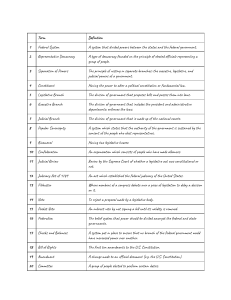
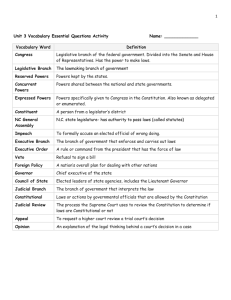
GOVERNMENT VOCABULARY WORDS Terms Definitions
advertisement
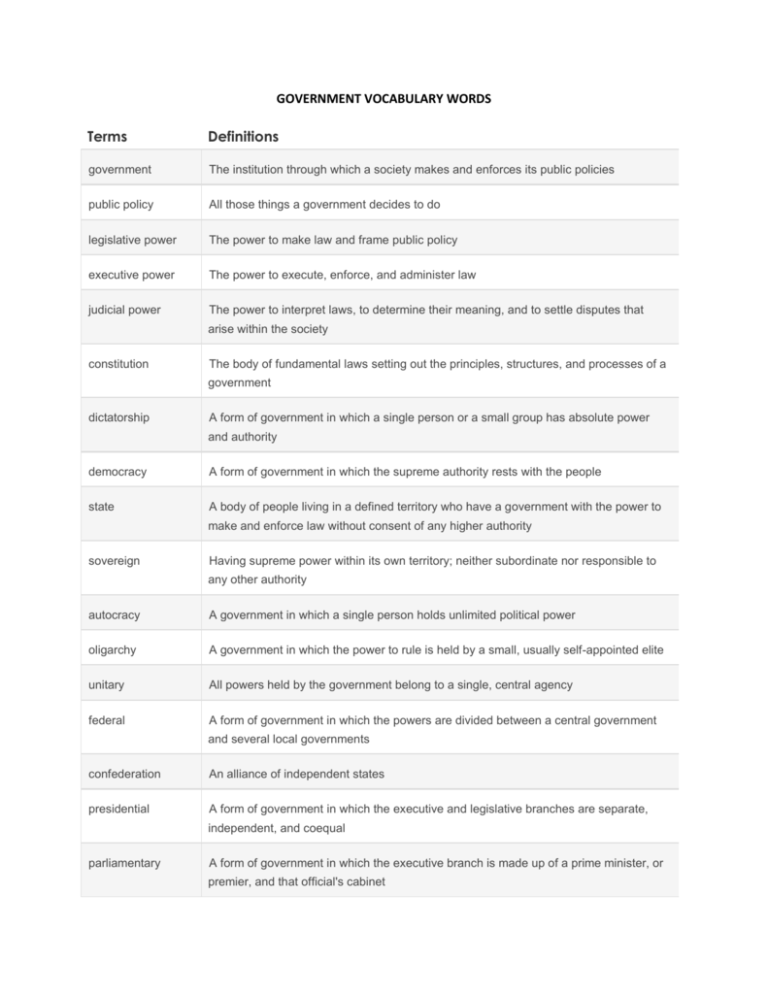
GOVERNMENT VOCABULARY WORDS Terms Definitions government The institution through which a society makes and enforces its public policies public policy All those things a government decides to do legislative power The power to make law and frame public policy executive power The power to execute, enforce, and administer law judicial power The power to interpret laws, to determine their meaning, and to settle disputes that arise within the society constitution The body of fundamental laws setting out the principles, structures, and processes of a government dictatorship A form of government in which a single person or a small group has absolute power and authority democracy A form of government in which the supreme authority rests with the people state A body of people living in a defined territory who have a government with the power to make and enforce law without consent of any higher authority sovereign Having supreme power within its own territory; neither subordinate nor responsible to any other authority autocracy A government in which a single person holds unlimited political power oligarchy A government in which the power to rule is held by a small, usually self-appointed elite unitary All powers held by the government belong to a single, central agency federal A form of government in which the powers are divided between a central government and several local governments confederation presidential An alliance of independent states A form of government in which the executive and legislative branches are separate, independent, and coequal parliamentary A form of government in which the executive branch is made up of a prime minister, or premier, and that official's cabinet compromise An adjustment of opposing principles or systems by modifying some aspect of each mixed economy An economy in which private enterprise exists in combination with a considerable amount of government regulation and promotion free enterprise An economic system characterized by private or corporate ownership of capital goods; and determined in a free market checks and balances a system in which each branch of government has some power over the others collective action problem a situation in which the members of a group would benefit by working together to produce some outcome, but each individual is better off refusing to cooperate and reaping benefits from those who do the work conservative one side of the ideological spectrum defined by support for lower taxes, a free market, and a more limited government; generally associated with Republicans culture wars political conflict in the united states between "red-state" Americans who tend to have strong religious beliefs and "blue- state" Americans who tend to be more secular economic individualism the autonomy of individuals to manage their own financial decisions without government interference factions groups of like- minded people who try to influence government. American government is set up to avoid domination by any one of these groups federalism the division of power across the local, state and national levels of government free market an economic system based on competition among businesses without government interference free rider problems the incentive to benefit from others' work without making a contribution, which leads individuals in a collective action situation to refuse to work together government the system for implementing decisions made through the political process ideology a cohesive set of ideas and beliefs used to organize and evaluate the political world liberal one side of the ideological spectrum defined by support for stronger government programs and more market regulation; generally associate with the Democrats libertarians those who prefer very limited government and therefore tend to be conservative on issues such as welfare policy, environmental policy, and public support for education, but liberal on issues of personal liberty such as free speech, abortion, and the legalization of drugs melting pot the idea that as different racial and ethnic groups come to America, they should assimilate into American culture, leaving their native languages, customs and traditions behind politics the process that determines what government does positive externalities benefits created by a public good that are shared by the primary consumer of the good and by society more generally public goods services, or actions, that once provided to one person, become available to everyone. Government is typically needed to provide public goods because they will be under-produced by the free market redistributive tax policies policies, generally favored by democratic politicians, that use taxation to attempt to create greater social equality separation of powers the division of government powers across the judicial, executive, and legislative branches