex. 6: Using parallelograms in real life FURNITURE DESIGN. A drafting table is made so that the legs can be joined in different ways to change the slope of the drawing surface. In the arrangement below, the legs AC and BD do not bisect each other. Is ABCD a parallelogram? C B A D Ex. 6: Using parallelograms in real life FURNITURE DESIGN. A drafting table is made so that the legs can be joined in different ways to change the slope of the drawing surface. In the arrangement below, the legs AC and BD do not bisect each other. Is ABCD a parallelogram? ANSWER: NO. If ABCD were a parallelogram, then by Theorem 6.5, AC would bisect BD and BD would bisect AC. They do not, so it cannot be a parallelogram. C B A D