Primary Economic Activity
advertisement

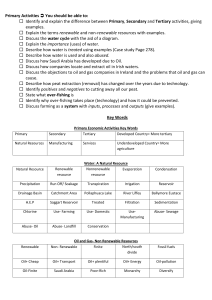
Primary Economic Activity Taking resources from the land or the sea Economic Activity • Economic Activity can be divided into 3 categories. These are; • • • 1. Primary Economic Activity 2. Secondary Economic Activity 3. Tertiary Economic Activity • What is Primary Economic Activity? • Primary economic activity involves taking natural resources from the land or the sea. • • Q. What is a natural resource? Q. What natural resources are available from the land or the sea? Primary Economic Activity • We now know that Primary economic activity involves taking natural resources from the land or the sea. We take resources from the land and the sea in the following ways; • • • • • 1. Farming 2. Fishing 3. Forestry 4. Mining 5. Quarrying • Q. Many people work in the primary economic sector. List some jobs that people do in the primary economic sector. Primary Economic Activities Primary Economic Activity • In developing (poorer) countries many people are employed in primary economic activities. • Q. Why do you think this is? • In developed (rich) countries less people are employed in primary economic activities. • Q. Why do you think this is? Natural Resources • Natural resources are things provided by nature which are useful to people. • Q. Make a list of things provided by nature which are useful to people. Natural Resources Natural Resources Types of Natural Resources • There are 2 types of natural resources. – 1. Renewable resources – 2. Non-renewable resources Q. How do you think these types of resources are different? Renewable Resources • Renewable resources are resources that can be used over and over again. With careful management, they will not run out. • For example, if we cut down trees to make wood, we can plant new trees to take their place. • Q. Can you think of any other examples? • Other examples include water, fish, plants/crops. • Q. Explain why these examples are renewable resources. Non-Renewable Resources • Non-renewable resources are resources that can only be used once. Each time such resources are used less of that resource is left for the future. Non-renewable resources will eventually run out. • Q. Can you think of any examples of non-renewable resources? • Examples include coal, oil, gas, and peat. • Q. Explain why these examples are non renewable resources. Water – A Renewable Natural Resource The Water Cycle Evaporation Condensation Run Off Precipitation Water – A Renewable Natural Resource • More than 2/3 of the earth is covered in water. However, only a very small amount of the water on our planet is fresh water. • • Fresh water is what we need for drinking, washing, and cooking. Fresh water is also needed for irrigating farmland and for making things in factories. In some countries, almost everyone has access to safe drinking water. However, in other countries many people do not have access to safe drinking water. • • Q. List 5 countries where everyone has access to safe drinking water. Q. List 5 countries where less than 33% of people have access to safe drinking water. Water Use Water Use and Wealth • People who live in wealthy countries use much more water than people who live in poor countries. • Q. Why do you think this is? • Q. In Ireland we do not have to pay for the water we use at home. Is this a good thing? How do we get our water? Water Supply Water Supply in Dublin • Most of Dublin’s water comes from Co. Wicklow. • A number of reservoirs have been built to store water which is then pumped to houses in Co. Dublin • Q. Why is Wicklow a good location to get the water needed for people living in Dublin? Water Quality • Water can be polluted by farming, and industrial activity. • Q. Why is the river quality in the Northwest of Ireland better than in the East of Ireland? • Q. What can be done to help ensure that water quality is improved in the East of Ireland? Water Contamination Toxic Waste in the Food Chain Fish eaten By humans Factory Spill or Run Off from Farms Chemical enters the river or the sea Plankton eaten By fish Chemicals eaten By plankton Water Conservation – Saving Water • Water is an important natural resource. It is important that we do not waste water. • Q. Estimate how much water you use per day. • Q. Discuss things you could do to conserve water. Irrigation Projects • Crops need water to grow. They normally get the water when it rains. • In places where there is little rainfall, irrigation is needed. • Irrigation means pumping water from a river or lake to farmland. The water is then sprinkled over the crops. • Q. Why is Irrigation common in the South of France and not in Ireland? Irrigation in