Heart & Circulatory System Exam Questions
advertisement
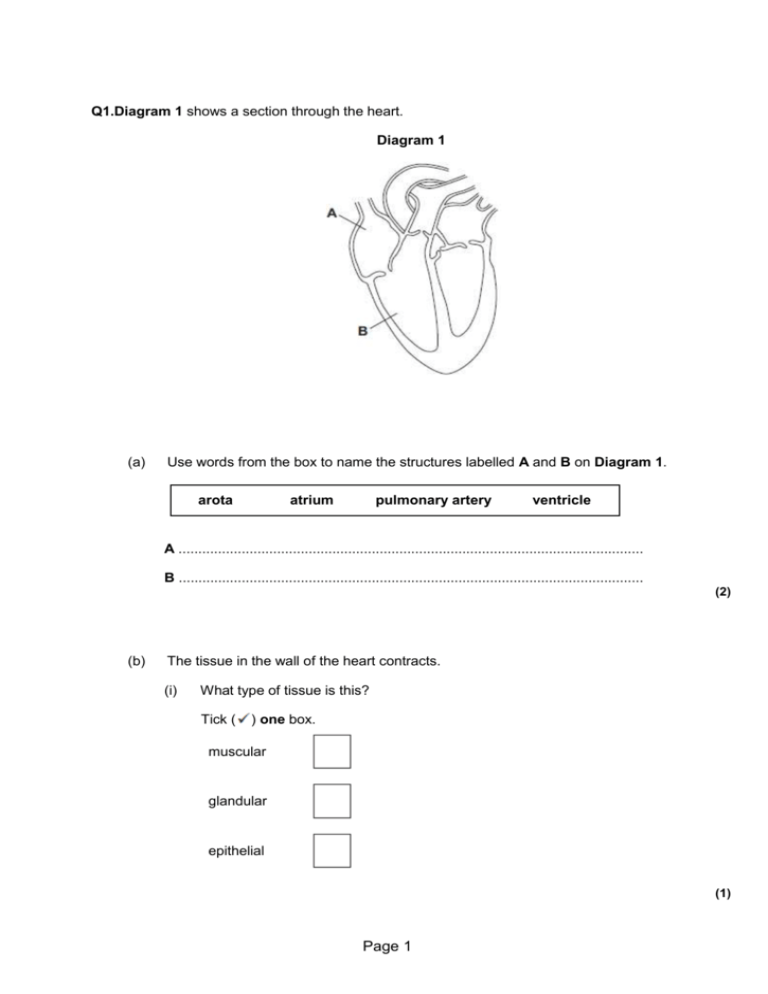
Q1.Diagram 1 shows a section through the heart. Diagram 1 (a) Use words from the box to name the structures labelled A and B on Diagram 1. arota atrium pulmonary artery ventricle A ...................................................................................................................... B ...................................................................................................................... (2) (b) The tissue in the wall of the heart contracts. (i) What type of tissue is this? Tick ( ) one box. muscular glandular epithelial (1) Page 1 (ii) What does the heart do when this tissue contracts? ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (1) (c) Draw arrows on Diagram 2 to complete the route taken by deoxygenated blood through the heart. Diagram 2 (2) (d) The graph shows the percentage (%) of adults in the UK who have coronary heart disease. Page 2 Age group (i) Look at the graph. Which group of people is most at risk of having coronary heart disease in the UK? ............................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Explain what happens to the heart in coronary heart disease. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (3) (Total 11 marks) Page 3 Q2.Diagram 1 shows a section through the heart. Diagram 1 (a) Use words from the box to label parts A, B, C and D. artery atrium capillary platelet vein ventricle (4) (b) Diagram 2 shows one treatment for a diseased coronary artery. Diagram 2 Page 4 © Nucleus Medical Art/Visuals Unlimited/Corbis (i) Name the treatment shown in Diagram 2. ............................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Explain how the treatment works. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (Total 7 marks) Q3. The diagram represents the human blood circulation system. Page 5 (a) A, B, C and D are blood vessels. (i) Give the letter of one blood vessel that is an artery. .................................... (1) (ii) Give the letter of one blood vessel that is a vein. .................................... (1) (b) A student pedalled an exercise cycle at constant speed for 5 minutes. The student’s heart rate was recorded at one-minute intervals during the exercise. The results are shown in the graph. Page 6 (i) What was the student’s heart rate before the exercise began? ................................................ per minute (1) (ii) How long was it before the student’s heart rate reached 124 beats per minute? ...................................................... .minutes (1) (c) Which of the following parts of the blood carries most oxygen? Draw a circle around one answer. plasma red blood cells white blood cells (1) (Total 5 marks) - Q4.The heart pumps the blood around the body. This causes blood to leave the heart at Page 7 high pressure. The graph shows blood pressure measurements for a person at rest. The blood pressure was measured in an artery and in a vein. Time in seconds (a) Which blood vessel, A or B, is the artery? Blood vessel .................... Give two reasons for your answer. Reason 1 ....................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................ Reason 2 ....................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................ (2) Page 8 (b) Use information from the graph to answer these questions. (i) How many times did the heart beat in 15 seconds? ............................. (1) (ii) Use your answer from part (b)(i) to calculate the person’s heart rate per minute. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... Heart rate = .................... beats per minute (1) (c) During exercise, the heart rate increases. The increased heart rate supplies useful substances to the muscles at a faster rate. Name two useful substances that must be supplied to the muscles at a faster rate during exercise. 1 ........................................................................................................................ 