Revenue Management
advertisement

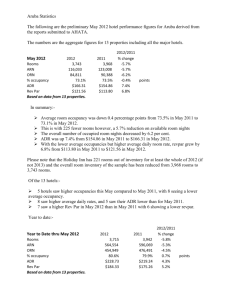
Revenue Management © 2009, Educational Institute Competencies for Revenue Management 1. Explain the concept of revenue management, and discuss how managers can maximize revenue by using forecast information in capacity management, discount allocation, and duration control. 2. Discuss common formulas managers use to measure and manage revenue. © 2009, Educational Institute (continued) 1 Competencies for Revenue Management (continued) 3. Explain how revenue management decisions are affected by group room sales, transient room sales, other revenue opportunities, local and area-wide activities, special events, and fair market share forecasting. 4. Discuss the revenue manager’s role and position, summarize typical revenue meetings, outline potential tactics to use in periods of high and low demand, discuss revenue management tactics, and explain how revenue management software helps hotel managers. © 2009, Educational Institute 2 Benefits of Revenue Management • • • • • Improved forecasting Improved seasonal pricing and inventory decisions Identification of new market segments Identification of market segment demands Enhanced coordination between the front office and sales divisions • Determination of discounting activity © 2009, Educational Institute (continued) 3 Benefits of Revenue Management (continued) • Improved development of short-term and long-term business plans • Establishment of a value-based rate structure • Increased business and profits • Savings in labor costs and other operating expenses • Initiation of consistent guest-contact scripting © 2009, Educational Institute 4 Revenue Management Methods • Capacity management Balances risks of overbooking against potential loss of revenue from reservation cancellations, early departures, and no-shows • Discount allocation Restricts time period and product mix (rooms) available at reduced or discounted rates • Duration control Places time constraints on accepting reservations in order to protect rooms for multi-day reservations (which represent higher levels of revenue) © 2009, Educational Institute 5 Revenue Management Formulas • • • • • • • Formula 1: Potential average single rate Formula 2: Potential average double rate Formula 3: Multiple occupancy percentage Formula 4: Rate spread Formula 5: Potential average rate Formula 6: Room rate achievement factor Formula 7: Yield statistic © 2009, Educational Institute 6 Revenue Management Formulas • • • • • • Formula 8: RevPAR Formula 9: Identical yields Formula 10: Equivalent occupancy Formula 11: Required non-room revenue per guest RevPAG GOPPAR © 2009, Educational Institute 7 Potential Average Single Rate Single Room Revenues at Rack Rate Number of Rooms Sold as Singles © 2009, Educational Institute 8 Potential Average Double Rate Double Room Revenues at Rack Rate Number of Rooms Sold as Doubles © 2009, Educational Institute 9 Rate Spread Potential Average Double Rate Potential Average Single Rate © 2009, Educational Institute 10 Potential Average Rate (Multiple Occupancy % Rate Spread) Potential Average Single Rate © 2009, Educational Institute 11 Room Rate Achievement Factor Actual Average Rate Potential Average Rate © 2009, Educational Institute 12 Yield Statistic Formulas Formula #1 Actual Rooms Revenue Potential Rooms Revenue Formula #2 Room Nights Sold Room Nights Available Actual Average Room Rate Potential Average Rate Formula #3 Occupancy Percentage Room Rate Achievement Factor © 2009, Educational Institute 13 RevPAR Formulas Formula #1 Actual Room Revenue Available Rooms Formula #2 Occupancy Percentage Average Daily Rate © 2009, Educational Institute 14 Identical Yields Identical Yield Occupancy Percentage = Current Average Rate Current Occupancy Percentage Proposed Average Rate © 2009, Educational Institute 15 RevPAG and GOPPAR RevPAG = Total Revenue Number of Guests GOPPAR = Departmental Revenues – Departmental Expenses Number of Available Rooms © 2009, Educational Institute 16 Elements of Revenue Management Strategies • • • • • • © 2009, Educational Institute Group room sales Transient room sales Other revenue opportunities Local and area-wide activities Special events Fair market share forecasting 17 Revenue Manager Skills and Qualities • • • • • • • Operational skills Analytical skills Strategic skills Organizing skills Communications skills Good listening skills Team-building skills © 2009, Educational Institute • • • • • • Team-building skills Training skills Patience Creativity Cooperativeness Flexibility 18 Revenue Management Meeting Participants • • • • • • © 2009, Educational Institute General manager Sales managers Catering managers Reservations manager Front office manager Food and beverage manager 19 High-Demand Tactics • • • • • • • • • • • Close or restrict discounts Apply minimum length of stay restrictions carefully Reduce group room allocations Reduce or eliminate 6 p.m. holds Tighten guarantee and cancellation policies Raise rates to be consistent with competitors Consider a rate raise for packages Apply full price to suites and executive rooms Select dates that are to be closed-to-arrivals Evaluate the benefits of sell-throughs Apply deposits and guarantees to last night of stay © 2009, Educational Institute 20 Low-Demand Tactics • • • • • • • • • © 2009, Educational Institute Sell value and benefits Offer packages Keep discount categories open Encourage upgrades Offer stay-sensitive price incentives Remove stay restrictions Involve your staff Establish relationships with competitors Lower rates 21 Four Revenue Management Tactics • • • • © 2009, Educational Institute Hurdle rate Minimum length of stay Close to arrival Sell-through 22 Revenue Management Software Revenue management software provides: • Continuous monitoring • Consistency • Information availability • Performance tracking • Special reports © 2009, Educational Institute 23