France Irrigation Egypt and the River Nile Oil – A Non-Renewable Resource Oil – A Non-Renewable Resource • Oil is a non-renewable resource. • Q. Why do you think oil is considered to be a non-renewable resource? • Oil is a very important source of energy in our world today. • Q. How is oil used as an energy source? • Oil is a non-renewable resource. Therefore it is important that we try to conserve the oil we have. • Q. What can we do to help conserve the earth’s oil? Play the Game. www.willyoujoinus.com/energyville Oil in the Persian Gulf Countries with big Oil Reserves Oil as an Energy Source • Oil is one of many energy sources used in the world today. • Q. Which of the energy sources shown on the graph do you think is the best? Why? • Q. List one positive and one negative effect of using nuclear power. Oil Producing Countries • Which country in the world produces the most oil? • Which country in the world uses the most oil? • Explain how an oil discovery in a country can be a positive thing. • Explain how an oil discovery in a country can be a negative thing. • Name a country where oil has had a positive effect and one where oil has had a negative effect. The Price of Oil The price of oil can go up and down depending on demand. The Price of Oil - In 1973 oil was only $2 per barrel. - In July 2008 it was $147 per barrel. - In November 2008 it was only $47 per barrel. Q. Why did oil increase in price in the 1970’s? Q. Why did oil reach a record price of $147 a barrel in July 2008 and fall to $47 per barrel by November? Q. Explain why high oil prices is a bad thing for Irish people. The Real Price of Oil? The Real Price of Oil? Saudi Arabia – An Oil Producing Country • Saudi Arabia produces more oil than any other country in the world. • Since the 1930’s Saudi Arabia has changed from a country where most people lived in the desert to one of the wealthiest countries in the world. • Q. How has Saudi Arabia used it’s oil money to improve the lives of its citizens? • Q. Explain how large amounts of Saudi oil money has been poorly spent. Oil and Gas in Ireland • Unfortunately we have not yet found large deposits of oil or gas off the Irish coast. • However, there is much exploration occurring around our coastline. • Gas from Kinsale has been used to supply gas to Dublin and other cities. • Gas has also been discovered in the Corrib Gas Field. However, there has been lots of controversy regarding where this gas should be brought ashore. Oil Use in Ireland • Q. How much oil per person was used in Ireland in the year 2000. • Q. How much oil per person was used in other EU countries. • Q. Suggest some reasons why Irish people use more oil than other European people. Exploitation of Peat • Peat is a non-renewable resource which is found in Ireland. • Peat is cut from bogs, either blanket bogs or raised bogs. • Q. List two differences between the two types of bogs. Blanket Bog • Blanket bogs are found mainly in the western counties in Ireland. • They are shallow bogs. • Their average depth is 2.6 metres. Raised Bogs • Raised Bogs occur mainly in the central plain of Ireland. • They are very deep bogs. • Their depth can be over 10 metres. Exploitation of Peat • Peat is exploited in 4 phases. Cutting Turf: For about 1,000 years turf has been cut by hand in Ireland using a peat spade called a Sleán. Commercial Turf Cutting: • Bord na Mona, the company which exploits peat in Ireland uses many large machines. • 1. A Grader: A machine like a bulldozer used to level the surface of bog. • 2. A Miller: A machine used to scrape peat from the surface of the bog. What is peat used for? • • • Q. Peat is mainly used for…? Q. Why is it convenient for Ireland to use peat to generate electricity? Q. What else is peat used for? Sources of Electricity in Ireland • • • Q. What % of Ireland’s electricity was made from peat in 1978? Q. What % of Ireland’s electricity was made from peat in 2002? Q. List two forms of electricity production which have increased since 1978. The Importance of Peat • Bord na Mona is the name of the company which exploits peat in Ireland. • Peat is very important to our economy. - Bord na Mona employs 2000 people. Many of these jobs are in regions where job creation is difficult. Peat is used to generate electricity. Peat is exported to other EU countries. - Renewable Energy Sources • We know that oil is a non-renewable resource. So are most of the other ways we get energy. Coal, peat, gas etc. • Therefore, we need to both conserve energy and also to try to make more use of renewable energy sources. There are many different types of renewable energy sources. • Q. Can you name any renewable energy sources? • Examples include; • • • • • 