2 ........................................................................................................................ (2) (Total 6 marks) Q5.Gas exchange takes place in the lungs. The diagram shows an alveolus next to a blood capillary in a lung. The arrows show the movement of two gases, A and B. Page 9 (a) (i) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. diffusion. Gases A and B move by osmosis. respiration. (1) (ii) Gas A moves from the blood to the air in the lungs. Gas A is then breathed out. Name Gas A. ............................................................................................................... (1) (iii) Which cells in the blood carry Gas B? Draw a ring around the correct answer. platelets red blood cells white blood cells (1) (b) The average number of alveoli in each human lung is 280 million. The average surface area of 1 million alveoli is 0.25 m2. Calculate the total surface area of a human lung. ........................................................................................................................ Answer ...................................................................... m2 (2) (c) An athlete trains to run a marathon. The surface area of each of the athlete’s lungs has increased to 80 m2. Give one way in which this increase will help the athlete. ........................................................................................................................ Page 10 ........................................................................................................................ (1) (Total 6 marks) ## The following sentences are about the blood system. Choose words from the list in the box to complete these sentences. You may use a word once or not at all. diffuse raised lowered spread narrow one two wide Capillaries have thin walls which are ................................... .cell thick. This allows nutrients from digested food to .................................... through and reach the cells of organs. Capillaries are very ................................. .and so blood flow through an organ is slowed down and blood pressure is ........................................ . (Total 4 marks) Q7. Four leaves were removed from the same plant. Petroleum jelly (a waterproofing agent) was spread onto some of the leaves, as follows: Leaf A: on both surfaces Leaf B: on the lower surface only Leaf C: on the upper surface only Leaf D: none applied Each leaf was then placed in a separate beaker, as shown in diagram 1. Page 11 Diagram 1 Each beaker was weighed at intervals. The results are shown in the graph. (a) Give evidence from the graph in answering the following questions. (i) Which surface (upper or lower) loses water most rapidly? ............................. Evidence ........................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) Page 12 (ii) Is water lost from both surfaces of the leaf? .................................................... Evidence ........................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Diagram 2 shows the appearance of each surface of the leaf as seen through a microscope. Upper Surface of Leaf Lower Surface of Leaf Diagram 2 (i) Name space X and cell Y. X ................................................................... Y ................................................................... (2) (ii) Use information in diagram 2 to explain why the results are different for leaves B and C. ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Page 13 Q8. (a) The diagram shows a cereal crop. Complete spaces (i) and (ii). (2) (iii) What sort of weather may cause the cereal crop to wilt? ........................................................................................................................... (1) (b) Describe the process of transpiration in plants. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (3) Page 14 (Total 6 marks) Q9. A student removed three similar leaves from a plant. The student spread petroleum jelly (a waterproofing substance) on some of the leaves, as follows: Leaf A: on the lower surface Leaf B: on the upper surface Leaf C: none. The student placed each leaf in a separate beaker. He weighed each beaker at intervals. The results are shown in the table. Time in hours Mass of leaf + beaker in grams Leaf A Leaf B Leaf C 0 50.00 55.01 51.99 0 49.99 54.95 51.90 3 49.97 54.90 51.85 5 49.95 54.86 51.80 (a) Which leaf, A, B or C, lost most water? (1) (b) The diagram shows the appearance of the upper and lower surfaces of one of the leaves under a microscope. Upper surface of leaf Lower surface of leaf Page 15 (i) Name cell X. ........................................ (1) (ii) The petroleum jelly had a greater effect when it was spread on the lower surface than when it was spread on the upper surface. Use information from the diagram to explain why. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (Total 4 marks) Q10. Some students used the apparatus shown in the diagram to measure the rate of water uptake by a plant cutting. Page 16 The students set up the apparatus in three different conditions: • no wind at 15 °C • no wind at 25 °C • wind at 25 °C For each experiment, the students recorded the movement of the air bubble along the scale. (a) (i) Name the two variables that the students chose to change in these experiments. 1 ............................................................................................................ 2 ............................................................................................................ (2) (ii) It was important to use the same plant cutting each time to make these experiments fair. Explain why. ............................................................................................................... (1) (b) The graph shows the students’ results. Page 17 Which line on the graph, A, B or C, shows the results for each of the three different experiments? Write each of the letters A, B or C in the correct boxes in the table. Condition Letter No wind at 15 °C No wind at 25 °C Wind at 25 °C (2) (c) Water is lost from the leaves of the plant cutting. Name this process. Draw a ring around one answer. distillation respiration transpiration (1) (Total 6 marks) Page 18 Q11.Plants exchange substances with the environment. (a) Use words from the box to complete each sentence. alveoli phloem root hairs stomata storage organs villi xylem (i) Most water enters a plant through ............................................................................... (1) (ii) The water is transported up the stem to the leaves in the .......................................... (1) (iii) Carbon dioxide enters leaves through ......................................................................... (1) (iv) A leaf uses the carbon dioxide to produce sugars. Sugars are transported to ................................................................. through the ................................................................. . (2) (b) A student set up the apparatus shown in the diagram. At the start of the experiment both balances showed a mass of 180.0 g. Page 19 The diagram shows the reading on each balance 24 hours later. (i) Look at the mass shown on each balance. Calculate the difference between the two masses. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... Difference in mass = .................................................. g (1) (ii) Suggest an explanation for the difference between the two masses. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (Total 8 marks) Q12.Plants exchange substances with the environment. (a) Plant roots absorb water mainly by osmosis. Plant roots absorb ions mainly by active transport. Explain why roots need to use the two different methods to absorb water and ions. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... Page 20 ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (4) (b) What is meant by the transpiration stream? ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (3) (c) Students investigated the loss of water vapour from leaves. The students: • • cut some leaves off a plant measured the mass of these leaves every 30 minutes for 180 minutes. The graph shows the students’ results. Page 21 (i) The rate of mass loss in the first 30 minutes was 7 milligrams per gram of leaf per minute. Calculate the rate of mass loss between 30 minutes and 180 minutes. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... Rate of mass loss = .............................. milligrams per gram of leaf per minute (2) (ii) The rate of mass loss between 0 and 30 minutes was very different from the rate of mass loss between 30 and 180 minutes. Suggest an explanation for the difference between the two rates. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (Total 11 marks) Q13. The diagram shows human blood seen through a microscope. Page 22 Write the correct letter, A, B, C or D, next to each function. Function Part of blood A, B, C or D Transports oxygen Helps blood to clot at the site of a cut Transports urea (Total 3 marks) Q14. The diagram shows four parts of blood. Page 23 (a) Letter A Complete the table to give the name and function of the parts labelled A, B and C. Name ...................................... Function ...................................................................... ...................................................................... B ...................................... ...................................................................... ...................................................................... C ...................................... ...................................................................... ...................................................................... (6) (b) Red blood cells contain haemoglobin. Explain how this enables red blood cells to pick up oxygen from the alveoli and release it to cells in other parts of the body. .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... .................................................................................................................................... (4) (Total 10 marks) Q15. (a) Explain, as fully as you can, how the body’s white blood cells respond to infections. Page 24 ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (4) (b) Describe, in as much detail you can, how one method of immunisation protects us from a named disease. Name of disease ......................................................................................................... How immunisation protects us from this disease. ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... ..................................................................................................................................... (3) (Total 7 marks) Page 25 M1.(a) A - atrium ignore references to right / left 1 B - ventricle 1 (b) (i) muscular 1 (ii) push blood accept pump / force 1 (c) arrows approx as indicated 1 arrow(s) showing flow from A to B from B out / up / to artery 1 (d) (i) male 1 65 and over 1 (ii) fatty deposits / material in (coronary) arteries allow correct points made about heart attacks 1 narrows / blocks / reduces flow Page 26 1 decreases oxygen supply (to heart muscle) 1 [11] M2.(a) A artery allow aorta 1 B ventricle ignore references to left and right 1 C atrium ignore references to left and right allow atria 1 D vein allow vena cava 1 (b) (i) stent 1 (ii) keeps (artery) open 1 so (more) blood can flow through allow blood can flow (more) easily ignore ref to blood clots 1 [7] Page 27 M3. (a) (i) A or C allow lower case 1 (ii) B or D allow lower case 1 (b) (i) 60 1 (ii) 4 1 (c) red blood cells 1 [5] M4.(a) A no mark - can be specified in reason part if B given - no marks throughout if unspecified + 2 good reasons = 1 mark high(er) pressure in A allow opposite for B do not accept ‘zero pressure’ for B pulse / described in A accept fluctuates / ‘changes’ allow reference to beats / beating ignore reference to artery pumping 2 (b) (i) 17 1 (ii) 68 accept correct answer from student’s (b)(i) × 4 1 Page 28 (c) oxygen / oxygenated blood allow adrenaline ignore air glucose / sugar extra wrong answer cancels - eg sucrose / starch / glycogen / glucagon / water allow fructose ignore energy ignore food 2 [6] M5.(a) (i) diffusion 1 (ii) carbon dioxide accept CO2 / CO2 do not accept CO2 1 (iii) red blood cells 1 (b) 70 if no / incorrect answer then 70 000 000 or 280 x 0.25 gains 1 mark ignore doubling the answer 2 (c) allows more gas / oxygen / CO2 (exchange) do not accept air 1 [6] Page 29 M6. one; 1 diffuse; 1 narrow; 1 lowered; 1 [4] M7. (a) (i) lower – B loses less (water / mass) than C or described in terms of petroleum jelly accept converse re Leaf C 1 (ii) yes - B and C lose less than D or B and C lose more than A or D loses the most or A loses the least do not accept just ‘all leaves lose some weight’ 1 (b) (i) X = stoma accept stomata / stomatal pore do not accept air space 1 Y = guard cell 1 (ii) petroleum jelly blocks stomata / pores or petroleum jelly prevents water loss or petroleum jelly waterproofs allow pores are blocked in B 1 water (mainly) lost via stomata / pores / X or stomata on lower surface only 1 [6] Page 30 M8. (a) (i) photosynthesis 