File - Mrs. Malinda Young, M.Ed

Geometry Chapter 7
By
Nolan Nguyen and Ethan Stroh
Assume all angles that appear to be right are right!
7.1 Apply The Pythagorean Theorem
• Pythagorean Theorem: In a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs.
• In other words, a 2 +b 2 =c 2
• Pythagorean Triple: A set of three positive integers a, b, and c that satisfy the equation a 2 +b 2 =c 2 .
• Examples of a Pythagorean Triple are:
• 3, 4, 5
• 5, 12, 13
• 8, 15, 17
• 7, 24, 25
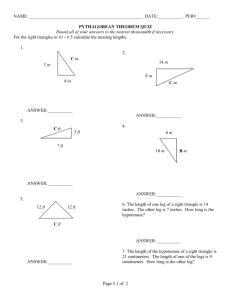
7.1 Practice
Find the value of x
48 cm
14 2 +48 2 =x 2
196+2304=x 2
2500=x 2 x=50 cm x
45 in
24 2 +45 2 =x 2
576+2025=x 2
2601=x 2 x=51 in
7.2 Use the Converse of the
Pythagorean Theorem
• Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem: If the square of the length of the longest side of a triangle is equal to the sum of the square of the lengths of the other two sides, then the triangle is a right triangle.
• This means that if c 2 =a 2 +b 2 , then triangle ABC is a right triangle
• Theorem 7.3: If the square of the length of the longest side of the triangle is less than the sum of the square of the lengths of the other two sides, then the triangle is an acute triangle.
• A triangle is acute if c 2 <a 2 +b 2
• Theorem 7.4: If the square of the length of the shortest side of the triangle is greater than the sum of the square of the lengths of the other two sides, then the triangle is an obtuse triangle.
• A triangle is obtuse if c 2 >a 2 +b 2
7.2 Practice
Identify the triangle
1. 13, 24, 28
169+576<784
Obtuse
2. 20, 72, 78
400+5184=6084
Obtuse
3. 27, 32, 42
729+1024>1764
Acute
7.3 Similar Right Triangles
• Theorem 7.5: If the altitude is drawn to the hypotenuse of a right triangle, the two triangles formed are similar to the original triangle and to each other
• Geometric Mean (Altitude) Theorem: In a right triangle, the altitude from the right angle to the hypotenuse divides the hypotenuse. The length of the altitude is the geometric mean of the two segments.
• Geometric Mean: a/x=x/b, where all values are positive
• Geometric Mean (Leg) Theorem: Ina right triangle, the altitude from the right angle to the hypotenuse divides the hypotenuse into two segments. The length of each length of each leg of the right triangle is the geometric mean of the lengths of the hypotenuse and the segment of the hypotenuse that is adjacent to the leg
7.3 Practice
Find the value of x
1.
18 cm
6 cm x x/5=18/6 x/5=3 x=15
5 cm x
3 ft
12
9 ft x/3=12/9 x/3=4/3 x=4
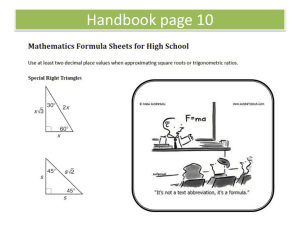
7.4 Special Right Triangles
• 45-45-90 Triangle Theorem: In a 45-45-90 triangle, the hypotenuse is √2 times as long as the legs
• 30-60-90 Triangle Theorem: In a 30-60-90 triangle, the hypotenuse is twice as big as the shorter leg and the longer leg is √3 times as long as the shorter leg
7.4 Practice
Find the value of x
1.
x
2.
x
60°
45° 45°
28 x=14√2
52 x=26
30°
7.5 Apply the Tangent Ratio
• Trigonometric Ratios: Ratio of the lengths of two sides of a triangle
• Tangent Ratio: “tan”
•
• Tan A=length of leg opposite
∠
A/ length of leg adjacent
∠
A
Use algebra to solve
C tan A=CB/BA
B A
1. Find TA
T
A
35°
8 ft tan35=x/8
8tan35=x x=5.6 ft
7.5 Practice
2. Find UF
F
71°
U
N
N
13 m tan71=13/x xtan71=13 x=13/tan71 x=4.48 m
7.6 Apply Sine and Cosine
• sine A= length of leg opposite
∠
A/ length of hypotenuse
• cosine A= length of leg adjacent
∠
A/ length of hypotenuse
• Angle of Elevation: Angle of your line of sight while looking up at an object
• Angle of Depression: Angle of your line of sight while looking down at an object
C sin A=CB/CA cos A=BA/CA
B A
1. Find SI
S
23 cm
N
67° sin67=23/x xsin67=23 x=23/sin67 x=25
7.6 Practice
2. Find CS
C
52°
21 in
I cos52=21/x xcos52=21 x=21/cos52 x=34.1
S
O
7.5-7.6 Special Right Triangles
• Keep in mind that you can find the tangent, sine, and cosine of an acute angle measuring 30, 45, or 60 by applying what you know about special triangles.
C
60° cos C=2
B 30° A
7.5-7.6 Help
If you’re struggling to remember the formulas of each of the trigonometric ratios, remember the phrase SOH CAH TOA
Sine
Opposite
Hypotenuse
Cosine
Adjacent
Hypotenuse
Tangent
Opposite
Adjacent
7.7 Solve Right Triangles
• To solve a right triangle, you have to find the values of all sides and angles. You can do this as long as you have a minimum of
1. Two side lengths
OR
2. One side length and the measure of one acute angle
Inverse Trigonometric Ratios
• Inverse Tangent: If tan A=x, then tan -1 x=m
∠
A
• Inverse Sine: If sin A=x, then sin -1 y=m
∠
A
• Inverse Cosine: If cos A=x, then cos -1 z=m
∠
A
7.7 Practice
Solve the Right Triangle
A
58°
9.43
5
AB
5 2 +8 2 =x 2
25+64=x 2
89=x 2 x≈9.43
C
32°
8
∠
B tan -1 5/8=x tan -1 .625=x x ≈32°
B
∠
C
180-90-32=x x=48