MEMORANDUM
advertisement

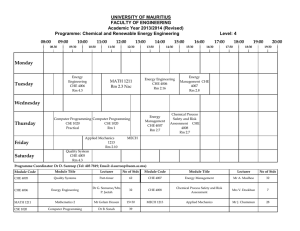
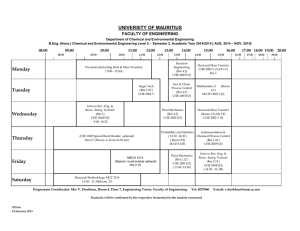
ChE 365 – Techniques for Process Simulation Fall 2013 Instructor E-mail Location Time My office hours Laurent Simon, Ph.D. laurent.simon@njit.edu TIER 344 W: 6.00PM – 9.05PM W: 4.00 PM – 5.00 PM Catalog Description: ChE 365 - Techniques for Process Simulation (3-0-2) Prerequisites: ChE 370. Corequisite: ChE 360. This course reviews chemical engineering applications of Laplace transforms, partial fractions, and linear algebra in preparation for the ChE course in process control. It introduces dedicated software for chemical process simulation and control used in the senior capstone courses. Textbook (required): “Problem Solving in Chemical and Biochemical Engineering with POLYMATH, Excel, and MATLAB” – 2nd ed., M. B. Cutlip and M. Shacham, Prentice-Hall, 2008. Companion web site: www.problemsolvingbook.com/bookowner/index.htm Selected Other Resources: Handouts and files for download. Summary of Topics Covered: 1. POLYMATH and applications (2 weeks) 2. Laplace transforms and applications (5 weeks) 3. MATLAB applications (3 weeks) 4. ASPEN (4 weeks) Grading scheme: Homework Exam 1 (Oct 3) Exam 2 (Oct 31) Exam 3 (Nov 21) Term Project (Nov 21 – Dec 5) Final (TBA) 15% 15% 15% 15% 15% 25% A final course grade will be assigned on the following basis: 1 90-100 85-89.9 80-84.9 75-79.9 70-74.9 60-69.9 <60 A B+ B C+ C D F Policies: 1. Students are encouraged to turn in their homework by the due dates. Remember that these assignments count toward 15% of the grade. Late homework will only be accepted under extraordinary circumstances. 2. Students are responsible for the material covered in class. Regular class attendance is expected. 3. Make-up exams and “incompletes” may be given under extraordinary circumstances and at the sole discretion of the instructor. Regular class attendance is expected. 4. Homeworks are due at the beginning of class, one week after assignment Course Objectives: 1. To assist students in applying conservation principles, Laplace transforms, partial fractions and linearization to model chemical engineering processes. 2. To assist students in developing their ability to use computational tools and software packages to solve problems and to describe the unsteady-state behavior of chemical processes. Relevant ABET Course Outcomes: a) an ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering. c) an ability to design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs within realistic constraints such as economic, environmental, social, political, ethical, health and safety, manufacturability, and sustainability. e) an ability to identify, formulate, and solve engineering problems. k) an ability to use the techniques, skills and modern engineering tools necessary for chemical engineering practice. 2 Relevant ABET Program Objective: 1. Engineering Practice: Alumni from our program are successfully engaged in the practice of chemical engineering within industry, academe and government, working in a wide array of technical specialties including, but not limited to, process and plant design operations. The NJIT Honor Code and standards of academic integrity will be enforced in this course. Any violation will be brought to the immediate attention of the Dean of Students. 3