BTEC National Diploma in Engineering Unit 6 & 53 Combined
advertisement

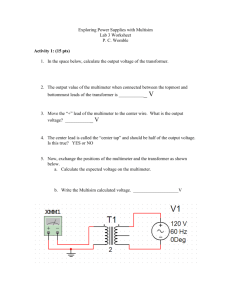
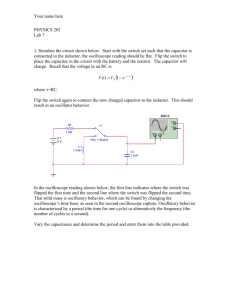
BTEC National Diploma in Engineering Unit 6 & 53 Combined Electrical and Electronic Principles + Electronic Measurement and Test Qualification BTEC National Diploma in Engineering Unit Number Assessor Name Learner Name Paul Lewis Achievement at a glance, deadlines given in module weeks, for example P1 should be completed by the 3rd week of the module Unit 6 Outcomes P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 P7 P8 P9 P10 P11 M1 M2 M3 D1 Tutor sign and date for each outcome achieved Learner sign and date for each outcome submitted Unit 53 Outcomes P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6 Tutor sign and date for each achieved outcome Learner sign and date for each submitted outcome P7 P8 M1 M2 M3 D1 D2 D2 Delivery Schedule and Deadlines Session 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Unit 6 Unit 53 P1 P2 (part 1) P2 (part 2) P4 P6 P5 P5 P10 & P11 P3 Deadline Hand in by Session 3 “ Referred? Completed Resubmit by Date P2 & P3 (part1) Session 6 “ Session 9 “ P1 “ P7 & P8 Session 12 ““ P4 & P5 P6 P7 & P8 P9 M1 M2 M3 D1 D2 M1 M2 M3 D1 D2 Session 15 “ “ “ Session 20 “ “ “ “ Session 25 “ “ “ “ Learner Declaration I confirm that the work submitted to complete the given tasks is my own. I have indicated where research and other resources have been used to confirm the conclusions reached within the submission and listed those resources in a bibliography. Sign………………………………………………… Date…………………………………………. Session 1 Use DC circuit theory to calculate current, voltage and resistance in DC Networks Unit 6 P1 For the circuit shown below: Circuit 1 Choose 5 different value resistors from the following table for resistors R1 – R5 Calculate the total power dissipation of your circuit then choose a suitable voltage from the table below based on this value Resistor values for R1 – R5 Voltage values for V1 10 Ω 3 volts 22 Ω 5 volts 33 Ω 6 volts 47 Ω 9 volts 100 Ω 10 volts 220 Ω 12 volts 330 Ω 15 volts 470 Ω 24 volts 1k Ω Calculate: The total circuit resistance Rt The total circuit current It The current flowing through R3 The voltage dropped across R2 The power dissipated by R1 Confirm the results of your calculation using the laboratory simulator (Multisim) Care should be taken by each student to ensure that the combination of components and supply voltage are unique for each assessment. Session 2 Unit 6 P2 (Part 1) Use a multi-meter to carry out circuit measurements in a DC circuit You are required to construct the circuit used for P1 above. You are to use test equipment to carry out the following measurements as listed in the table below. You need to have the witness statement signed by the lecturer or trainer demonstrator. Parameter Total circuit resistance Total circuit current Current flowing through R3 Voltage dropped across R2 Power dissipated in R1 Calculated values Measured values Simulated values For this observation the learner: Safely constructed a DC network comprising of 5 resistors Connected the network to a DC source (5 volts) Correctly demonstrated the safe use of a multimeter Used a multimeter to measure voltage, current and resistance in accordance with the set tasks Was able to contrast and compare the readings taken by a multimeter with calculated and simulated results Signed Observer ……………………………….. Date ……………………………. Session 4 Unit 53 P2 (Part 1) Describe the function, features and characteristics of a power supply Produce an information sheet describing the functions, features and characteristics of the HQ PS1503SB Power supply. Unit 53 P3 (Part 1) & Unit 6 (Part 2) Use test equipment and measuring techniques to take measurements from a power supply (battery) and determine its internal resistance Measure the offload voltage of a given battery using a multimeter Measure the onload voltage of the battery when connected to the virtual cat circuit using a multimeter Measure the current drawn by the virtual cat circuit using a multimeter Use the data from the measurements to calculate the internal resistance of the battery Include all of the above data in a technical report Session 5 Describe the function and type of capacitors Unit 6 P4 Describe the basic construction and function of a capacitor. This should include a labelled diagram of a capacitor showing the plates and dielectric, a circuit symbol, the unit of capacitance and a brief description of permittivity. Describe the following list of capacitors in terms of their capacitance, typical range of working voltages, dielectric, and energy storage. Give one example of a typical application for each type of capacitor. Electrolytic Mica Plastic Paper Ceramic Fixed and variable Session 6 Calculate the charge, voltage and energy values in a DC network for both three capacitors in series and three capacitors in parallel Unit 6 P6 Choose 3 random capacitors from the following list and calculate the charge, voltage, capacitor and energy values stored by each capacitor for the following networks. Choose from 100 nF, 1 uF, 10 uF, 22 uF, 33 uF, 47 uF, 100 uF Session 7 Carry out and experiment to determine the relationship between voltage and current for a charging and discharging capacitor Unit 6 P5 Choose a capacitor and resistor combination that will give a time constant between 