week3-ee522
advertisement

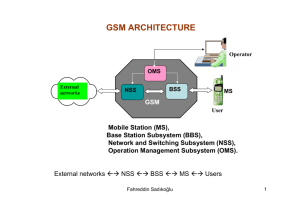
GSM: Overview Formerly: Groupe Spéciale Mobile (founded 1982) Now: Global System for Mobile Communication Pan-European standard (ETSI, European Telecommunications Standardisation Institute) 1 Architecture of the GSM system GSM is a PLMN (Public Land Mobile Network) several providers setup mobile networks following the GSM standard within each country Main Components MS (mobile station) BS (base station) MSC (mobile switching center) LR (location register) Subsystems RSS (Radio SubSystem): covers all radio aspects, consist of BSS (BSC + several BTSs)and MS. NSS (Network and Switching Subsystem): call forwarding, handover, switching, comprising an MSC and associated registers. OSS (Operation SubSystem): management of the network 2 GSM: Architecture Overview OMC, EIR, AUC HLR VLR fixed network PSTN GMSC NSS with OSS MSC VLR MSC BSC BSC BTS RSS BTS BTS MS BTS BSS – Base Station Sub-system BSC – Base Station Controller HLR – Home Location Register BTS – Base Transceiver Station VLR – Visitor Location Register TRX – Transceiver AuC – Authentication Centre MS – Mobile Station MSC – Mobile Switching Center GMSC – Gateway MSC EIR – Equipment Identity Register OMC – Operations and Maintenance Centre PSTN – Public Switched Telephone Network BTS 3 GSM: Architecture Overview Core 4 GSM: elements and interfaces radio cell MS Several interfaces are defined between different parts of the system: •'A' interface between MSC and BSC •'Abis' interface between BSC and BTS •'Um' air interface between the BTS (antenna) and the MS BSS MS Um radio cell MS BTS RSS BTS Abis BSC BSC A MSC NSS MSC VLR signaling VLR GMSC HLR IWF ISDN, PSTN PDN O OSS EIR AUC OMC 5 GSM: system architecture radio subsystem network and switching subsystem BTS ISDN PSTN MS BSC MSC Um BTS Abis BSC EIR SS7 BTS BSC BSS HLR VLR BTS BTS fixed partner networks A MSC IWF ISDN PSTN PSPDN CSPDN 6 System architecture: radio subsystem radio subsystem MS network and switching subsystem Components MS (Mobile Station) BSS (Base Station Subsystem): MS consisting of Um BTS Abis BTS BSC MSC BTS (Base Transceiver Station): radio components including sender, receiver, antenna - if directed antennas are used one BTS can cover several cells BSC (Base Station Controller): switching between BTSs, controlling BTSs, managing of network resources, mapping of radio channels (Um) onto terrestrial channels (A interface) Interfaces Um : radio interface Abis : standardized, open interface with A BTS BTS BSC MSC 16 kbit/s user channels A: standardized, open interface with 64 kbit/s user channels BSS 7 Tasks of a BSS are distributed over BSC and BTS BTS comprises radio specific functions BSC is the switching center for radio channels Functions Management of radio channels Frequency hopping (FH) Management of terrestrial channels Mapping of terrestrial onto radio channels Channel coding and decoding Rate adaptation Encryption and decryption Paging Uplink signal measurements Traffic measurement Authentication Location registry, location update Handover management BTS X X X X X X BSC X X X X X X X X X X 8 BSS Network Topologies Base stations are linked to the parent BSC in one of several standard network topologies. The actual physical link may be microwave, optical fiber or cable. Star: most popular configuration for first GSM systems • Expensive as each BTS has its own link • One link failure always results in loss of BTS Ring: Redundancy gives some protection if a link fails • More difficult to roll-out and extend - ring must be closed Chain: cheap, easy to implement • One link failure isolates several BTSs 9 The Mobile Station The mobile station consists of: mobile equipment (ME) subscriber identity module (SIM) The SIM stores permanent and temporary data about the mobile, the subscriber and the network, including: The International Mobile Subscribers Identity (IMSI) MS ISDN number of subscriber Authentication key (Ki) and algorithms for authentication check The mobile equipment has a unique International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI), which is used by the EIR. The IMEI may be used to block certain types of equipment from accessing the network if they are unsuitable and also to check for stolen equipment. The two parts of the mobile station allow a distinction between the actual equipment and the subscriber who is using it. 10 System architecture: Network and Switching Subsystem network subsystem fixed partner networks ISDN PSTN MSC • Components MSC (Mobile Switching Center) IWF (Interworking Functions) ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) PSPDN (Packet Switched Public Data Net.) CSPDN (Circuit Switched Public Data Net.) EIR SS7 • HLR Databases HLR (Home Location Register) VLR (Visitor Location Register) EIR (Equipment Identity Register) VLR MSC IWF ISDN PSTN PSPDN CSPDN 11 Network and switching subsystem NSS is the main component of the public mobile network GSM switching, mobility management, interconnection to other networks, system control Components Mobile Services Switching Center (MSC) and GMSC controls all connections via a separated network to/from a mobile terminal within the domain of the MSC - several BSC can belong to a MSC Databases (important: scalability, high capacity, low delay) Home Location Register (HLR) central master database containing user data, permanent and semipermanent data of all subscribers assigned to the HLR (one provider can have several HLRs) Visitor Location Register (VLR) local database for a subset of user data, including data about all user currently in the domain of the VLR 12 Mobile Switching Center The MSC (mobile switching center) plays a central role in GSM switching functions additional functions for mobility support management of network resources VLR interworking functions via Gateway MSC (GMSC) integration of several databases MSC Functions of a MSC specific functions for paging and call forwarding termination of SS7 (signaling system no. 7) mobility specific signaling location registration and forwarding of location information provision of new services (fax, data calls) support of short message service (SMS) generation and forwarding of accounting and billing information 13 Gateway MSC A Gateway Mobile Switching Centre (GMSC) is a device which routes traffic entering or exiting a mobile network to the correct destination The GMSC accesses the network’s HLR to find the location of the required mobile subscriber A particular MSC can be assigned to act as a GMSC The operator may decide to assign more than one GMSC HLR VLR MSC GMSC VLR fixed network MSC 14 Visitor Location Register Each MSC has a VLR VLR stores data temporarily for mobiles served by the MSC Information stored includes: VLR IMSI Mobile Station ISDN Number MSC Mobile Station Roaming Number Temporary Mobile Station Identity Local Mobile Station Identity The location area where the mobile station has been registered Supplementary service parameters 15 Home Location Register Stores details of all subscribers in the network , such as: Subscription information Location information: mobile station roaming number, VLR, MSC International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) MS ISDN number AuC Tele-service and bearer service subscription information Service restrictions HLR Supplementary services Together with the AuC, the HLR checks the validity and service profile of subscribers Notice that the VLR stores the current Location Area of the subscriber, while the HLR stores the MSC/VLR they are currently under. This information is used to page the subscriber when they have an incoming call. 16 Operation subsystem The OSS (Operation Subsystem) enables centralized operation, management, and maintenance of all GSM subsystems Components Authentication Center (AUC) generates user specific authentication parameters on request of a VLR authentication parameters used for authentication of mobile terminals and encryption of user data on the air interface within the GSM system Equipment Identity Register (EIR) registers GSM mobile stations and user rights stolen or malfunctioning mobile stations can be locked and sometimes even localized. The EIR controls access to the network by returning the status of a mobile in response to an IMEI query Operation and Maintenance Center (OMC) different control capabilities for the radio subsystem and the network subsystem 17 Activities and Operations Main activities which the network must carry out are: Switching mobile on (IMSI attach) Mobility management Switching mobile off (IMSI detach) Location updating Making a call (mobile originated) Receiving a call (mobile terminated) Cell measurements and handover Mobile Station (MS) Base Station (BS) 18 IMSI Attach (Switch on) Mobile camps on to best serving BTS Mobile sends IMSI to MSC MSC/VLR is updated in HLR Subscriber data including current location area is added to local VLR MSC and HLR carry out authentication check - challenge and response using Ki Optionally EIR checks for status of mobile (white/grey/black) BSC VLR MSC AuC HLR EIR 19 IMSI Detach (Switch off) Mobile informs MSC it is switching off HLR stores last location area for mobile VLR