Earth's Motions
advertisement

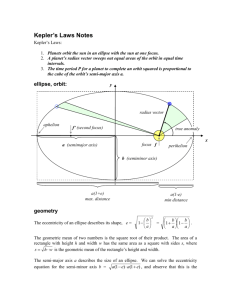
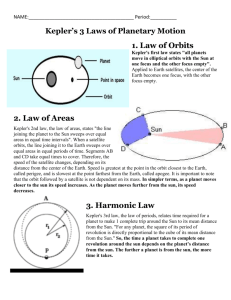
Earth’s position in space – how has it changed over thousands of years…. Background: • Pre-1500’s – Geocentric model of the universe (Earthcenter) •Models were generally wrong because they were based on wrong “first principles”, believed to be “obvious” and not questioned: 1. Geocentric Universe: Earth at the Center of the Universe. •1500’s Nicolaus Copernicus challenged the Geocentric model of the solar system. He described a HELIOCENTRIC (sun-centered) model of the solar system, which placed Earth and the other planets in circular orbits. He proposed that all planets orbit in the same direction, but each planet orbits at different speed and distance from the Sun. •1600’s Galileo Galileo’s observations confirmed a Copernicus’ model. Earth’s position in space – how has it changed over thousands of years…. • Johannes Kepler used Tycho Brahe’s observations in mathematical terms and Developed the 3 Laws of Planetary motion. • Kepler’s First Law of Motion – Planet move around the sun in ellipses with the sun at one focus. An ellipse is an oval-shape geometric figure whose shape is determined by two points with the figure. Each point is called “focus”. In the solar system, the Sun is at one focus of the orbit of each planet; the second focus is empty . • Eccentricity – is the amount of flattening of an ellipse, or how much the shape of the ellipse deviates from a perfect circle. A circle which has only one central focus has an eccentricity of 0. The greater the eccentricity, the less circular the ellipse. Essential Question: How has Earth’s Position Changed over Time? Kepler’s first law: You will examine this by drawing 3 ellipses with foci that are at different distances apart. (0.5 cm, 2 cm, and 4 cm) Hypothesis: •If the distance between foci ___________, then the eccentricity _________, because _______________________________________________________________________ Procedure: 1. Obtain a piece of string approximately 12-14 cm long. Tie the ends Of the string into a loop about 6-7 cm across. 2. Fold the “drawings” paper in thirds, then flatten it out. The folds Divide the paper into spaces where you will draw and compare ellipses. Measure and mark two dots 0.5 cm apart in the center of the top third, mark two more 2 cm apart in the middle third, and in the bottom third, Make two dots 4 cm apart. 3. Put the paper over the cardboard, and push thumbtacks into one set of points, far enough to be firm, but not flat against the paper. These are the ellipses foci. Put the string around the foci, pulling the string tight against the tacks. Have one partner hold the tacks steady if needed. 4. Repeat step 3, for the other two set of foci. It is okay If the ellipse goes off the paper at the top and bottom, as long as the major-semi axis (across the tacks) is on the paper. Put some scrap paper down so You don’t draw on the desk. Kepler’s first law continued…. 5. Calculate the Eccentricity(“out-of-roundness) Eccentricity – is the amount of flattening of an ellipse, or how much the shape of the ellipse deviates from a perfect circle. A circle which has only one central focus has an eccentricity of 0. The greater the eccentricity, the less circular the ellipse. a. b. c. Measure the distance between thumbtacks for each ellipse. Put the data in the chart below (a) Draw a line across the foci to the edges of the ellipse. This is the major axis. Measure that (b) Calculate the eccentricity (c). Eccentricity (e)=F÷A. It should be between 0 and 1. SHOW ALL WORK IN THE DATA TABLE! Why does the elliptical eccentricity have no units? ___________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ Ellipse (a)Distance between foci (mm) (b)Length of major axis (mm) A B C 6. Look at the planet table in the back of your textbook Which planet has the most elliptical orbit? Which planet has the most circular orbit? (c) Eccentricity : a÷b Show all work! Which is roundest? Least roundest? Kepler’s first law continued… 7. Because a planet’s orbit is elliptical, its distance from the Sun varies throughout its “year” (one revolution around the Sun). Label the points that represent perihelion and aphelion on the ellipse diagram below. Answer the following questions: a. Earth is at perihelion on ______________; on that date, Earth is approximately ___________km from the sun. b. Earth is at aphelion on ______________; on that date, Earth is approximately ___________km from the sun. c. Based on your understanding of Kepler’s First law, explain why the distance from a Planet to the Sun is typically given as an AVERAGE DISTANCE. Equal Area …Equal Time? • Kepler’s second law of motion states that a line drawn from the Sun to a planet sweeps equal area in equal time. A planet’s orbital velocity (speed at which it travels around the Sun) changes as its position in its orbit changes. Its velocity is fastest when it is closest to the Sun and slowest when it is farthest from the Sun. 1. If Area A = Area C on the diagram, what can be inferred about the orbital velocities as the planet travels along its orbit through area A compared to area C? Which is faster? 2. A planet’s orbital velocity is fastest at the position it orbits called Perihelion/Aphelion (circle on). During what season (in the northern hemisphere) is Earth at this position?