Unit 3 Jeopardy Review
advertisement
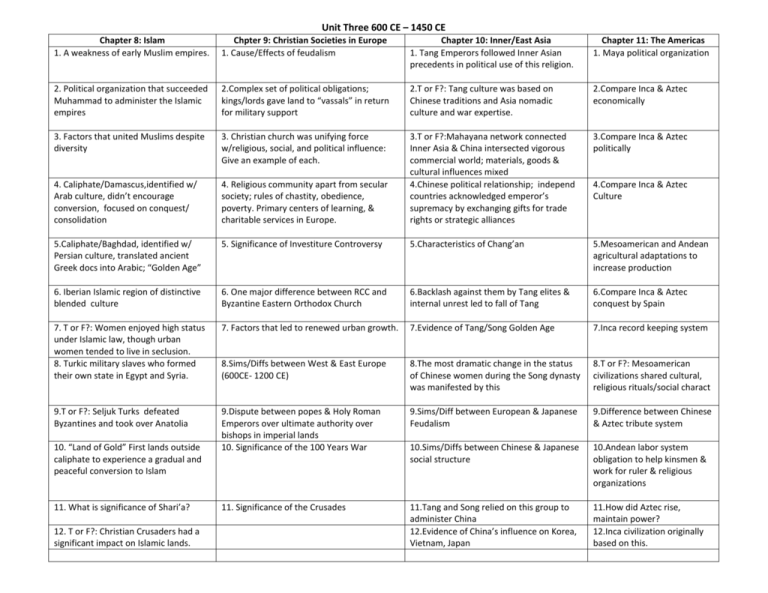
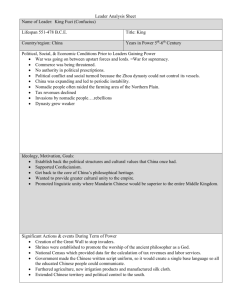
Unit Three 600 CE – 1450 CE Chapter 8: Islam 1. A weakness of early Muslim empires. Chpter 9: Christian Societies in Europe 1. Cause/Effects of feudalism Chapter 10: Inner/East Asia 1. Tang Emperors followed Inner Asian precedents in political use of this religion. Chapter 11: The Americas 1. Maya political organization 2. Political organization that succeeded Muhammad to administer the Islamic empires 2.Complex set of political obligations; kings/lords gave land to “vassals” in return for military support 2.T or F?: Tang culture was based on Chinese traditions and Asia nomadic culture and war expertise. 2.Compare Inca & Aztec economically 3. Factors that united Muslims despite diversity 3. Christian church was unifying force w/religious, social, and political influence: Give an example of each. 3.Compare Inca & Aztec politically 4. Caliphate/Damascus,identified w/ Arab culture, didn’t encourage conversion, focused on conquest/ consolidation 4. Religious community apart from secular society; rules of chastity, obedience, poverty. Primary centers of learning, & charitable services in Europe. 3.T or F?:Mahayana network connected Inner Asia & China intersected vigorous commercial world; materials, goods & cultural influences mixed 4.Chinese political relationship; independ countries acknowledged emperor’s supremacy by exchanging gifts for trade rights or strategic alliances 5.Caliphate/Baghdad, identified w/ Persian culture, translated ancient Greek docs into Arabic; “Golden Age” 5. Significance of Investiture Controversy 5.Characteristics of Chang’an 5.Mesoamerican and Andean agricultural adaptations to increase production 6. Iberian Islamic region of distinctive blended culture 6. One major difference between RCC and Byzantine Eastern Orthodox Church 6.Backlash against them by Tang elites & internal unrest led to fall of Tang 6.Compare Inca & Aztec conquest by Spain 7. T or F?: Women enjoyed high status under Islamic law, though urban women tended to live in seclusion. 8. Turkic military slaves who formed their own state in Egypt and Syria. 7. Factors that led to renewed urban growth. 7.Evidence of Tang/Song Golden Age 7.Inca record keeping system 8.Sims/Diffs between West & East Europe (600CE- 1200 CE) 8.The most dramatic change in the status of Chinese women during the Song dynasty was manifested by this 8.T or F?: Mesoamerican civilizations shared cultural, religious rituals/social charact 9.T or F?: Seljuk Turks defeated Byzantines and took over Anatolia 9.Dispute between popes & Holy Roman Emperors over ultimate authority over bishops in imperial lands 10. Significance of the 100 Years War 9.Sims/Diff between European & Japanese Feudalism 9.Difference between Chinese & Aztec tribute system 10.Sims/Diffs between Chinese & Japanese social structure 10.Andean labor system obligation to help kinsmen & work for ruler & religious organizations 11. Significance of the Crusades 11.Tang and Song relied on this group to administer China 12.Evidence of China’s influence on Korea, Vietnam, Japan 11.How did Aztec rise, maintain power? 12.Inca civilization originally based on this. 10. “Land of Gold” First lands outside caliphate to experience a gradual and peaceful conversion to Islam 11. What is significance of Shari’a? 12. T or F?: Christian Crusaders had a significant impact on Islamic lands. 4.Compare Inca & Aztec Culture Chapter 12: The Mongols 1 Positive economic effect of Mongol conquest Chapter 13: Tropical Asia and Africa 1.Ibn Battuta’s primary job for many of his Islamic hosts. Chapter 14: The Latin West 1. What document laid foundation for Parliamentary Government in England? Misc 1.Chinese Admiral who established contacts with south Asian & African peoples 2.Negative effect of Mongol conquest 2.The environment of Tropical Africa and Asia is governed by these wind patterns 2. T or F?:The Renaissance was a time of peace/ harmony betwn Italian city-states. 2. Franciscan ambassador who traveled from Constantinople to the court of Mongke Khan 3. T or F?: Mongols encouraged religious tolerance and occasionally converted. 