records that mobile is no longer available on network Mobile powers down BSC VLR MSC AuC HLR 20 Location Updates Automatic Location Update –when mobile moves to new location area BSC Periodic Location Update – checks that mobile is still attached to network Updates location area in VLR BSC If move is to a new MSC/ VLR then HLR is informed BSC VLR MSC VLR MSC AuC HLR 21 Mobile Terminated Call HLR 1: calling a GSM subscriber 2: forwarding call to GMSC calling 3: signal call setup to HLR station 1 4, 5: request (Mobile station roaming number)MSRN from VLR 6: forward responsible MSC to GMSC 7: forward call to current MSC 8, 9: get current status of MS 10, 11: paging of MS 12, 13: MS answers 14, 15: security checks 16, 17: set up connection 4 5 3 6 PSTN 2 GMSC 10 7 VLR 8 9 14 15 MSC 10 13 16 10 BSS BSS BSS 11 11 11 11 12 17 MS 22 Mobile Originated Call 1, 2: connection request 3, 4: security check 5-8: check resources (free circuit) 9-10: set up call VLR 3 4 6 PSTN 5 GMSC 7 MSC 8 2 9 MS 1 10 BSS 23 MTC/MOC MS MTC BTS MS MOC BTS paging request channel request channel request immediate assignment immediate assignment paging response service request authentication request authentication request authentication response authentication response ciphering command ciphering command ciphering complete ciphering complete setup setup call confirmed call confirmed assignment command assignment command assignment complete assignment complete alerting alerting connect connect connect acknowledge connect acknowledge data/speech exchange data/speech exchange 24 Network Area • • • • With the mobility of a subscriber handover occurs. As mobile moves around it monitors signal strength and quality from neighbor cells BSS determines when handover should occur, based on cell measurements and traffic loading on neighbor cells. A subscriber outside of their PLMN service area may access their normal service with a roaming agreement. 25 4 types of handover 1: within a cell (from a channel to another) 2: within the same location area (from a cell to another under the control of the same BSC) 3: within the same MSC/VLR service area (under the same MSC control) 4: within the PLMN service area(from one MSC to another) From PLMN service area to another PLMN (operator): Roaming 1 2 3 4 MS MS MS MS BTS BTS BTS BTS BSC BSC BSC MSC MSC 26 Handover decision I Many handover strategies prioritize handover requests over call initiation receive level receive level requests when allocating unused channel BTSold BTSnew in a cell site. Since having a call abruptly terminated while in a middle of a Actual measured power conversation is more annoying than being blocked occasionally on a new call Average of measured power attempt. Guard channel concept :a fraction of the total available channels is reserved exclusively for handover requests from ongoing calls which may be handed off HO_MARGIN onto the cell. Handover must be performed successfully and as infrequently as possible, and be MS MS imperceptible to the users. Def: Dwell time is the time over which a BTSold BTSnew call may be maintained within a cell, without handover. Depends on (signal propagation, interference, distance between MS and BS, speed, etc.) 27 Handover decision II MAHO: Mobile assisted handover. ∆ = 𝑃𝑟 ℎ𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑜𝑓𝑓 − 𝑃𝑟 min 𝑎𝑐𝑒𝑝𝑡𝑎𝑏𝑙𝑒 ∆ too large, unnecessary handover. ∆ too small, there may be insufficient time (depends on the speed of MS)to complete a handover before a call is lost due to weak signal condition. ∆ 28 Umbrella Cell High speed MS pass through the coverage area of a cell within a matter of seconds, whereas pedestrian MS may never need a handoff during a call. Umbrella cell: provide large coverage area to high speed MS while providing small coverage area to MS travelling at low speed. Large Umbrella cell (Macrocell) for high speed traffic Small microcells for slow speed traffic 29 Handover procedure in GSM MS BTSold BSCold measurement measurement report result MSC HO decision HO required BSCnew BTSnew HO request resource allocation ch. activation HO command HO command HO command HO request ack ch. activation ack HO access Link establishment clear command clear command clear complete HO complete HO complete clear complete 30 Roaming Allows subscriber to travel to different network areas, different operator’s networks, different countries - keeping the services and features they use at home. Billing is done through home network operator, who pays any other serving operator involved. Requires agreements between operators on charge rates, methods of payments etc. Clearing house companies carry out data validation on roamer data records, billing of home network operators and allocation of payments. 