Lesson 3, 4, 5 - Relative rate and effect of
advertisement
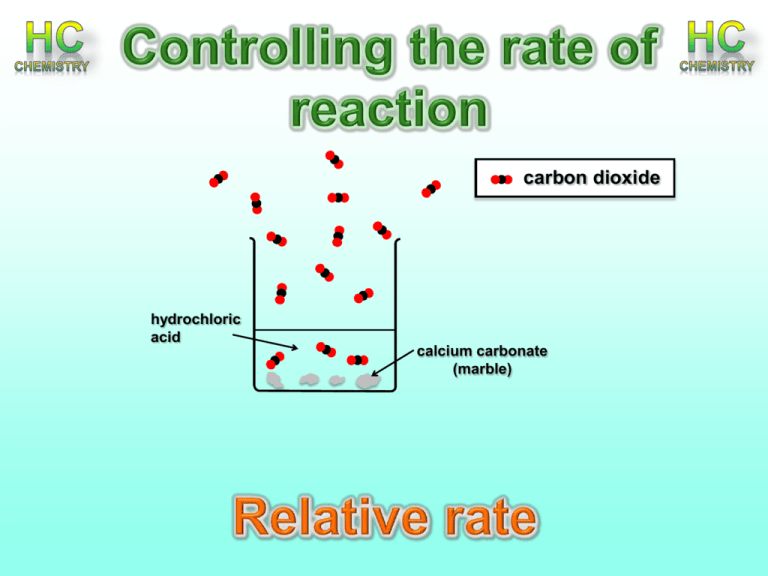
carbon dioxide hydrochloric acid calcium carbonate (marble) Relative rate After completing this topic you should be able to : • Relative rate for a reaction is the reciprocal of the time taken for the reaction. • Calculating relative rate from raw experimental data • Units for relative rate are s-1 Effect of concentration • The higher the concentration, the more particles in a given space, the more chance there is of successful collisions. Relative Rate Definition: Relative rate for a reaction is the reciprocal of the time taken for the reaction. Units for relative rate are s-1 Mathematics Effect of concentration on Magnesium and hydrochloric acid Aim: To investigate the effect of varying the concentration of hydrochloric acid concentration on the rate of reaction between hydrochloric acid and magnesium Mg(s) + 2HCL (aq) MgCl2 + H2 Method: Devising a standard set of conditions You might like to begin with the reaction between magnesium ribbon and hydrochloric acid. The relative rate of this reaction can be measured in terms of the time taken for a piece of ribbon to react completely. You will have to find out how reliable this method is. Is the length of ribbon critical for accurate measurements? Do you have to clean it first? If the acid is in a conical flask will you stir it/ shake it, gently /vigorously, intermittently or just leave it alone? Does the volume of acid affect your results? What happens to the temperature of the acid during the reaction? How reproducible are your results using the same conditions? Are you able to devise a set of conditions that will allow you to make meaningful comparisons when you change other variables? Results: Concentration of HCl (mol l-1) Time (s) Relative rate (1/t) s-1 1 2 3 4 Graph: Plot a graph of concentration of HCl (x-axis) and relative rate (s-1) (y-axis) Conclusion: Describe the effect of HCl concentration on its rate with magnesium ribbon Iodine clock reaction – introduction to chemical kinetics Effect of concentration –the chemical clock challenge 2I- (aq) + H2O2 (aq) I2 (aq) + 2S2O32- + 2H+ (aa) (aq) 2H2O (l) + I2 2I- (aq) + S4O62- (aq) (ag) The reaction mixture stays colourless as the iodine molecules are converted back to iodide molecules by the thiosulphate ions. Once all the thiosulphate ions have been used, a blue black colour appears suddenly as iodine reacts with starch. Relative Rate = 1 t Units s-1 t being a measure of how long it takes for the blue/black colour to form. (when excess I2 forms) Effect of concentration –the chemical clock challenge 1) Using syringes measure out 10cm3 sulphuric acid 0.1moll-1 10cm3 sodium thiosulphate 0.005moll-1 1cm3 starch solution 25cm3 potassium iodide solution 0.1mol l-1 Into a dry 100cm3 beaker 2) Measure out 5cm3 of hydrogen peroxide 0.1moll-1 into a syringe. Add it to the mixture as quickly as possible and start the timer. 3) Stop the clock when the mixture suddenly turns dark blue. 4) Repeat, using 20 cm3 of potassium iodide solution and 5cm3 of water with, then using repeated dilutions Effect of concentration –the chemical clock challenge Volume of water (cm3) Volume of 0.1 mol l-1 KI (aq) (cm3) O.0 25.0 5.0 20.00 10.0 15.0 15.0 10.0 20.0 5.0 Time (s) Rate (1/t) Effect of concentration –the chemical clock challenge RESULTS - Plot a graph showing the volume of potassium iodide x axis and the rate of reaction on the y axis. Effect of concentration –the chemical clock challenge Your challenge is to create a series of solutions that will change colour in time to music. Be creative and if you can’t think of anything you can take up one of these three challenges. Element Challenge Roxanne challenge That moment when your jam comes on Effect of concentration –the chemical clock challenge Listen to the song and identify points where you want to have a colour change come in Time them accurately. Allocate times to each member of your group. Look at your results and check that these are times you can achieve Calculate the rate that each time requires (rate = 1/t) Read off the required concentration from your graph Effect of concentration –the chemical clock challenge You will carry out the reaction using a series of dilutions of the iodide solution. This will be diluted by replacing some of the volume with water. Effect of concentration –the chemical clock challenge Use the relative concentration to help you work out the volume of water and KI(aq) needed to make up 100 cm3 of the required concentration. Good luck!