Exam 1 Review
advertisement

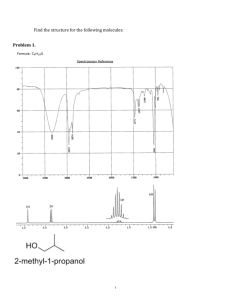
1) Draw a structure consistent with the following data: •The MS shows a molecular ion at 59 amu. •The IR spectrum shows a double-humped strong absorbance at around 3300 cm–1 (the only absorbance in the functional group region). Odd molecular ion peak tells you there is a nitrogen. 59-14=45 45/12=3 carbons 45-36=9 hydrogens C3H9N. 2(3)+2-9+1=0 The peak at 3300 cm–1 tells us that the N is part of an amine NH2 2) Either 2-butanone, 2-methyl-2-nitropropane, 3-pentanone, 1nitropropane, nitroethane, or 2-bromopropane is responsible for the 1H NMR spectrum shown. Draw the structure of the responsible compound. (doublet and heptet) There are two signals in the spectra so we can eliminate 2-butanone, 2-methyl-2-nitropropane and 1-nitropropane because they have either more or less than 2 types of protons. Next you can eliminate 3-pentanone because it would have a triplet and a quartet which is not seen in the spectra. Also nitroethane can be eliminated because it would have a doublet and a quartet. While the answer is 2-bromopropane which has a doublet and a heptet. Br 3) Either 2-butanone, 2-methyl-2-nitropropane, 3-pentanone, 1nitropropane, nitroethane, or 2-bromopropane is responsible for the 1H NMR spectrum shown. Draw the structure of the responsible compound. (quartet, singlet and a triplet) Because there are 3 signals it is either 2-butanone or 1nitropropane. 1-nitropropane should have a doublet, a quartet and a triplet While our answer, 2-butanone should have a singlet, a quartet and a triplet.. O O2N 4) The molecular formula of a compound is C6H12O. Determine the structure of the compound based on its molecular formula and its 13C NMR spectrum. (4 PEAKS) First 2(6)+2-12=2/2=1 so either a ring or double bond. No peak shows up in the double bond region, C=C or C=O. So that leaves a ring. Four peaks and with this structure we have 4 different types of carbon. OH 5) Identify the compound with molecular formula C3H5Cl3 that gives the following 13C NMR spectrum. (The resonance at 0 ppm is due to the TMS standard, not the unknown.) First, 2(3)+2-5-3=0 so no double bonds or rings. Secondly there are 3 peaks, so 3 different kinds fo carbon. So that leaves two choices that are correct. Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl 6) What would the proton NMR peak look like for the indicated hydrogen? CH3 H3C CH O CH3 Because the two sets of adjacent protons are equivalent this peak would follow the n+1 rule and be a septet. 7) What type of electromagnetic radiation is used in nuclear magnetic resonance? Radio waves 8) What is the most abundant peak in a mass spectrum called? Base peak 9) Using the MS and IR spectra attached (1A and 1B) propose the formula and structure of this compound. (106 and 108) MS shows a molecular ion peak at 106 and a M+2 peak at 108.. So 106-35=71 so 71/12=5 carbons so 71-60=11 hydrogens so C5H11Cl 2(5)+2-11-1=0 However, there is a carbonyl peak in the IR So need to add an oxygen. -CH4 gives C4H7ClO so 2(4)+2-7-1=2/2=1 So this is taken by the C=O bond. One more thing, there is no peak at 2750 so no aldehyde, our carbonyl is a ketone O O O Cl Cl Cl The first one can be eliminated because of the base peak at 43 in the MS, a loss of 63 accounts for the loss of a –C2H4Cl group. 10) What is the major product of the following reaction? HBr peroxide H Br Br Br Br 11) What is the major product of the following reaction? Br2 CCl4 Br Br Br Br Br Br 12) What is the major product of the following reaction? HBr H H Br Br Br 8) What alkene should be used to synthesize the following alkyl bromide? Br H + Br Br 9) What alkene, when allowed to react with HBr, would produce the following alkyl bromide? (There is more than one correct answer.) H Br Br Br 10) What five-carbon alkene will give the same, single product whether it reacts with HBr in the presence or the absence of a peroxide? Br H Br Br Br H Br Br Br 11) Draw the major product of the following reaction, including its stereochemistry. (Use squiggly bonds to indicate a reaction that is not stereoselective.) Assume only one equivalent of the reagent is available to react with the substrate. HBr H Br Br Br 12) Draw the major product of the following reaction, including its stereochemistry. (Use squiggly bonds to indicate a reaction that is not stereoselective.) Assume only one equivalent of the reagent is available to react with the substrate. HBr H Br Br Br 13) Br Br H Br Br + Br 14) Br H Br Br 15) NBS hv Br H Br Br Br + Br