3. Diff of Islam in India and Africa 3. T or F?: Black death caused end of feudalism. 3. Significance of Bantu Migrations 4. Christian merchant who traveled extensively when employed by Kubalai Khan 5. What did Mongols and Turks have in common? 4. Major cultural impact of Delhi Sultanate on India. 4. What led to population increases between 1000-1200? 4. Muslim quadi who wrote of his extensive travels in a rihla during the 14th century. 5.Delhi Sultanate contributed to agriculture by doing this. 5. Identify changes in land use during this period 5. Native of Muslim Spain who wrote an extensive account of his travels during the late 12th century. 6. One region that Mongols tried to conquer but were unsuccessful. 6.Dominant political structure in east Africa 6. Chinese sea trade reached its peak during which dynasty? 7. T or F?: Nomadic societies rarely traded with sedentary societies 7.T or F?: Trade spurred introduction of Islam & Hinduism to Indonesia 6.Identify changes in economic commercial, business patterns during this period 7. Identify changes in cultural patterns. 8. Why is history of the Yuan dynasty difficult to understand? 8.T or F?: Trade on Indian Ocean was highly competitive and divisive 8. Interesting coincidence or conspiracy? One group exits the Indian Ocean, another group fills the void. 9. Chinese dynasty that emerged after Yuan dynasty. 9. Compare trade networks of West & East Africa. 8.T or F?: Cultural contact w/ Muslims exposed Europe to ancient Greek learning and stimulated other changes in European thought and society 9. The Renaissance: What? Where? Why? So What? 10. T/F? Under Ming leadership China withdrew and began a protracted period of isolation. 10. His pilgrimage resulted new mosques , Quranic schools & interest from Muslims 10. What social, political, military, developments contributed to rise of European nations? 10. How did the Portuguese gain control of the East Indian Ocean trade? 7.T or F?: By 1600, Asia no longer initiated the majority of overland and maritime trade 9.Who should we thank for the invention of the magnetic compass and the astrolabe Changes and Continuities 1. Describe and analyze the changes and continuities associated with the impact of the Crusades from 600-1450 on Europe. During the time period 600-1450 CE the Crusades changed Europe by broadening and exchanging knowledge with the Arab world, and by causing people to question organized religion and their practices, but the Church continued to expand its influence. 2. Describe and analyze the changes and continuities associated with The Black Death from 600-1450 CE in Europe. The Black Death changed Europe from 600-1450 CE by initiating the decline of feudalism and the loss of faith in the Catholic Church, while the trade along the Asian Silk Routes continued. 3. Describe and analyze the social and economic changes and continuities in China from 600- 1450 CE. During the time period 600-1450 CE China changed by having the population double due to new crops, and the subordination of women using footbinding, but continued to have a Chinese bureaucracy focused on civil service. 4. Describe and analyze the changes and continuities associated with the impact of the Muslim Empire from 600-1450 CE on Africa. During the time period 600-1450 the Muslim Empire changed Africa by expanding its trade and economy to include the Mediterranean and India, and created an increase of interaction and trade routes to Sub-Saharan Africa, while continuing to spread Islam throughout the time period. 5. Describe the changes and continuities of the role of women from 600-1450 CE. Between 600-1450 CE the role of women changed in China and Japan as women had more access to education as a result of Confucianism, and in the Muslim Empire where women were equal in religion, but women continued to be restricted culturally and legally around the world. Compare and Contrast Christianity and Islam Sui, Tang and Song dynasties Maya, Aztecs, Inca Mongol domination in Russia and China Mali and Delhi empires The Catholic and Eastern Orthodox churches Japan and China in 600ce-1450ce