1 – 5 seconds. Tasks Connect the circuit to the power supply as shown Calculate the time constant of the circuit Set up an oscilloscope to measure the voltage across the capacitor using suitable time and amplitude settings Switch on the circuit and measure the rise in capacitor voltage for 5 time constants. You can take a photo of this process to use as documentary evidence Switch off the circuit and measure the decay in capacitor voltage for 5 time constants. Once again you can use a photo as documentary evidence Show how the rise in capacitor voltage is related to v =Vmax (1 – e –t/cr) Show how the decay in current is related to i = Imaxe-t/cr Session 8 Unit 53 P1 Describe the function, features and characteristics of a measurement instrument Task 1. Describe the function, features and characteristics of an oscilloscope. Session 9 Unit 53 P2 (Part 2) Describe the function, features and characteristics of a function generator Unit 53 P7 Use a virtual measurement and test system to carry out a test on a piece of electronic equipment For the following circuit Set up the function generator to produce a sine wave with a frequency of 1 kHz Set the function generator how have an amplitude of 10 volts peak to peak Connect the function generator to the circuit Set up and oscilloscope to measure the input and output signals When the oscilloscope is successfully measuring the input and output signals connect it to a computer via a USB cable and start up the virtual instrument software Compare the input signal to the output signal in terms of amplitude using the software cursors Adjust the frequency of the function generator until the output signal = 0.7 times the input signal Use the software cursors to measure the phase angle at this point Describe the process used to test the low pass filter and take measurements from it using the oscilloscope software controls on the computer. Photographs, illustrations, screen dumps and calculations are all required to complete this section Unit 53 P8 Describe the measurement techniques, instrument connection, hardware and software used Measurement techniques is a description of what values were measured and how the data was gathered. For example how the oscilloscope and function generator were set up to conduct the test Instrument connection deals with how the function generator was connected to your circuit, how the oscilloscope was connected to take measurements and how the oscilloscope was interfaced with the computer You should give a brief description of the hardware and software used to carry out this test. Hardware to include the physical oscilloscope and computer. Software to include the OWON Virtual Oscilloscope Session 10 Unit 6 P10 Use single phase AC circuit theory to determine the characteristics of a sinusoidal waveform Sketch a sinuisoidal waveform then label and define the following parameters: Amplitude Frequency Periodic time RMS value Phase shift Find the instantaneous voltage after 10 mS have elapsed for the following sine wave: Vinst = 240Sin(100πt +/- 0) Unit 6 P11 Use an oscilloscope to measure and determine the inputs and outputs of a single phase AC circuit In conjunction with the data gathered for Session 9 Find the bandwidth for a low pass filter with the following components: R = 1000Ω C = 10 nF (0.00000001 Farads) Simulate the circuit using Multisim and prove that your calculations are correct. Compare your calculated results with the simulation. Session 11 Unit 6 P3 Compare the forward and reverse characteristics of two different semi-conductor diodes You are required to use test equipment to measure the forward and reverse characteristics of two semiconductor diodes. You should use a 1N4001 diode and a zener diode to carry out this experiment. Tasks Use the following circuit as a basis for this test: Draw and label a diagram of the 1N4001 general purpose diode connected in forward bias and reverse bias mode Measure the forward characteristic of the diode between 0.5 volts and 0.7 volts using steps of 0.01 of a volt by adjusting the resistance box R1 Measure and record the reverse characteristic of the diode using Multisim between 49.9 volts and 50.01 volts using steps of 0.01 of a volt Carry out a similar experiment on a zener diode (of your choice) using its data sheet as a guide to the magnitude of voltages required to test its forward and reverse characteristics Draw and label graphs of both data sets Compare the two graphs showing the conduction characteristics of both diodes, consult the data sheets and evaluate your findings in terms of forward and reverse voltages, power dissipation and maximum operating current Session 12 Explain the importance of test specifications as an aid to ensuring the validity and consistency of measurements Unit 53 P4 Scenario Imagine you are an Electronics company manager; you have just designed and built a prototype circuit that meets your client’s specifications. They request an order of 1,000 circuits to be made. To deal with this demand you enlist a team of test engineers. You need some way of ensuring that the tests to be carried out will get the results that meet the specification. How can you ensure they get valid and consistent measurements every time? Define Validity and consistency. Explain why both are important parameters when taking measurements. Explain what a test specification is Why is a test