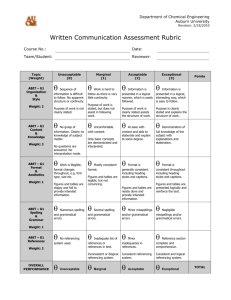
Outcomes Assessment 2 Program Assessment
advertisement

Outcomes Assessment 2 Program Assessment Joseph A. Shaeiwitz West Virginia University Daina M. Briedis Michigan State University joseph.shaeiwitz@mail.wvu.edu briedis@egr.msu.edu Outline ABET and engineering criteria Program objectives Program outcomes Assessment performance criteria assessment measures – direct and indirect rubrics Review Outline ABET and engineering criteria Program objectives Program outcomes Assessment performance criteria assessment measures – direct and indirect rubrics Review Initial Quiz What do you know about ABET? Describe the engineering criteria? According to ABET’s definitions, what is the difference between outcomes and objectives? Identify four assessment methods. Classify each as direct or indirect. Initial Quiz What do you know about ABET? Describe the engineering criteria? According to ABET’s definitions, what is the difference between outcomes and objectives? Identify four assessment methods. Classify each as direct or indirect. Initial Quiz What do you know about ABET? Describe the engineering criteria? According to ABET’s definitions, what is the difference between outcomes and objectives? Identify four assessment methods. Classify each as direct or indirect. Initial Quiz What do you know about ABET? Describe the engineering criteria? According to ABET’s definitions, what is the difference between outcomes and objectives? Identify four assessment methods. Classify each as direct or indirect. Initial Quiz What do you know about ABET? Describe the engineering criteria? According to ABET’s definitions, what is the difference between outcomes and objectives? Identify four assessment methods. Classify each as direct or indirect. ABET and Engineering Criteria ABET = Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology Engineering criteria changed to assessment basis (TQI) around 2000 Must prove that students are achieving objectives and outcomes measure output, feedback model previously, feed forward model Feed Forward Model input curriculum output assumed education process Feedback Model one class one course entering college one class one course graduate alumnus The Two Loops of the Engineering Criteria Determine educational objectives Input from Constituencies Determine Outcomes Required to Achieve Objectives Evaluate/Assess Determine How Outcomes will be Achieved Formal Instruction Student Activities Determine How Outcomes will be Assessed Establish Indicators that Objectives are Being Achieved ABET and Engineering Criteria 8 criteria students program educational objectives program outcomes and assessment professional component faculty facilities institutional support and financial resources program criteria ABET and Engineering Criteria Focus of this workshop program educational objectives definition how to establish how to assess program outcomes and assessment definition how to establish how to assess Minute Paper Clearest vs. Muddiest Point What have you just learned about ABET and assessment? What points are the clearest? What points are the “muddiest?” Outline ABET and engineering criteria Program objectives Program outcomes Assessment performance criteria assessment measures – direct and indirect rubrics Review Program Objectives* “…broad statements that describe the career and professional accomplishments that the program is preparing the graduates to achieve.”* “Our graduates will be successful …” must define “successful” *Criteria for Accrediting Engineering Programs, 2007-2008 Cycle, ABET, Inc., Baltimore, MD, http://www.abet.org Program Objectives* must be detailed and published include constituencies/periodically evaluated educational program to achieve outcomes (defined later) and to prepare graduates for accomplishments that achieve objectives ongoing evaluation to determine extent objectives attained, use results for program improvement *Criteria for Accrediting Engineering Programs, 2007-2008 Cycle, ABET, Inc., Baltimore, MD, http://www.abet.org Exercise New program in nanobiomolecular engineering Define two program objectives. Outline ABET and engineering criteria Program objectives Program outcomes Assessment performance criteria assessment measures – direct and indirect rubrics Review Program Outcomes* “…statements of what students are expected to know and be able to do by the time of their graduation.” Outcomes must “…foster attainment of the program objectives…” Process to produce outcomes Assessment process, with documented results demonstrating measurement demonstrating degree of achievement Evidence results used for program improvement *Criteria for Accrediting Engineering Programs, 2007-2008 Cycle, ABET, Inc., Baltimore, MD, http://www.abet.org Program Outcomes Minimum outcomes “a-k” plus program criteria Opportunity to be unique, i.e., define unique outcomes, not just repeat “a-k” Helpful to map program-defined outcomes