Life Science Review

Life Science
Review
Living Organism
Relationships (8.11A)
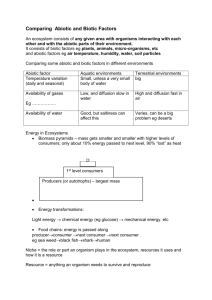
1. Label the parts, A-D, of the food pyramid to the side as either: primary consumer, tertiary consumer, producer or secondary
consumer.
Tertiary Consumer
Secondary Consumer
Primary Consumer
Producer
Living Organism
Relationships (8.11A)
2. Circle in green all the producers in the food web, orange all the primary consumers, blue all the secondary consumers and red all the tertiary consumers. Color in the corresponding parts of the food pyramid.
Predator
Living Organism
Relationships (8.11A)
Prey
*This is just ONE possible answer, there are MANY other correct answers!
3. Circle in purple one example of a predator/prey relationship and label the predator and prey.
Living Organism
Relationships (8.11A)
4. Which organism(s) should appear at Level B of the energy pyramid?
A) plants
B) fox and toad
C) owl and snake
D) mouse and squirrel
Living Organism
Relationships (8.11A)
5. At which level(s) of the food web above would the greatest amount of energy most likely exist?
A) Owl and snake
B) Grasshopper and squirrel
C) Fox and rabbit
D) plants
Living Organism
Relationships (8.11A)
6. At which level(s) of the food pyramid would the greatest amount of energy most likely exist?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Living Organism
Relationships (8.11A)
7.
Match the following symbiotic relationship words with their correct definition: parasitism, commensalism, mutualism.
the other is neither helped nor harmed.
and the other is harmed.
Living Organism
Relationships (8.11A)
8. Which of the following is an example of a parasite-host relationship between two organisms?
A) Mistletoe, a flowering plant, imbeds its root system in a tree limb for food and water. The tree limb becomes weak and breaks.
B) Army ants travel along a forest floor and stir up different kinds of flying insects. Birds follow the ant colony and eat the flying insects.
C) Birds called cattle egrets search for insects in livestock fields. Livestock like cattle and horses stir up insects as they walk through the fields.
D) Clownfish protect themselves from predators by hiding among the tentacles of sea anemones. Clownfish eat butterflyfish, which eat sea anemones.
Abiotic & Biotic (8.11B)
9. List some common abiotic and biotic factors that you would find in each of the following ecosystems:
Desert
Tundra
Forest
Rain Forest
Grassland
Marine Areas
Freshwater
Areas
Estuaries
Abiotic Factors
Very little water
Very Little water
Little water saltwater
COLD
Moderate water
Changes w/ seasons
Lots of water & humid
Warm warm freshwater
HOT
Biotic Factors
Little vegetation: cacti
Lizards, snakes, camels
Frozen soil: small root plants like grasses Caribou, polar bears
Good vegetation: trees, shrubs…
Squirrels, owls, deer
Lots of vegetation: trees, vines…
Monkeys, birds, snakes
GRASSES, shrubs, few trees…
Rabbits, bison, gophers
Algae & phytoplankton
Fish, shark, whales, shellfish
Algae & plankton
Catfish, bass, minnows
Fresh & salt water Algae & plankton
Oysters, crab, young fish
Abiotic & Biotic (8.11B)
10.
Which of these environments has the MOST biodiversity?
A) a tropical rain forest
B) a polar ice cap
C) a desert
D) a stream
Biodiversity- the variety of life in a particular habitat or ecosystem.
Abiotic & Biotic (8.11B)
11. Which of the following best explains why specific physical conditions, such as temperature ranges and light, should be maintained in an ecosystem?
A) All organisms require the same physical conditions in order to survive.
B) The physical conditions of an ecosystem control the food chains in the environment.
C) Organisms are specifically adapted to live in the physical conditions of their ecosystem.
D) Organisms move to a different ecosystem if the physical conditions change in their original ecosystem.
Abiotic & Biotic (8.11B)
12. Which of the following is NOT an example of a biotic factor in an ecosystem?
A) Bacteria
B) Beetle
C) Shrub
D) Water
Abiotic & Biotic (8.11B)
13. Which is an example of competition for a biotic factor?
A) groundhogs competing for places to dig burrows.
B) birds competing for berries to eat.
C) plants growing tall to get more sunlight than other plants.
D) Snakes competing for sunny places to warm themselves.
Abiotic & Biotic (8.11B)
14. Which of the following would be an abiotic component of a grassland environment?
A) cactus
B) palm
C) fertile soil
D) banana tree
Environmental
Changes and
Organism Traits
(8.11C)
15.
Which of the following would most likely have a long-term, negative effect on the hyacinth macaw’s survival?
