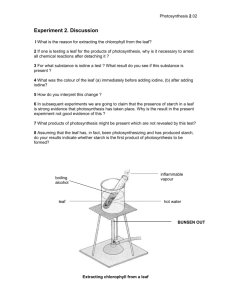
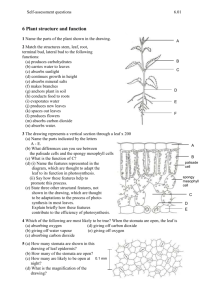
3-3 Photosynthesis
advertisement

How is active transport different from passive transport? Chapter 3 Section 3 Where does the energy come from? Page 86 To write the chemical formula for photosynthesis. To list the raw materials and end products for photosynthesis. To describe what happens during the process of photosynthesis. Photo means light Synthesis means putting together Process that plants use to convert the sun’s energy into food Takes place in the chloroplasts in leaves of the plants The sun provides energy for all living things either directly or indirectly. Autotrophs are organisms that make their own food through the process of photosynthesis. Heterotrophs are organisms that need to eat. Light is required The energy of the sunlight is captured by the chlorophyll in the chloroplast http://www.osovo.com/diagram/photosynthesisdiagrams.htm Light is not required The captured energy is converted into the energy found in food Raw materials needed are carbon dioxide and water Produces glucose and oxygen Also known as the Calvin cycle http://faculty.stcc.edu/nash/cells.htm Looking at Pigments page 89 Place a sprig of elodea in a test tube and count the bubbles that are released in 1 minute when inside. Take your test tube out and count the bubbles that are released in 1 minute. Is there a difference? What do you think makes the difference? What does this difference mean? Stomata are the guard cells that allow gases to enter and leave a leaf. They are located on the underside of the leaf. Scanning electron micrograph of Equisetum (horsetail or scouring rush) epidermis. Note the oval stomatal apparatuses in the center of the stem. The above image is from http://www.mcs.csuhayward.edu/sem/images/horsel4.gif. http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookPLANTANAT.html Stomatal apparatus as seen on a leaf epidermal peel of corn. The above image is from gopher://wiscinfo.wisc.edu:2070/I9/.image/.bot/.130/Leaf/Corn_epidermal_pe el. Note the two sets of guard cells. http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookPS.html Pea Leaf Stoma, Vicea sp. (SEM x3,520). This image is copyright Dennis Kunkel at www.DennisKunkel.com, used with permission. http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookPS.html Take a leaf and put clear nail polish on the leave. Let dry and put a second coat of clear nail polish on leaf. When dry carefully peel the nail polish off of the leaf. Place the nail polish on a microscope slide and look at it under the microscope. Count the number of stomata that you can identify in the view of the microscope with out moving it. Do you find more stomata on the top or the underside of the leaf? Raw Materials Carbon dioxide + Water Needed but not used up Sunlight and Chlorophyll End Products Glucose + Oxygen http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookPS.html Needed for respiration O2 CO2 http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/BioBookPS.html 6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2 Carbon Dioxide + Water + Light Energy produces or yields ( in chlorophyll ) Glucose + Oxygen Guided Reading and study Workbook pages 44-46. What are the substances needed (raw materials) for photosynthesis? What are the substances (products) produced during photosynthesis? Isolate chlorophyll