Cultural Competency - The Raymond John Wean Foundation
advertisement

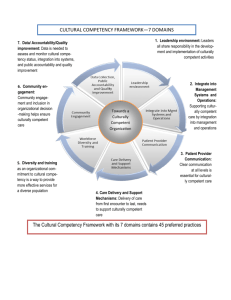
Building A Culturally Competent Framework Through: Diversity, Equity, and Inclusivity Presenter: YVONNE MATHIS, M.B.A. PRESIDENT/CEO THE MATHIS GROUP, LLC September 18, 2014 8th Annual Nonprofit Summit: Sharing Ideas, Inspiring Action Sponsored By: The Raymond John Wean Foundation Workshop Objectives… Participants will gain a better understanding of the meaning of diversity/inclusion and equity. 2. Participants will gain a better understanding of cultural competency. 3. Participants will learn that when embraced collectively, diversity/inclusion and equity comprise the “Action Took Kit” necessary to build a level playing field and culturally competent non-profit organization. 1. An Interactive Participant Activity … The Diversity “Is” Letter Game 1. Participants will use the Diversity Letter Game handout to complete this activity. 2. Participants will jot down as many words they can come up with from each letter in the word Diversity. 3. Participants will have an opportunity to share the words they chose for each letter with the entire group. 4. Participants will have 5 minutes to complete this activity. D I V E R S I T Y Diversity Is … Any dimension that can be used to differentiate groups and people from one another. Showing respect for and appreciation of differences in ethnicity, gender, age, national origin, disability, sexual orientation, education, and religion. Common Definitions of Diversity… “The individual qualities characteristics, customs, values and beliefs that are products of our background and which distinguish each of us as unique.” “The mosaic of people who bring a variety of backgrounds, styles, perspectives, values and beliefs as assets to the groups and organizations with which they interact.” An Organizational Diversity Definition … “The collective mixture of differences and similarities that includes individual and organizational characteristics, values, beliefs, experiences, backgrounds, preferences, and behaviors.” Dimensions of Diversity … Visible Diversity Traits Skin color Gender Physical Abilities Religion Marital Status Culture Personality Behaviors Body Size/Type Parental Status Ethnicity Invisible Diversity Traits Physical Traits Age Beliefs Socio-economic Status Values Education Communication Style Work Background Sexual Orientation Habits Geographic Location Thinking Styles Military Experience Native born/non native Level in Organization 7 The Three Dimensions of Diversity … WHAT DIVERSITY LOOKS LIKE … Diversity Is Not … Equal Employment Opportunity (EEO) Affirmative Action (AA) Compliance Driven Short-Term EEO/AA LAWS … Equal Pay Act of 1963 Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967 (ADEA), as amended Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) Distinction Between EEO, Affirmative Action and Diversity & Inclusion … Equal Employment Opportunity The enforcement of statutes to prevent employment discrimination. Affirmative Action Diversity & Inclusion The effort to achieve parity in the workforce through outreach and eliminating barriers in hiring. Leveraging differences in the workforce and services if offers to achieve better results. Equal Employment Opportunity Eliminates discrimination in human resources policies and practices. Provides equal access and opportunity – no one excluded from participation. Legally mandated Diversity Affirmative Action Level Playing Field Inclusive of Diverse productive workforce all groups More equitable and accessible Focuses on work environment developing an Inclusive environment where environment all employees valued that maximizes Work environment free the potential of from discrimination. all employees by valuing diversity interpersonally and institutionally. Business necessity given workforce trends. Broader than ethnicity, race, and gender. Not legally mandated. Targets outreach to underutilized groups. Helps to prevent discrimination. Measures good faith efforts in making affirmative action progress for minorities and women. Legally mandated Inclusion Is … The state of being valued, respected, and supported. About focusing on the needs of every individual and ensuring the right conditions are in place for each person to achieve his or her full potential. It should be reflected in an organization’s culture, practices, and relationships that are in place to support a diverse workforce and the clients it serves. Organizational Inclusion … Equity of Practices Organizational Culture Voice & Participation Extent to which the organization provides fair and equitable treatment to all employees and groups. Extent to which culture avoids assimilationist strategies and is open to learning from different and non-traditional sources. Extent to which the organization draws upon diverse sources of knowledge and experience for planning and operations. Benefits of Organizational Diversity & Inclusion … Improved understanding of those you work for, with, and around. Creates a work environment that allows everyone to reach their full potential. Provides multiple perspectives on problem solving. Better performance outcomes. Increases employee productivity. Increased retention rates. Boosts employee morale. Improved customer relations. Reduces complaints and grievances. It’s the right thing to do! How Can Managers Promote Diversity & Inclusion? … Lead employees by example; respect people and differences in the workplace and with clients you serve. Create a welcoming, inclusive environment in which to conduct business and meet with clients. Incorporate diversity in policies, strategic plans, operational procedures. Learn and practice early conflict resolution strategies. Practice regular, effective, and open communication; empower your employees; requires trust. Demonstrate executive commitment to diversity on an ongoing and regular basis. Walk the talk. Culture Is… The integrated patterns of the human behavior of a racial ethnic, religious or social group that include: Language Thoughts Communications Actions Customs Beliefs Values Institutions All Communication is Filtered Through Individual Cultural Perspective … Age National origin Race Sexual orientation Religion Disability Gender Education Work role/experience Personality Customs Geographic location Functional discipline Languages used Values Communication style Work Style Learning style Economic status Family situation Military experience Philosophical perspective A New Metaphor for American Culture … The “melting pot” theory of American society has evolved, instead consider a vegetable soup metaphor. You can easily identify and taste the unique flavors of the individual parts. Members of various cultural groups may not want to be assimilated, they want their tastes, looks and texture to remain whole. To reap the business benefits of diversity, you must employ inclusive work, communications, and outreach strategies. Organizational Culture … Refers to the values, norms, beliefs, and practices that characterize the functioning of a particular institution. Organizational Culture … The expression of an organization’s collective values, beliefs, and behaviors. Key Questions 1. Do staff, volunteers, or program participants “check their individual identities at the door?” 2. What’s wrong with just being “colorblind” or “gender-blind” or whateverkind of blind? 