specification important in measurement taking? Use one of the Tasks in P3 as an example to showcase this Unit 53 P5 Describe the principles and need for the calibration of an item of electronic test equipment Produce a report highlighting the reasons why electronic test and measurement equipment needs to be calibrated on a regular basis. Your report should include references to: Primary, secondary, working standards and SI units Metrology, calibration, accuracy, precision, sensitivity and resolution A reasonable calibration interval for equipment in regular use (4+ hours per day) 3 reasons why an instrument might need to be calibrated within the calibration interval 3 reasons why calibration is normally carried out by specialist companies The effect that temperature and relative humidity can have on measurements The impact of calibration on quality, productivity and safety Session13 Unit 53 P6 Describe the health, safety and configuration issues that need to be considered when connecting test equipment to an item of electronic equipment that needs testing Scenario You have been employed as a junior electrical/electronic technician for a small local firm specializing in the repair, installation and commissioning of direct online starting equipment for small to medium power electrical motors. One of your best customers has a motor starter which has developed a fault. You have been tasked with finding the fault and testing the equipment before handing it back to the client. The motor will need to be tested using a 440 volt 3 phase supply. Describe the procedures you would take to ensure that this equipment can be tested safely. You description could include illustrations, diagrams and examples from industry. Here are some of the areas you should include: Precautions to be taken when working with live electrical equipment Procedures which ensure that electrical/electronic test equipment is suitable and safe for use with live electrical equipment (use of manuals and manufacturer’s procedures) The importance of checking that electrical equipment is properly bonded to earth Safe isolation techniques for electrical/electronic equipment Hidden dangers of working with electronic equipment which has been safely isolated The importance of electrical safety cut-outs such as RCD’s Removing and replacing inspection covers Session 14 Unit 6 P7 Describe the characteristics of a magnetic field Draw the magnetic field associated with a permanent bar magnet and use the diagram to carry out the following tasks. Give 5 general properties of a magnetic field. Define flux, flux density and magnetic field strength Describe the effects of reluctance and hysteresis with respect to magnetic circuits. Define the term ferromagnetic and give three examples of a ferromagnetic material Describe the process and advantages of magnetic screening Unit 6 P8 Describe the relationship between flux density (B) and field strength (H) Plot the B/H curve on a suitable graph for the materials shown on the table from the given data and determine the relative permeability (µr) of the material for each stage. Given that µo = 4 x 10-7 H/m find the range of relative permeability for each material. Use the data plotted on the graph to analyse and explain the relationship between the two given materials in terms of flux density (B) and magnetizing force (H) Remember relative permeability µr = B/(H x µo) Plot the graph that shows relative permeability against the magnetizing force Describe what happens to a material as the magnetizing force is increased in terms of flux density and relative permeability Magnetizing Mild steel Cast Iron Force (H) At/m Flux density (B) Tesla’s Flux density (B) Tesla’s 1000 0.7 0.3 2000 1.24 0.48 3000 1.45 0.6 4000 1.55 0.67 5000 1.6 0.72 Session 15 Describe the principles and applications of electromagnetic induction Use the following tasks to describe the principles and applications of electromagnetic induction. Define Faraday’ laws in your own words using diagrams where appropriate. Define Lenz’s law in your own words using diagrams where appropriate. Draw a diagram of a simple AC generator and use Fleming’s right hand rule to demonstrate the direction of the current in the rotating conductor when it is perpendicular to the North Pole. Explain the principle of operation of a simple transformer with reference to Faradays law of electromagnetic induction Explain the principle operation of a 3 phase AC induction motor with reference to Faradays law of electromagnetic induction Session 16 Unit 6 M1 Use Kirchoff’s laws to determine the current in various parts of a network having four nodes and the power dissipated in a load resistor containing two voltages sources For the circuit shown below: Use the same table as for Unit 6 P1 in order to choose component values. Circuit 2 From the attached table choose different values for R1 – R3 From the attached table choose different voltages for V1 –V2 Use Kirchoff’s laws to determine the current flowing through R1, R2 and R3 Determine the power dissipation in R1 Use Multisim to confirm the results of your calculations and attach to the assignment as a screen dump Session 17 Unit 6 M2 Evaluate capacitance, charge, voltage and energy in a network containing a series-parallel combination of three capacitors Choose 3 random capacitors from the same table used for Unit 6 P6 and calculate the