31 Security issues Authentication: Procedure of verifying the authenticity of an entity (user, terminal, network, network element). In other words, is the entity the one it claims to be? Data integrity: The property that data has not been altered in an unauthorised manner. Confidentiality: The property that information is not made available to unauthorised individuals, entities or processes. Anonymity: Preventing unencrypted transmission of user ID information such as IMSI number over the air interface. 32 Security in GSM Security services access control/authentication user SIM (Subscriber Identity Module): secret PIN (personal identification number) SIM network: challenge response method confidentiality voice and signaling encrypted on the wireless link (after successful authentication) anonymity temporary identity TMSI “secret”: (Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity) is given to the user • A3 and A8 available after switching on which use IMSI. via the Internet newly assigned at each new location update (LUP) • network providers encrypted transmission can use stronger mechanisms 3 algorithms specified in GSM A3 for authentication (“secret”, open interface) A5 for encryption (standardized) A8 for key generation (“secret”, open interface) 33 GSM - authentication SIM mobile network Ki AuC RAND 128 bit RAND 128 bit RAND Ki 128 bit A3 128 bit A3 SIM SRES* 32 bit MSC SRES* =? SRES SRES SRES 32 bit Ki: individual subscriber authentication key 32 bit SRES SRES: signed response 34 GSM - key generation and encryption MS with SIM mobile network (BTS) Ki AC RAND 128 bit RAND 128 bit RAND 128 bit A8 cipher key BTS Ki 128 bit SIM A8 Kc 64 bit Kc 64 bit data A5 encrypted data SRES data MS A5 35 GSM: Mobile Services GSM offers several types of connections voice connections, data connections, short message service multi-service options (combination of basic services) Three service domains offered to the end user: Telematic Services: service completely defined including terminal equipment functions - telephony and various data services. Bearer Services: basic data transmission capabilities protocols and functions not defined Supplementary Services. 36 Tele Services I Telecommunication services that enable voice communication via mobile phones All these basic services have to obey cellular functions, security measurements etc. Offered services mobile telephony primary goal of GSM was to enable mobile telephony offering the traditional bandwidth of 3.1 kHz Emergency number - mandatory for all service providers -free of charge -connection with the highest priority (preemption of other connections possible) -Emergency calls can override any locked state the phone may be in -May be initiated from a mobile without a SIM - common number throughout Europe (112) -If the national emergency code is used the SIM must be present Multinumbering several ISDN phone numbers per user possible 37 Tele Services II Additional services Non-Voice-Teleservices group 3 fax voice mailbox (implemented in the fixed network supporting the mobile terminals) electronic mail (MHS, Message Handling System, implemented in the fixed network) Short Message Service (SMS) alphanumeric data transmission to/from the mobile terminal using the signaling channel, thus allowing simultaneous use of basic services and SMS DTMF - Dual Tone Multi-Frequency - used for control purposes – remote control of answering machine, selection of options. Cell Broadcast - short text messages sent by the operator to all users in an area, e.g. to warn of road traffic problems, accidents 38 Bearer Services Telecommunication services to transfer data between access points Specification of services up to the terminal interface (OSI layers 1-3) Different data rates for voice and data (original standard) data service (circuit switched) synchronous: 2.4, 4.8 or 9.6 kbit/s asynchronous: 300 - 1200 bit/s data service (packet switched) synchronous: 2.4, 4.8 or 9.6 kbit/s asynchronous: 300 - 9600 bit/s 39 Supplementary services Services in addition to the basic services, cannot be offered stand-alone Similar to ISDN services besides lower bandwidth due to the radio link May differ between different service providers, countries and protocol versions Important services identification: forwarding of caller number suppression of number forwarding automatic call-back conferencing with up to 7 participants locking of the mobile terminal (incoming or outgoing calls) ... 40