A) Hyacinth macaws mainly eating palm-tree nuts
B) Some hyacinth macaws nesting in the holes of cliffs
C) Removal of 10,000 hyacinth macaws for the pet-trade business
D) Hyacinth macaws spreading the manduvi tree’s seeds in their droppings
Environmental
Changes and
Organism Traits
(8.11C)
16.
Farmers within the hyacinth macaw’s range set yearly grass fires that often destroy the bird’s nesting trees. Which of the following best explains why this action would lead to either a short-term or long-term effect on the hyacinth macaw population?
A) Short-term effect, because the hyacinth macaws can nest in cliffs
B) Short-term effect, because the nesting trees will grow back quickly
C) Longterm effect, because the hyacinth macaws’ nesting sites are destroyed
D) Long-term effect, because yearly fires do not preven more dangerous fires
Environmental Changes and
Organism Traits (8.11C)
17.
In 1995, gray wolves were restored to Yellowstone
National Park. As a result, the gray wolves began to control the park’s large elk population, which had been overeating trees growing along the park’s streams. The recovery of the trees, in turn, has cooled the stream flows to normal temperatures.
Which of the following organisms would probably benefit most from the streams’ cooler waters?
A) Migrating birds that need nesting areas
B) Native trout that live in the park’s water
C) Trees that provide habitats for native birds
D) Beavers that use willow branches to make dams
Environmental Changes and Organism Traits (8.11C)
18.
Which of the following conclusions is best supported by the information given above?
A) Polar bears will adapt to a los of Arctic sea ice and find new sources of food.
B) The amount of sea ice available for polar bears has generally increased since 1978.
C) The extent of Arctic sea ice each year depends on the size of the polar bear population.
D) The polar bears’ survival is threatened because less sea ice makes it more difficult for them to hunt.
Environmental Changes and
Organism Traits (8.11C)
19.
The theory of natural selection explains how-
A) farmers develop certain types of crop plants.
B) variations appear in a species.
C) environments change over time.
D) useful traits spread through a population.
Environmental Changes and
Organism Traits (8.11C)
20.
What is most likely to happen if an environment changes and a species does not have variations that are helpful in the new conditions?
A) Members of the species will try to change the environment.
B) Members of the species will develop new adaptations.
C) A new species will form from the existing species.
D) The species will become extinct.
Body Systems
Match the following body systems with the correct definition.
_____1. Transports materials throughout the body.
_____2. Protects against disease.
_____3. Exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide.
_____4. Secretes hormones to regulate body.
_____5. Supports body & protects organs.
_____6. Sends and receives signals through body.
_____7. Moves the body.
_____8. Skin that protects body.
_____9. Breaks food down into nutrients.
_____10. Produces offspring.
_____11. Removes wastes from the body.
A) Excretory System
B) Endocrine System
C) Circulatory System
D) Skeletal System
E) Immune System
F) Respiratory System
G) Nervous System
H) Muscular System
I) Digestive System
J) Reproductive Sys.
K) Integumentary Sys.
Protista
Fungi
Plantae
Animalia
Kingdoms
Kingdom Cell Type
(Prokaryotic or
Eukaryotic?)
Unicellular or
Multicellular
Cell Walls
(Present or not?)
Energy Source Habitat or
Examples of
Organisms
Archaebacteria
Eubacteria
Name of
Tool
Measures Units
Living Organism
Relationships (8.11A)
4. Which organism(s) should appear at Level B of the energy pyramid?
A) plants
B) fox and toad
C) owl and snake
D) mouse and squirrel
Living Organism
Relationships (8.11A)
5. At which level(s) of the food web above would the greatest amount of energy most likely exist?
A) Owl and snake
B) Grasshopper and squirrel
C) Fox and rabbit
D) plants
Living Organism
Relationships (8.11A)
6. At which level(s) of the food pyramid would the greatest amount of energy most likely exist?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
Living Organism
Relationships (8.11A)
8. Which of the following is an example of a parasite-host relationship between two organisms?
A) Mistletoe, a flowering plant, imbeds its root system in a tree limb for food and water. The tree limb becomes weak and breaks.
B) Army ants travel along a forest floor and stir up different kinds of flying insects. Birds follow the ant colony and eat the flying insects.
C) Birds called cattle egrets search for insects in livestock fields. Livestock like cattle and horses stir up insects as they walk through the fields.
D) Clownfish protect themselves from predators by hiding among the tentacles of sea anemones. Clownfish eat butterflyfish, which eat sea anemones.
Abiotic & Biotic (8.11B)
10.
Which of these environments has the MOST biodiversity?
A) a tropical rain forest
B) a polar ice cap
C) a desert
D) a stream
Abiotic & Biotic (8.11B)
11. Which of the following best explains why specific physical conditions, such as temperature ranges and light, should be maintained in an ecosystem?
A) All organisms require the same physical conditions in order to survive.
B) The physical conditions of an ecosystem control the food chains in the environment.