total capacitance, total charge, the voltage dropped across each capacitor and the total energy stored for the following network. Session 18 Unit 6 M3 Compare the results of adding and subtracting two sinusiodal AC waveforms graphically and by phasor diagram V1 is a voltage of 15 V r.m.s at a phase angle of 25®, V2 is a voltage of 12 V r.m.s at a phase angle of -30®. Show the result of V1 + V2 and V1 - V2 graphically and by phasor diagram Session 19 Unit 6 D1 Analyse the operation and the effects of varying component parameters of a power supply circuit that includes a transformer, diodes and capacitors Tasks Use an oscilloscope to measure the output voltage of this circuit at the point shown Compare the output voltage with the input voltage V1 (Screen dump) From you initial measurements use the graphing function in Multisim to measure the ripple voltage of this circuit Adjust R1 until the ripple voltage of the circuit reads 200 mV From your results calculate the time constant for this circuit If R1 = 100Ω what value of capacitance would be required to produce a ripple voltage of 200 mV? If the instantaneous current conducted by the capacitor on its charge phase is I = C x dv/dt, find the repetitive forward current conducted by the circuit on each charge phase (use the grapher function) Explain the importance of the Vrrm rating when designing power supply circuits Explain why the voltage rating of the capacitor and the diodes should be at least twice the Vrrm rating given Session 20 Task 14 (D2) Evaluate the performance of a motor and a generator by reference to electronic theory 1) Draw and label the component parts of a basic DC machine. 2) Describe the action of a two segment commutator using appropriate diagrams. 3) Define: a. Wave windings b. Lap Windings 4) Briefly describe the operation of DC machines that are wound in: a. Shunt b. Series c. Compound 5) Briefly describe armature reaction and show one way in which it can be overcome. 6) A 4 pole generator has a lap-wound armature with 50 slots with 16 conductors per slot. The useful flux per pole is 20 mWb. Determine the speed at which the machine must be driven to generate an e.m.f. of 300V. 7) A d.c. shunt-wound generator running at constant speed generates a voltage of 120 V at a certain value of field current. Determine the change in the generated voltage when the field current is reduced by 25%, assuming the flux is proportional to the field current. 8) With reference to the basic construction of a d.c. machine state the principle difference between a d.c. generator and a d.c. motor. 9) The armature of a d.c. machine has a resistance of 0.25 Ω and is connected to a 300 V supply. Calculate the e.m.f. generated when it is running: a. as a generator giving 100 A b. as a motor taking 80 A Session 21 Unit 53 M1 Explain the importance of resolution, accuracy, sensitivity bandwidth and input impedance on the performance of a piece of test equipment Explain the importance of resolution, accuracy, sensitivity bandwidth and input impedance on the performance of an oscilloscope. You can use any of the tests in the pass section (which required an oscilloscope) as a basis for your submission, especially the tasks carried out for P3 Session 22 Unit 53 M2 Use a manufacturer’s recommended procedure together with laboratory instruments and standards to calibrate and configure an item of electronic test equipment Use the manufacturer’s recommended procedure to calibrate and configure a laboratory oscilloscope. Use the calibrated scope to check the accuracy of a laboratory function generator with respect to frequency and amplitude. Check the accuracy of your measurements against that given by the manufacturer of the function generator. Based on your findings, would you recommend that the function generator needs to be sent back to the manufacturer for calibration? You need to justify this recommendation. Session 23 Task 10 (M3) Use appropriate software to display and analyse voltage/time data captured from a virtual oscilloscope This is a natural extension of the task given for P7. In this case you are required to analyse a waveform. The best way to accomplish this is to use either task 1 or 2 for P3 as a basis for comparing the captured data with the results predicted by theory Session 24 Unit 53 D1 Evaluate the accuracy of your own test measurements and relate them to limitations of the test equipment, test procedures or possible emergent fault conditions You can use any of the tests carried out in the various exercises or practical projects as a basis for this evaluation. The submission needs to be an ‘in-depth’ investigation of the effects of connecting test/measurement equipment to a circuit under test and how the results are limited by the characteristics of the test equipment and test procedures. As an example, an oscilloscope is incapable of accurately displaying a transient pulse due to its finite bandwidth. This could be the basis of an investigation carried out by you to explain why? Session 25 Unit 53 D2 Devise and demonstrate a calibration procedure for an item of electronic test equipment Devise and demonstrate a calibration procedure for a x10 oscilloscope probe to be used with the laboratory oscilloscopes. Explain why the probe needs to be calibrated and under what circumstances such a probe might be required in preference to a standard x1 probe.