1. Hydroelectricity 2. Solar power 3. Geothermal energy 4. Tidal energy 5. Wind Energy • Q. Which of these renewable energy sources could we make use of in Ireland? Renewable Energy Sources Hydroelectric Power (HEP) • Hydroelectric Power is created using the power of falling water. A dam is built across a river to trap the water. When part of the dam is opened the water rushes in. The water is used to turn a turbine which creates electricity Hydroelectric Power (HEP) Hydroelectric Power (HEP) Hydroelectric Power (HEP) Solar Energy • Solar energy uses the power of the sun to create electricity. • Heat and light from the sun are captured by solar cells. • The cells convert the heat and light to electricity. Solar Energy Solar Power Geothermal Energy • Geothermal energy works by pumping water down deep into the earth’s crust. • The water is then heated by hot rocks in the earth’s crust. • The heated water is pumped back to the surface where it can be used to heat homes. • The hot water can also be converted to steam which is used to turn turbines to create electricity. Geothermal Energy Geothermal Energy Tidal Energy • Tidal energy uses the power of the rising and falling tides to turn turbines. This creates electricity. Tidal Power Tidal Power Wind Energy • Wind power is becoming a very popular source of renewable energy. • Wind power has been used for a long time. The Dutch built windmills to pump out the water when they were creating their Polders. • Modern wind turbines are very big. They are usually grouped together in what is known as a wind farm. Wind Energy • Wind farms are increasingly being built out at sea. This is because it is a windy location and it prevents visual pollution on the landscape. • Smaller wind turbines are also available. They can be put on top of your house or school to generate renewable energy. Wind Power • • • Q. Using evidence from the graph, explain how we know wind power is becoming more popular. Q. Why do you think wind power is becoming more popular? Q. ‘Ireland is an ideal place for wind farms’. Discuss. Fishing – Over Exploitation of a Resource • • • Fish are renewable resources. If we catch a fish and eat it, other fish will be born to replace it. However, in many parts of the world too many fish have been caught. The number of fish has gone down a lot. Q. People have always caught fish to eat. Why do you think that the problem of over fishing has arisen only recently? How do People Fish? How do People Fish? How do People Fish? Most fish are caught in the continental shelf. This means they are caught around the coast of the continents. Ireland’s Fishing Ports • Ireland has many fishing ports. • Fishing is extremely important to many of these small fishing villages. • Fishing has been carried out in these areas for generations. Over Fishing • • Over fishing has occurred because fishermen are using large fishing nets to catch huge numbers of fish. They are also using what are called Factory Ships which can stay at sea for long periods. They use high tech radar and sonar to find the fish. Types of Fish and where they are caught Sustainable Exploitation of Fish • • Many types of fish are now endangered because of over fishing. Governments and the EU are trying to limit the amount of fish being caught. • They have taken the following steps; • • • • • • 1. Made conservation zones around some countries. 2. Excluded foreign fishing boats from fishing in Irish waters. 3. Reduce the number of fishing boats. 4. Introduced yearly quotas for fish catches. 5. Banned the fishing of some endangered species. 6. Made the fishing season shorter for some types of fish. Q. Do you think these steps are a positive thing? Why? Q. Many people are against the quotas. Explain why it may be difficult for some people to accept these changes. The Irish Box • The Irish Box was a rich fishing ground. • In 2003 it was made smaller when a Conservation Zone was made. • Strict quotas have been implemented in this zone to help fish stocks to recover. Fish Farms • Fish farming is becoming more and more popular. Salmon are grown in many fish farms around the coast of Ireland. Q. What has happened to the value of farmed fish since 1998? Q. Why do you think fish farming is becoming more popular? Farming • Farming is an example of a primary economic activity. There are many different types of farming which produce different types of produce. Examples include; 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Dairy farming Cereal farming (Tillage) Market gardening Beef farming Mixed farming Work on the Farm Percentage of People Working in Farming How do People Farm? How do People Farm? How do People Farm? How do People Farm?