3.4 - Distance and Pythagorean Converse
advertisement

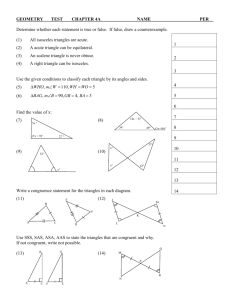
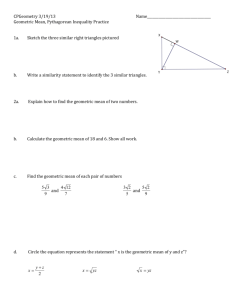
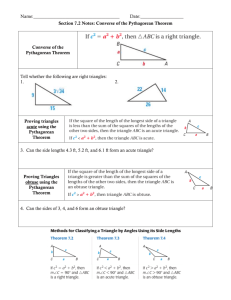
3.4 Is It A Right Triangle? Pg. 13 Pythagorean Theorem Converse and Distance 3.4 – Is It A Right Triangle?_______________ Pythagorean Theorem Converse and Distance In lesson 3.3, you learned how to use the Pythagorean Theorem. Today you are going to use this information to find the length between two points on a graph. You are also going to determine if the triangle is acute, right, or obtuse. 3.24 – DISTANCE Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the following. A 2 l h 2 72 + 32 = d2 49 + 9 = d2 58 = d2 58 d 2 7 d 3 B b. A(-6, 2)and B(-2, -3) 2 l h 42 52 = 2 2 A d2 + 16 + 25 = d2 41 = d2 41 d d 5 4 B c. A(-1, 2)and B(3, 4) 2 l h 22 42 = 2 2 d2 + 4 + 16 = d2 20 = d2 2 5d 4 2 A x B Distance Formula: x y d 2 2 2 y2 – y1 x2 – x1 3.25 – DISTANCE FORMULA Find the distance between the two points. Simplify your square roots. a. A(2, 4)and B(8, 19) x y d 2 2 2 62 + 152 = d2 36 + 225 = d2 261 = d2 d = 3 29 b. A(-2, 3)and B(-8, 6) x y d 2 2 2 62 + 32 = d2 36 + 9 = d2 45 = d2 d= 3 5 c. A(-5, 2)and B(-2, -7) x y d 2 2 2 32 + 92 = d2 9 + 81 = d2 90 = d2 d = 3 10 3.26 – WHAT'S THE PATTERN? Use the tools you have developed to find the lengths of the missing sides of the triangles below. If you know a shortcut, share it with your team. Look for any patterns in the triangles as you solve. Are any triangles similar and multiples of others? Keep answers in exact form. 5 10 5000 x 3 4 2 2 2 x 6 8 2 2 2 x 2 30002 40002 12 132 x 2 5 2 24 262 x 2 102 120 130 2 x 2 502 3.27 – PYTHAGOREAN TRIPLES 5 4 3 13 12 5 3.28 – EXTRA PRACTICE Find the area of the shapes using Pythagorean triples to help find the missing sides. 3 4 8 A triangle rectangle A 1 bh 2 bh 1 A 4 3 8 3 2 24 A 6 30un 2 8 1 A bh 2 1 A 36 8 2 A 144un 2 30 5 20 30 20 5 A = 100un2 Acute Triangle Right Triangle b c b c Obtuse Triangle c b a a a c a b c a b c a b 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 3.29 – TRIANGLE CLASSIFICATION For each set of numbers, determine if the triangle is acute, right, or obtuse. SHOW WORK! a. 8, 15, 17 17 8 15 289 64 225 289 289 2 2 2 ACUTE, RIGHT, or OBTUSE b. 3, 5, 7 7 3 5 49 9 25 49 34 2 2 2 ACUTE, RIGHT, or OBTUSE c. 8, 10, 12 12 8 10 144 64 100 144 164 2 2 2 ACUTE, RIGHT, or OBTUSE d. 2 89 5 8 89 25 64 89 89 2 2 ACUTE, RIGHT, or OBTUSE e. 8 5 3 7 2 2 2 64 25 63 64 88 ACUTE, RIGHT, or OBTUSE f. 12 2 10 2 2 9 144 40 81 144 121 ACUTE, RIGHT, or OBTUSE 2