C) Organisms are specifically adapted to live in the physical conditions of their ecosystem.
D) Organisms move to a different ecosystem if the physical conditions change in their original ecosystem.
Abiotic & Biotic (8.11B)
12. Which of the following is NOT an example of a biotic factor in an ecosystem?
A) Bacteria
B) Beetle
C) Shrub
D) Water
Abiotic & Biotic (8.11B)
13. Which is an example of competition for a biotic factor?
A) groundhogs competing for places to dig burrows.
B) birds competing for berries to eat.
C) plants growing tall to get more sunlight than other plants.
D) Snakes competing for sunny places to warm themselves.
Abiotic & Biotic (8.11B)
14. Which of the following would be an abiotic component of a grassland environment?
A) cactus
B) palm
C) fertile soil
D) banana tree
Environmental
Changes and
Organism Traits
(8.11C)
15.
Which of the following would most likely have a long-term, negative effect on the hyacinth macaw’s survival?
A) Hyacinth macaws mainly eating palm-tree nuts
B) Some hyacinth macaws nesting in the holes of cliffs
C) Removal of 10,000 hyacinth macaws for the pet-trade business
D) Hyacinth macaws spreading the manduvi tree’s seeds in their droppings
Environmental
Changes and
Organism Traits
(8.11C)
16.
Farmers within the hyacinth macaw’s range set yearly grass fires that often destroy the bird’s nesting trees. Which of the following best explains why this action would lead to either a short-term or long-term effect on the hyacinth macaw population?
A) Short-term effect, because the hyacinth macaws can nest in cliffs
B) Short-term effect, because the nesting trees will grow back quickly
C) Longterm effect, because the hyacinth macaws’ nesting sites are destroyed
D) Long-term effect, because yearly fires do not preven more dangerous fires
Environmental Changes and
Organism Traits (8.11C)
17.
In 1995, gray wolves were restored to Yellowstone
National Park. As a result, the gray wolves began to control the park’s large elk population, which had been overeating trees growing along the park’s streams. The recovery of the trees, in turn, has cooled the stream flows to normal temperatures.
Which of the following organisms would probably benefit most from the streams’ cooler waters?
A) Migrating birds that need nesting areas
B) Native trout that live in the park’s water
C) Trees that provide habitats for native birds
D) Beavers that use willow branches to make dams
Environmental Changes and Organism Traits (8.11C)
18.
Which of the following conclusions is best supported by the information given above?
A) Polar bears will adapt to a los of Arctic sea ice and find new sources of food.
B) The amount of sea ice available for polar bears has generally increased since 1978.
C) The extent of Arctic sea ice each year depends on the size of the polar bear population.
D) The polar bears’ survival is threatened because less sea ice makes it more difficult for them to hunt.
Environmental Changes and
Organism Traits (8.11C)
19.
The theory of natural selection explains how-
A) farmers develop certain types of crop plants.
B) variations appear in a species.
C) environments change over time.
D) useful traits spread through a population.
Environmental Changes and
Organism Traits (8.11C)
20.
What is most likely to happen if an environment changes and a species does not have variations that are helpful in the new conditions?
A) Members of the species will try to change the environment.
B) Members of the species will develop new adaptations.
C) A new species will form from the existing species.
D) The species will become extinct.
Body Systems
Match the following body systems with the correct definition.
A) Excretory System
B) Endocrine System
C) Circulatory System
D) Skeletal System
E) Immune System
F) Respiratory System
G) Nervous System
H) Muscular System
I) Digestive System
J) Reproductive Sys.
K) Integumentary Sys.
Kingdoms
Kingdom Cell Type
(Prokaryotic or
Eukaryotic?)
Unicellular or
Multicellular
Cell Walls
(Present or not?)
Energy Source Habitat or
Examples of
Organisms
Archaebacteria
Prokaryotic
Unicellular
Eubacteria
Protista
Fungi
No cell walls
Prokaryotic
Eukaryote
Unicellular
No cell walls
Unicellular or simple multicellular
May have cell walls
Eukaryote
Mainly multicellular
Cell walls
Plantae
Eukaryote
Complex multicellular
Cell walls
Animalia
Eukaryote
Complex multicellular
No cell walls
Take in food
Live in extreme environments
Take in food
Some make food; some take in food
Absorb food
Bacteria in soil, bacteria that cause disease
Amoebas, slime molds, euglena, algae
Yeast, molds, mushrooms
Make food Mosses, ferns, grasses, trees
Eat food
Invertebrates such as sponges and worms; vertebrates such as fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammels.
Name of
Tool
Triple Beam
Balance
Measures
Mass
Volume Graduated
Cylinder
Thermometer Temperature
Units
Grams
Liters (or milliLiters)
Celcius
Ruler
Spring Scale
Length
Weight
Meters (or centimeters)
Newtons