3. Does the “way we’ve always done it” close out contributions from staff, volunteers, program participants and community partners? 4. Is there some way you “ought to be” in order to fit in the association and its programs? Impediments to Cross-Cultural Communication … Irrational Assumptions Misunderstanding Prejudice Fear Cultural Competency Is… The ability to respond effectively and appropriately to different cultural/generational contexts in the workplace. Common Definitions of Cultural Competency… “The ability of organizations and systems to function effectively in cross-cultural situations.” “Cultural competency is an engaging, life-long journey of expanding your horizons, thinking critically about power and oppression, and behaving appropriately.” Cultural Competency… Respect others’ opinions. Acknowledge cultural/ generational differences and historical injustices without becoming defensive. Be open to learning about other cultures and ideas. Give others the benefit of the doubt in a dispute. Seek first to understand others’ point of views; then to be understood. Don’t stereotype. Don’t judge others by your own cultural standards. Don’t assume your culture’s way is the only way. Don’t talk down to anyone; communicate effectively. Cultural Competency… To truly describe how organizations function in culturally specific ways, we must broaden our definition of culture. Many demographic groups may have their own specific culture. Culture can include norms, language, slang, symbols, music, behaviors, the meaning of certain behavior, and patterns of interaction or exchange. These behaviors and practices are distinct from those of the dominant culture. Consequently, the term culture can refer to any subpopulation group that identifies itself as different from the dominant culture: persons with disabilities, gay men & lesbians, the Amish, goths, nudists, etc. Cultural Competency… Organizations become culturally competent when: They have organization structures that foster equity in resource sharing, program development, and administration. Recruit people from a diversity of ethnic backgrounds. Provide on-going training and education about race and cultural issues (for clients and staff). Plan cultural and social activities that are culturally appropriate and inclusive of all organization participants. Cultural Competency … Cultural Competency should occur in at least 4 Levels in organizations: 1. 2. 3. 4. Individuals Management Staff (commitment of organizational leaders) Organization as a whole Linkages between the organization and its external environment (local community; service users; other organizations; political system). Cultural Competency … How it can be carried out in your organizations Action Tool Kit For Organizations … LEADERSHIP COMMITMENT: Communicate and practice commitment to diversity inclusion, and cultural competency often. Reinforce diverse work and employment practices, including diversity of thought. Practice constructive conflict management. Educate the workforce on the business value of diversity, inclusion and the need to be culturally competent. Mentor and coach culturally diverse employees. Action Tool Kit For Organizations … LEADERSHIP COMMITMENT … Explicit commitment to diversity and empowerment among organizational leaders. A strategic plan to increase cultural competency. Diversity hiring. On-going efforts to maintain a diverse workforce. Recognition of issues in the organization related to the interaction of power/status and gender/culture. (For example, staff members may be assigned a mentor). Staff training in cultural competency. Evaluating the implementation of the cultural competency plan as well as the outcomes produced. Action Tool Kit For Organizations … LEADERSHIP COMMITMENT: Acknowledge and accept differences in cognitive, behavioral, philosophical, social, and communicative styles that arise from different cultural generational contexts. Be role models for staff. Seek to understand; ask for clarification or reasons for the behavior. Communicate policies, procedures clearly to employees if you are a manager. Action Tool Kit For Organizations … STAFF COMMITMENT: Practice positive, constructive work habits in the workplace; work cooperatively towards a common goal. Live up to the social contract; contribute to your fullest potential; strive for excellence. Recognize and respect others and their individuality. Think before you speak and be sensitive to others. Talk about your differences and ask tactful questions about how people want to be treated. Eliminate stereotypes and generalizations. Action Tool Kit For Organizations … ORGANIZATIONAL COMMITMENT … Have a cultural competency plan Form advisory boards with diverse members. Provide applications and other materials in different languages and Braille; pre-test material to make sure it’s usable. Provide translation services (including sign language). Provide culturally acceptable treatments. Providing cultural competency training. Make sure service providers have specialized assessment and treatment skills needed to treat diverse clients (ethnicity and sexual orientation). Action Tool Kit For Organizations … ORGANIZATIONAL COMMITMENT … Recruitment outreach efforts should target a wide variety of academic, professional and community organizations for the most talented and qualified persons in culturally diverse groups. Action Tool Kit For Organizations … ORGANIZATIONAL COMMITMENT … Make efforts to use the following methods for finding out about the cultural backgrounds of service users: Cultural guides Establish linkages with community leaders Staff should attend cultural events in the community The organization can sponsor culturally specific events or multicultural gatherings. Hiring and retaining a diverse workforce Provide on-going staff training Involving service users in organization governance, program planning, and evaluation. Service user controlled service delivery (for example, ethnic social service agencies or feminist organizations). An Ending Quote To Ponder … “You must be the change you wish to see in the world.” Mahatma Gandhi