into a-k Helpful to map outcomes into classes Necessary to map outcomes into objectives WVU ABET a. apply math, sci, engr 1 chemical process 2 communicate 3 computers 4 learn independently and group work 7 safety, societal, environmental 8 ethics f. professional and ethics g. communication h. broad education global impact i. life-long learning j. contemporary issues k. use techniques, skills, modern engineering tools 9 broad education d. multidisciplinary teams e. identify, formulate, solve engineering problems 6 continuing education b. expts - design, conduct, analyze, interpret data c. design system 5 lab and data analysis 1 chemical process 2 communicate 3 computers 4 learn independently and group work CHE 320 CHE 325 WVU outcome WVU class CHE 201 CHE 202 CHE 230 CHE 310 CHE 311 CHE 312 CHE 315 CHE 450/451 CHE 455/456 5 lab and data analysis 6 continuing education 7 safety, societal, environmental 8 ethics 9 broad education Exercise Define three unique program outcomes for the nanobiomolecular engineering program. Outline ABET and engineering criteria Program objectives Program outcomes Assessment performance criteria assessment measures – direct and indirect rubrics Review Performance Criteria What will students do to demonstrate achievement of outcome Example: “An ability to communicate effectively.” (3g in ABET list) What are attributes of effective communication? Performance Criteria for Effective Communication When making an oral presentation, students will maintain eye contact … A written report will follow a prescribed format demonstrate proper grammar and punctuation adhere to commonly accepted word usage Professionally responsible Contemporary Issues 1.Has knowledge of current technological issues related to XXX engineering and society 2. Is able to discuss major political and societal issues and their pertinence to XXX engineering Exercise Define two or three performance criteria for one of the outcomes previously defined. Outline ABET and engineering criteria Program objectives Program outcomes Assessment performance criteria assessment measures – direct and indirect rubrics Review Indirect vs. Direct Assessment Indirect – based mostly on student selfevaluation surveys interviews focus groups Direct – by faculty or some other means of evaluation of student performance (advisory boards evaluate design projects) Indirect vs. Direct Assessment Indirect necessary, but not sufficient provides uncalibrated snapshot self-assessment not necessarily reliable Terminology may be unfamiliar Direct necessary for quality assessment plan not now for all, but new Program Evaluators are being trained to look for this feature relies on faculty experience, expertise, and judgment How do we know if the students have the requisite outcomes? When the students think they do, based on student survey results With direct evidence from student work Evidence is the key to accreditation Faculty evaluation of student work is the key to providing evidence Assessment Measures Primary assessment of student outcomes should be based on student work (direct) Secondary evidence e.g., student portfolios, student projects, assignments and exams, some employer surveys where skill is observed Senior exit surveys, alumni surveys, employer surveys (qualitative evidence based on opinion), other Combination of both methods – triangulation Indirect Assessment Measures Surveys Interviews Course satisfaction surveys Direct Assessment Measures End-of-Course Assessments Targeted Assignments Capstone Experiences Capstone Exams Portfolios End-of-Course Assessments Course should have objectives perhaps set by department committee Related to program outcomes Assigned problems (assignments, exams, projects) each related to course objectives Evaluation/reflection by instructor End-of-Course Assessments Advantages Disadvantage quick and easy assessment can be done in parallel with grading not comprehensive no big picture Opinion a component of assessment plan Targeted Assignments/Problems Key assignments that relate to specific program outcomes Multiple assignments per outcome recommended Integrate through curriculum can demonstrate progress toward achievement of program outcome Targeted Assignments/Problems Advantages quick and easy assessment can be done in parallel with grading Disadvantages none really need consistent evaluation method with reliable inter-rater reliability Capstone Experiences Can be design, laboratory, research All programs have them Where students are supposed to demonstrate and synthesize what learned Usually includes teamwork, communication Capstone Experiences Advantages already required in program assessment can be done in parallel with grading Disadvantages none really need consistent evaluation method with reliable inter-rater reliability Capstone Exams FE Exam detailed, subject-related results available Department-generated Capstone Exams Advantages FE is standardized the most direct measure