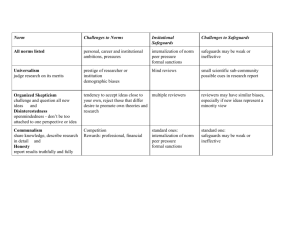
From Tatum's Why Are All the Black Kids Sitting Together in
advertisement

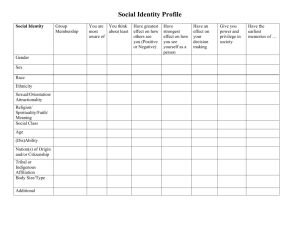
From Tatum’s Why Are All the Black Kids Sitting Together in the Cafeteria? Systemic Advantage/Disadvantage “…There are at least seven categories of ‘otherness:” Race or ethnicity Gender Religion Sexual identity Socioeconomic status Age Physical or mental ability With each category, there is a group that is dominant (systematically advantaged) and a group that is subordinate or targeted (systematically disadvantaged) Mythical Norm Somewhere, on the edge of consciousness, there is what I call a mythical norm, which each one of us within our hearts knows “that is not me.” In america, this norm is usually defined as white, thin, male, young, heterosexual, christian and financially secure. It is with this mythical norm that the trappings of power reside within society. Those of us who stand outside that power often identify with one way in which we are different, and we assume that to be the primary cause of all oppression, forgetting other distortions around difference, some of which we ourselves may be practicing. Audre Lord Even as I focus on Race and racism in my own writing and teaching, it is helpful to remind myself and my students of the other distortions around difference that I (and they) may be practicing. It is an especially useful way of generating empathy for our mutual learning process. Beverly Tatum pp 2223. Stages of Identity Development Subordinate (William Cross)(pp. 54-5) Dominant (Janet Helms)(pp. 94-5) Contact Pre-encounter Disintegration Encounter Reintegration Immersion/emersion Pseudo-independent Internalization Immersion/emersion Internalization/commitment Autonomy Tatum notes that these stages are more cyclical than linear and that there is no assured, straight-line development. Progress is not assured or predictable. Trauma or unfamiliar surroundings can quickly put someone back into a stage he/she may have felt in the past. Cross’s Theory of Minority Identity Development Pre-encounter. Unquestioned acceptance of cultural norm. (“It is better to be White.”) Encounter. An event or series of events brings a realization of the personal impact of being in a targeted group. Immersion/emersion. Can involve rejecting and retreating from the dominant culture. Can result in self-segregation, immersing oneself in the targeted culture. Can be compared to learning another language, eased by being immersed in the culture where that language is spoken. Internalization. Positive sense of identity that includes the marginalized and targeted subordinate part. Prepared to perceive and transcend the disadvantaged aspect of self. Internalization/commitment. Able to translate one’s personal sense of identity into ongoing action and commitment on behalf of the disadvantaged aspect of self. Helms’ Theory of Majority Identity Development Contact. Pay little attention to racial identity. “I’m just normal.” Disintegration. System of privilege and it’s lack become increasingly apparent. Guilt, shame and anger are often present. Reintegration. Return to collusion and silence about privilege. Can “blame the victim.” Pseudo-independent. Exhibits deeper intellectual understanding. “Guilty white liberal.” May want to associate w/ people who lack privilege. Immersion/emersion. Seeking a more positive identity embracing the privileged status and taking responsibility for it. Understanding one’s sphere of influence. May emerge as an ally of those who lack privilege. Seeks other similarly privileged people to address the issue. Autonomy. Integrating new vision of privilege and confronting and rejecting privilege daily. Continually open to new information about privilege and new ways of thinking about it. Self-actualizing. Increasing effectiveness in multi-cultural settings and interactions.