Literary Terms
advertisement

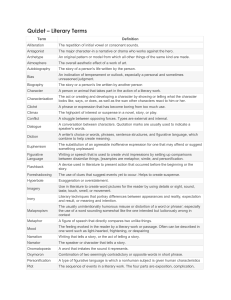
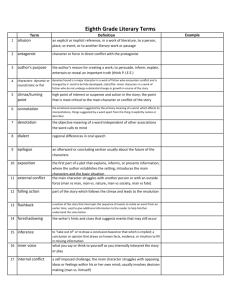
Literary Terms Allusion An allusion is a figure of speech that makes a reference to something else, either directly or by implication. Character A character is a person or an animal that takes part in the action of a literary work. Antagonist/Protagonist •The antagonist is the character or force in conflict with a main character, or protagonist. Diction • Diction is the manner in which • we express words; the wording used. = enunciation Imagery Imagery is words or phrases that appeal to one or more of the five senses. MOOD Mood, or atmosphere, is the feeling created in the reader by a literary work or passage. Writer’s use many devices to create mood, including images, dialogue, setting, and plot. Plot Plot is the sequence of events. The plot usually begins with an exposition that introduces the setting, the characters, and the basic situation. This is introduced and developed. The conflict then increases until it reaches a high point of interest or suspense, the climax. The climax is followed by the falling action, or end, of the central conflict. Any events that occur during the falling action make up the resolution. PLOTLINE Climax Resolution Exposition Conflict Introduced Conflict Conflict is the struggle between opposing forces in a story or play. There are two types: External Conflict External conflict exists when a character struggles against some outside force, such as another character, nature, society, or fate. Man vs. Man Man vs. Nature Internal Conflict Internal conflict exists within the mind of a character who is torn between different courses of action. Man vs. Himself Flashback A flashback is a literary device in which an earlier episode, conversation, or event is inserted into the sequence of events. Foreshadowing Foreshadowing is the author’s use of clues to hint at what might happen later in the story. Writers use foreshadowing to build their readers’ expectations and to create suspense. This is used to help readers prepare for what is to come. Suspense Suspense is the growing interest and excitement readers experience while awaiting a climax or resolution in a work of literature. It is a feeling of anxious uncertainty about the outcome of events. Writers create suspense by raising questions in the minds of their readers. Point of View Point of View is the perspective from which a story is told. First-person is told by a character who uses the first-person pronoun “I”. Third-person limited point of view is the point of view where the narrator uses third-person pronouns such as “he” and “she” to refer to the characters. Setting The setting of a literary work is the time and place of the action. Details such as dialect, clothing, customs, and modes of transportation are often used to establish setting. Style Style is the distinctive way in which an author uses language. Word choice, phrasing, sentence length, tone, dialogue, purpose, and attitude toward the audience and subject can all contribute to an author’s writing style. Theme The theme of a literary work is its central message, concern, or purpose. A theme can usually be expressed as a generalization, or general statement, about people or life. The theme can be given directly or indirectly. Tone Tone is a reflection of a writer’s or speaker’s attitude toward a subject of a poem, story, or other literary work. Tone may be communicated through words and details that express particular emotions and that evoke an emotional response from the reader. Figures of Speech A figure of speech is a specific device or kind of figurative language, such as hyperbole, metaphor, personification, simile, or understatement. Figurative language is used for descriptive effect, often to imply ideas indirectly. It is not meant to be taken literally. Metaphor A Metaphor is a type of speech that compares two unlike things without using a connective word such as like, as, than, or resembles. Example: Life is a bowl of cherries. Simile A Simile is another figure of speech that compares seemingly unlike things using the words like or as. Example: Her voice was like nails on a chalkboard. Oxymoron An Oxymoron is a figure of speech that is a combination of seemingly contradictory words. Examples: Same difference Pretty ugly Roaring silence Personification Personification is a figure of speech in which an animal, object, force of nature, or idea is given human qualities or characteristics. Example: Tears began to fall from the dark clouds. Alliteration Alliteration is the repetition of sounds, most often consonant sounds, at the beginning of words. Alliteration gives emphasis to words. Example: Peter Piper picked a peck of pickled peppers Irony • Contrast between expectation and reality. Types of Irony • Verbal irony- when a writer or speaker says one thing but really means something completely different. • Situational irony- when there is a contrast between what would seem appropriate and what really happens. • Dramatic irony- when the audience or reader knows something that the character does not know. Hyperbole • Figure of speech that uses exaggeration to express strong emotion or to create a comic effect. Symbolism • Person, place, thing or event that stands for itself and something beyond itself as well. Euphemism • The substitution of a mild, indirect, or vague expression for one thought to be offensive, harsh, or blunt. Analogy • Comparison mad between two things to show how they are alike in some respects.