possible Disadvantages FE may not set bar as high as some want students may not take departmentgenerated exam seriously if results do not impact grades or graduation Portfolios Collection of student work demonstrating outcomes Must also evaluate the portfolio Can also have students reflect on work in portfolio Portfolios Advantage comprehensive Disadvantages portfolio evaluation is additional work need consistent evaluation method with reliable inter-rater reliability Other Direct Assessment Methods Journals Concept maps Oral presentations with follow-up questions (like M.S./Ph.D. defense) Exercise Select an assessment method to be used for direct assessment of program outcomes previously defined. Outline ABET and engineering criteria Program objectives Program outcomes Assessment performance criteria assessment measures – direct and indirect rubrics Review Rubrics A set of categories developed from the performance criteria that define extent to which the performance criteria are met (progression towards attaining). Developing Rubrics Define levels of performance for each performance criterion best first to define top and bottom levels of performance – then fill in middle ground 3-5 levels of performance recommended Developing Rubrics Standardized method to ensure interrater reliability Specific definitions of terms like excellent, understand, not acceptable, exceeds expectations Initial effort and periodic review required Developing Rubrics If have five levels of performance, can make each level a grade if have three levels, can make each level A/C/F, and interpolate for B/D Use rubric for assessment and grading Advantage: Students and faculty have clearly defined criteria for grading of what appears to be subjective (lab and design reports, oral reports, etc.) “Application of math & science” Problem Assessment Form Connects physical model with math model Able to write unsteady state mass balance Makes appropriate substitution for flow terms Makes appropriate simplification for flow terms Converts differential equation into Laplace form correctly Understands idea for output/input form of transfer function Correctly combines Laplace transforms in series Correct answer Rubrics – Assessment Scale “Application of math & science” (5=high) Level 5 Formulates models correctly Applies calculus or linear algebra to solve problems Correct calculations Correct statistical analysis ... Level 1 Level 3 Formulates models with some trouble Some understanding of calc/linear algebra applications Minor calc errors Minor statistical errors ... Not able to model Cannot apply calc/linear algebra Incorrect calculations Does not apply statistics ... Professionally responsible Contemporary Issues 1.Has knowledge of current technological issues related to XXX engineering and society 2. Is able to discuss major political and societal issues and their pertinence to XXX engineering Outcome: A knowledge of contemporary issues Performance Criteria Scoring Rubrics Rating Scale & Element Needs Improvement 1 2 Met Expectations 3 4 Exceeded Expectations Has knowledge of current technological issues related to chemical engineering and society (global warming, resource depletion, waste proliferation, etc.) Has minimal knowledge of technological issues and their relevance to chemical engineering; has weak connection between the issue and scientific principles for analysis and has trouble developing solutions. Has reasonable knowledge of technological issues; some may not be directly relevant to chemical engineering; can apply scientific principles to analysis and suggest solutions when guided. Has thorough knowledge of current technology issues related to chemical engineering and is able to analyze them and propose solutions using scientific principles Has knowledge of and is able to discuss major societal and political issues and their pertinence to chemical engineering Has minimal knowledge of societal and political issues; if given an issue, does not see its connection to engineering without instruction; is minimally effective in discussion and presentation of such issues Has reasonable knowledge of societal and political issues; recognizes some connection to chemical engineering, but misses the details; is somewhat effective in discussing and presenting such issues when prompted Has thorough knowledge of societal and political issues related to chemical engineering; recognizes the “big picture” and the details; presents strong discussion of such issues 5 N/A Rubric for Oral Presentations Attribute Effective use of Visual Aids (VA) Clarity and readability Use of space on VA Lettering readable Color, over- or under-use (if used) Wording concise Appropriate amount of information per VA Presentation Organization Logical order of topics Appropriate use of time: Not too long /short Complete "story" told Introduction: Problem stated 1-Not proficient 2-Progressing to proficiency 3-Proficient 4-Superior proficiency not