1 (ii) respiration do not credit combustion do not credit decay 1 (iii) dry accept hot or windy or drought 1 (b) any three from * evaporation (of water) or loss of water vapour * (mostly) from the leaf / leaves do not credit incorrect reference to leaves * through the stomata accept through each stoma accept through the stomas(sic) * causing a pull or causing an increase in osmotic potential (at the top of the plant) or causing an increase in water potential (at the top of the plant) or causing a decrease in osmotic pressure (at the top of the plant) * (so that) water moves up (through the plant) do not credit water vapour moves up through the plant * as the transpiration stream * water enters through roots (and goes up plants) 3 [6] Page 31 M9. (a) C 1 (b) (i) guard (cell) 1 (ii) temperature water movement / transpiration through stomata / pores / holes /(region) X or petroleum jelly blocks / covers stomata / pores / holes / X 1 stomata / pores / holes / X found on lower surface 1 [4] M10. (a) (i) wind 1 temperature answers in either order ignore weather 1 (ii) different plants have different sizes / different numbers of leaves / different sizes of leaves / different plants take up different amounts of water ignore reference to validity allow different plants need Page 32 different amounts of water 1 (b) in table, in sequence: C all 3 correct = 2 marks B A all 3 correct = 2 marks 2 correct = 1 mark 0 or 1 correct = 0 mark 2 (c) transpiration 1 [6] M11.(a) (i) root hairs if clear which word then allow 1 (ii) xylem if clear which word then allow 1 (iii) stomata if clear which word then allow 1 (iv) storage organs in this order 1 phloem 1 Page 33 (b) (i) 23.2 1 (ii) loss of water (from flask with plant) from leaves / plant 1 via transpiration / via evaporation if no other marks allow used in photosynthesis for one mark 1 [8] M12.(a) solution in soil is more dilute (than in root cells) concentration of water higher in the soil (than in root cells) 1 so water moves from the dilute to the more concentrated region so water moves down (its) concentration gradient or water moves from a high concentration of water to a lower concentration 1 concentration of ions in soil less (than that in root cells) 1 so energy needed to move ions or ions are moved against concentration gradient the direction of the concentration gradient must be expressed clearly accept correct reference to water potential or to concentrations of water 1 (b) any three from: Page 34 • movement of water from roots / root hairs (up stem) • via xylem • to the leaves • (water) evaporates • via stomata 3 (c) (i) 0.67/0.7 accept 0.66, 0.6666666... or ⅔ or 0.6 correct answer gains 2 marks with or without working if answer incorrect allow evidence of do not accept 0.6 or 0.70 for 1 mark 2 (ii) during the first 30 minutes any one from: • it was warmer • it was windier • it was less humid • there was more water (vapour) in the leaves 1 so there was more evaporation ignore ‘water loss’ or stomata open during first 30 minutes or closed after 30 minutes (1) so faster (rate of) evaporation in first 30 min or reducing (rate of) evaporation after 30 min (1) 1 [11] M13. B Page 35 1 C 1 A 1 [3] M14. (a) A white blood cell/leucocytes / phagocytes / lymphocytes SEPARATE MARKING POINTS 1 make/contain antibodies/antitoxins or destroy/engulf/kill bacteria do not accept fight infection do not accept fight disease 1 B platelets 1 help clot the blood do not accept stick together do not accept from scabs 1 C plasma 1 carries/transports all the cells/digested food/waste products/hormones/carbon dioxide/platelets/dissolved minerals/antibodies/antitoxins/water allows blood to flow 1 (b) any four from: (oxygen) diffuses 1 has affinity for/combines with oxygen / forms oxy-haemoglobin Page 36 do not accept absorbed 1 in areas of high oxygen concentration n.b. ‘pick up oxygen’ is stem of question 1 in conditions of low oxygen concentration it breaks down and releases the oxygen low oxygen concentration can be implied e.g. active muscles 1 [10] M15. (a) engulf bacteria produce antibodies produce antitoxins effect of antibodies/antitoxins for 1 mark each 4 (b) method must be related to disease dead/weakened microbes (as appropriate) stimulate antibody production antibody production rapid if microbe enters again for 1 mark each 3 [7] Page 37