________________ Therefore, Earth moves Fastest/Slowest (circle one) in the summer than in the winter, so summer in the Northern hemisphere must be Longer/Shorter (circle one) than winter. Kepler’s third law of planetary motion….. Kepler’s 3rd Law relates a planets period of revolution (the time it takes to complete on orbit of the Sun) to its average distance from the Sun. Kepler determined the mathematical Relationship between period and distance and concluded that the square of the planet’s period is proportional to the cube of its mean distance from the Sun. The formula used to determine this relationship for any planet is T2=R3, where T is the planet’s period in Earth years and R is the planet’s mean distance from the Sun in astronomical units (AU, where 1 AU equals the mean distance from the Earth to the Sun =150 million km). Sample problem: Planet X has an average distance from the Sun of 1.76AU. What is the planet’s period of revolution, in Earth years? T2=R3 T2=(1.76)3 T2=5.45 T = 5.45 T = 2.33 Earth years Calculate the period of revolution of each of the following planets Planet Mean distance to Sun (AU) Mercury 0.387 Mars 1.524 Saturn 9.539 Pluto 39.440 Planet Unknown 1 Period of Revolution (Earth years) Haley's Comet's last appearance was in 1986, and its average period of revolution around the Sun is 76 years. What is Haley’s Comets average distance from the Sun (in AU)? Calculate the average distance of Haley’s Comet in AU and SHOW ALL YOUR WORK! Earth’s Motions 1,000 mph. The Earth rotates on its axis, and we rotate along with it Speeds in highest at the equator. 26,000 years. The earth isn't perfect--it has a wobble! When a top spins we can see it vary its spin a little with a wobble. The earth does the same as it spins on its axis. It is, however, a very slow wobble. It takes approximately 26,000 some years to occur and this motion is known as Precession Earth’s Motions Earth’s Revolution – 67,000 mph: The Earth circles the sun once a year as it completes the 587 million mile orbit The Earth is located about 30,000 Ly from the center of the Milky Way Galaxy (which is 100,000). We travel 500,000 mph around the black hole located at the center of the galaxy. At this rate it takes approximately 250 million years to make one complete revolution. 1,300,000 mph – The Milky Way galaxy is speeding out into space! WOW! We have traveling partners – our Local Group (a group of about 4 large galaxies and 30 small galaxies). We are hurling toward our sister galaxy, the Andromeda Galaxy at about 290,000 mph and will collide with it in a couple billion years! The Milky Way Galaxy the size of Universe until the 1920’s The Milky Way Galaxy is a giant disk of stars 100,000 light-years across and 1,000 light-years thick. The Sun is located at the edge of a spiral arm, 30,000 light-years from the center It takes 250 Million years for the Sun to complete one orbit There are over 100 Billion stars in the Milky Way The Spiral arms are only 5% more dense than average, and are the locations of new star formation Before 1929 – the Universe was only the Milky Way…Hubble Discovered….More galaxies than the Milky Way 1920’s 14 Big Bang Theory 1920’s… Lemaitre (just ideas needs evidence) Evidence #1 - Hubble’s Law (1929) Visualizing the Expansion of Space – Early in this century Edwin Hubble discovered that the universe is expanding. Galaxies are moving outward from us, and the farther out they are, the faster they are moving. In fact if you compare the speed of a galaxy with another one twice as far away, the one twice as far out will be moving twice as fast. In other words, the speed is proportional to the distance. This effect has become known as Hubble’s Law. The proportional nature of the expansion has interesting consequences. 1. We appear to be at the center of the expansion because galaxies are moving away from us symmetrically in all directions. However, “observers” in other galaxies far away would observe the same symmetric expansion and perceive the center is an illusion. There really is NOT a center to the expansion. Everything is moving away from everything else. 2. If we trace the expansion backward in time, all the matter is in the universe would arrive at the same point at the same time in the past. Matter coming from twice as far away is moving twice as fast, matter coming 10 times as far away is moving 10 times as fast, so everything catches up at once. Thus appears that the universe got to its present state by expansion from a tiny, hot dense fireball by what is popularly called the “Big Bang”. 3. Go to Mrs. Fischl’s website, graph the distance vs. velocity of 17 galaxies. Once you have graphed the data – analyze the data. What is the relationship between the galaxies velocity and their distance. What Is a Redshift? How do I know which direction a galaxy rotates? Hubble’s Law describes the observations in cosmology that the velocities of galaxies are receding from Earth proportional to their distances. Blue Shift (to higher frequencies, Shorter wavelength) Red Shift (to lower frequencies, Longer wavelength) Hubble’s law continued….. 4. SPUD…BANG! We are going to simulate how galaxies distances are proportional to their velocities. You will symbolize a galaxy or an object in space. As a class we are going to go outside and huddle in a mass (to represent a primeval fireball). Mrs. Fischl will yell BANG – everyone should run, skip, crawl….move outwards ‘til Mrs. Fischl yells stop! Once all has stopped turn and count how many paces you are away from Mrs. Fischl (the center of the universe). Once back in the classroom, record your data on google doc. Calculate the velocity of “galaxies” (velocity = distance/time). Finally, graph your classes data (distance vs. velocity). •What is the relationship between Distance and Velocity? •Compare and Contrast the simulated graph of Hubble’s Law to the graph, question number 4 of Hubble’s law you constructed in question number 3. Evidence # 2 to support Big Bang…. Abundance of Hydrogen & Helium 380,000 years until the universe was cool enough for atoms to form at that time – Hydrogen (the lightest element) formed … 73% of visible universe is Hydrogen 25% of visible universe is Helium Where did all the other elements form? Evidence #3 for the Big Bang Theory…Background Radiation Technology played a vital role in developing & supporting the Big Bang Theory…Inflationary Theory. Astronomy is now a science with empirical data instead of wild plausible ideas. 18 Our understanding of Earth’s place in the Universe has changed time! What is most likely true about the Big Bang Theory or The Inflationary Theory as technology improves? 19