clear or readable VA unreadable because too crowded font unreadable colors too hard to distinguish, colors do not project well slides full of text so much information per VA or so much missing information to make VA useless difficulty reading clear and readable superior clarity and readability VAs very well laid out totally disjointed, no organization some items presented out of order organization as per guidelines far too long or far too short story missing, no story told problem not stated, somewhat too long or too short story incomplete appropriate length problem poorly stated problem clearly stated too little or too much appropriate information of VA amount of information on VA font too small font readable poor choice and use primary/easily use of color of colors distinguishable enhances clarity of colors presentation slides too wordy slides appropriate too much appropriate level information per VA, of information per missing information slide such as size of total pie superior organization enhances communication complete story told problem clearly stated, good perspective on problem shown Score Rubric for Written Presentations Attribute 1-Not proficient 2-Progressing to proficiency 3-Proficient 4-Superior proficiency inappropriate content of most sections of report some content in inappropriate section of report content appropriate to all sections of report Complete Story Told no story told, very incomplete aspects of complete story missing complete story told Aesthetics unacceptable – e.g., tables and figures cannot be read/understood, fonts difficult to read so many format errors as to make report useless some portions are sloppy and difficult to read text, tables, figures readable and understandable unique organization enhances readability and/or understandability of report additional material enhances quality of report text, tables, figures so clear and understandable as to enhance report impact some format errors format followed Spelling any spelling errors no spelling errors Grammar and Punctuation too many grammar and punctuation errors far too long or too short only spelling errors are different spellings for same pronunciation grammar and punctuation errors Report Mechanics Organization Format Length too long or too short only a very few minor grammar or punctuation errors appropriate length unique format aspects that enhance report impact no grammar or punctuation errors Score Rubric for Majors and Design Projects Attribute Design of equipment, Analysis of performance of existing equipment, Understand interrelationship between equipment in process Design of individual equipment Understand interrelationship between equipment on flowsheet 1-Not proficient 2-Progressing to proficiency 3-Proficient 4-Superior proficiency major errors in individual equipment design no understanding of equipment interrelationship some errors in equipment design equipment designed unique aspects of correctly equipment design enhance result clear understanding exploitation of of equipment equipment interrelationship interrelationship to enhance result constraints/ exploitation of limitations clearly constraints/ understood limitations to enhance result response to response to questions shows questions shows clear understanding superior understanding Constraints/limitations of individual equipment and flowsheet understood constraints/ limitations not understood minimum understanding of equipment interrelationship not all constraints/ limitations understood Response to questions indicates understanding of ChE principles response to questions demonstrates lack of understanding response to questions shows gaps in understanding Significance of conclusions understood lack of understanding, no explanations gaps in understanding, few explanations clear understanding and explanations superior understanding with in-depth explanations Apply chemistry, math, physics, life science, engineering science Apply engineering science inability to apply principles a few basic principles applied most principles applied, demonstration of effect on design all principles applied and interwoven with engineering to complete design Score Rubrics Additional rubrics at http://www.che.cemr.wvu.edu/ugrad/outcomes/rubrics/i ndex.php Instructions on rubrics http://webquest.sdsu.edu/rubrics/weblessons.htm Exercise For the two or three performance criteria for one of the outcomes previously defined, and assuming the assessment method previously defined, begin to develop an evaluation rubric. Outline ABET and engineering criteria Program objectives Program outcomes Assessment performance criteria assessment measures – direct and indirect rubrics Review Recommendation Strongly recommend adopting direct assessment measures into assessment activities Will be expected in the near future! Exercise What are the two most important things that you learned in this workshop? What is still unclear to you about program assessment? Questions