Light thinning
advertisement

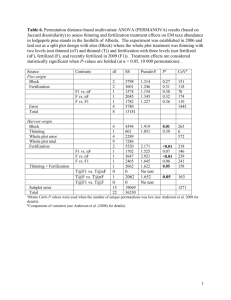
Plantation Density and Thinning Effect on the Length of Tracheid and Maturing Age of Japanese- cedar Grown in Taiwan Speaker : Pei-Yu Kuo Introduction Large percentage of plantation Even-aged Low economic value Plantation density Thinning intensity Anatomy of the wood Japanese-cedar is one of the important resources in Taiwan. Material and Method – site location Material and Method – data of the site Original numbers Site (1968) Light thinning treatment (1990) A1 A2 2200 trees / ha (Type A) Intensity of thinning treatments (2001) Average Basel Area (cm2) Heavy thinning (40%) 621.93 550 trees / ha Medium thinning (25%) 600.45 A3 Light thinning (10%) 571.28 B1 Medium thinning (25%) 587.50 Light thinning (10%) 504.32 No thinning 477.23 B2 B3 3000 trees / ha (Type B) 750 trees / ha Result and Discussion 1 The anatomy from pith to bark and their relationship tracheid length (mm) of tracheid (mm) length Result and Discussion 4.00 3.00 2.00 y = 0.6767Ln(x) + 0.9719 R2 = 0.9714 1.00 0.00 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Ring number from pith(years) Ring number from pith The growing curve of trachied is a log curve 35 Result and Discussion MFA (degree) 50 y = -7.2902Ln(x) + 39.27 R2 = 0.9406 40 30 20 10 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 Ringnumber number from from pith Ring pith(years) (years) The MFA decreased rapidly at first and then remained constant. MFA(degree) Result and Discussion 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 y = -10.649x + 50.009 R2 = 0.7126 0 1 2 3 4 tracheid length (mm) The degree of MFA and the length of tracheid have contrary trend. Result and Discussion 33rd to 36th 23rd to 32nd 1st to 22nd Second thinning First thinning Plantation density We not only discuss the average data, but also separate those data into three sections and discuss the effect of each treatment. Result and Discussion Tracheid length Average 1st – 22nd 23rd – 32nd 33rd – 36th A1 2.65 ± 0.46 2.26 ± 0.43 3.02 ± 0.10 2.99 ± 0.11 A2 2.65 ± 0.65 2.27 ± 0.65 3.10 ± 0.16 3.19 ± 0.16 A3 2.63 ± 0.50 2.20 ± 0.42 3.03 ± 0.11 3.12 ± 0.12 B1 2.63 ± 0.58 2.28 ± 0.60 3.04 ± 0.06 3.06 ± 0.07 B2 2.73 ± 0.57 2.42 ± 0.62 3.06 ± 0.10 3.20 ± 0.13 B3 2.68 ± 0.64 2.26 ± 0.64 3.05 ± 0.13 3.23 ± 0.04 Result and Discussion 2 Three methods to distinguish the maturing age Result and Discussion tracheid (mm)(mm) tracheid of length length 4.00 3.00 2.00 y = 0.6767Ln(x) + 0.9719 R2 = 0.9714 1.00 0.00 0 5 10 15 20 25 Ring number fromfrom pithpith (years) Ring number 30 35 Method 1 : the elongation ratio of log curve is less than 1% Result and Discussion (mm) of tracheid length tracheid length (mm) 3.5 3 2.5 y = 0.1431x + 1.1541 2 2 R = 0.9344 1.5 The tracheid length between 1995 and 2000 1 from pith to 10th ring 0.5 0 0 7 14 21 28 Ring number from pith pith(years) from Ring number Method 2 : Reducing the numbers of sample 35 Aaccumulated width of annual ring (mm) Result and Discussion 14 y = 3.8373Ln(x) - 1.5889 R2 = 0.9786 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 1 4 7 10 13 16 19 22 25 Ring number from pith (years) 28 31 Method 3 : the elongation ratio of log curve is less than 3% Result and Discussion A B Method 1 a(year) 20 20 22 16 17 22 Method 2 a(year) 19 18 22 18 16 18 Method 3 a(year) 19 19 17 18 16 22 Maturea Wood 3.00 ±0.09 3.11 ±0.15 3.03 ±0.14 3.02 ±0.07 3.08 ±0.11 3.09 ±0.14 Juvenileb Wood 2.24 ±0.37 2.13 ±0.62 2.25 ±0.42 2.04 ±0.53 2.12 ±0.54 2.01 ±0.59 Maturea Wood 14.09 ±3.17 15.74 ±2.03 17.14 ±1.41 17.26 ±1.5 17.35 ±1.96 16.63 ±1.20 Juvenileb Wood 24.87 ±9.14 25.35 ±6.00 24.39 ±5.08 26.00 ±5.99 28.07 ±8.77 27.06 ±6.85 Tracheid length (mm) Microfibril Conclusions The anatomy from pith to bark and their relationship The length of tracheid decreases with the increasing MFA. It shows negative linear regression (R2=0.71) when the length of tracheid is versus the angle of MFA. The effect of planation density and thinning The average lengths of high plantation density or one to twenty years grown tracheid have significant longer lengths than low plantation density tracheid. But, there is no significant difference in thinning treatment. Conclusions Three methods to distinguish the maturing age Using the three mentioned methods to determine the age of maturity, we can conclude that it is 19 years old. Morerover, there is no significant difference between the results of these methods above to judge the age. No matter in the length of tracheid or the angle of MFA, mature wood has significant longer tracheid length and smaller MFA than juvenile wood. Thank you for your attention Comments and Questions are Welcome