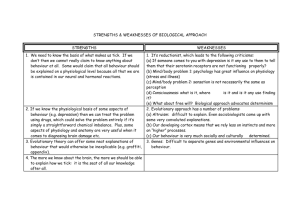
In Section C of the exam you are required to have detailed
advertisement

The Approaches in Psychology In Section C of the exam you are required to have detailed knowledge about the approaches. Milgram Social Approach Pilliavin Assumptions Reicher All behaviour occurs in a social context, even when nobody else is physically present. A major influence on people’s behaviour, thought processes and emotions are other people and the society that they have created An individual’s behaviour is effected by situational factors. Strengths of the Social Approach Social influences have been shown to have a often stronger effect than dispositional factors The approach can provide explanation for a great many phenomenon The approach is useful in explaining prejudice and discrimination The approach often adopts scientific methods to conduct research. Weaknesses of the Approach Underestimates what people bring to a social situation Provides only superficial ‘snapshots’ of behaviour and ignores their development over time. Studies are often using unrepresentative samples Often conducted in laboratories, therefore lack ecological validity. The Individual Differences Approach Rosenhan Assumptions Thigpen & Cleckley Griffith Behaviour which deviates from the norm is considered abnormal. Aims to make generalisations about differences between people Focuses on the unique characteristics of the individual Strength of studying Individuals Differences The approach allows us to understand human behaviour and find causes for psychological disorders. (T&C) The approach may help us to find causes Weaknesses The studies in this field often have small samples due to the rarity of the participants and so may lack generalisability. (T&C) The studies may be susceptible to ethical The Approaches in Psychology for prejudice and discrimination and in turn help to reduce it. (Rosenhan) Loftus & problems such as exploitation of the participants. (Rosenhan) Palmer SavageRumbaugh Cognitive Psychology Baron-Cohen Assumptions Behaviour can largely be explained in terms of how the mind operates The mind works in a manner which is similar to a computer; inputting, storing and retrieving data. Strength of the Cognitive Approach The cognitive approach used rigorous scientific methods to investigate behaviour Has many useful applications Has contributed to our understanding of human phenomenon and has integrated well with other approaches. Sperry Weaknesses Can be over simplistic, ignores other complexities of human functioning compared to that of a computer. Deterministic! Unrealistic – and studies often lack ecological validity. Ignores emotion and freewill in humans. Physiological Approach Assumption Maguire Dement Behaviour and experience can be reduced to the functioning of physiological systems. All that is psychological is first physiological – that is since the mind appears to reside in the brain , all thoughts, feelings and behaviours ultimately have a physical/biological cause. All behaviour has a genetic basis Strengths of the Physiological Approach Weaknesses The Approaches in Psychology The approach is very scientific and is grounded in hard science It provides substantial evidence for then nature in the nature/nurture debate Helps us to understand behaviour which would not be possible to test any other way. E.g. dreaming. Bandura Samuel Reductionist – the approach explains all behaviour as a reaction between chemical and neurons. The approach ignores the interaction of other elements. Can not explain how the mind and body interact. Over simplistic –ignores the influence of the environment and simplifies complex human behaviour. The Developmental Approach Assumptions All behaviour is adulthood is effected by experiences in childhood. Development changes are a results of inherited factors (nature), which include events that occur as a result of maturation, such as puberty. Lifetime experiences (nurture), which include interactions with other people. Strengths of the developmental approach Allow us to understand the effects of childhood, The area contributes to our understanding of the nature and nurture debate. The approach allows us toe measure behaviour over time Freud Weaknesses Due to the nature of the investigation the studies can often be based on qualitative data, which is susceptible to bias. May focus greatly on childhood and in turn be deterministic The studies may take a long time to conduct and require greater resources. May lack generalisability due to samples used and may ignore historical and cultural influences. The Psychodynamic Approach Assumptions Human development is a dynamic process (i.e. it is driven or motivated by certain forces) Early experience is very important for it shapes personality, relationships. The Approaches in Psychology Different areas of the mind (ID,EGO,SUPEREGO) are in constant conflict, and understanding these will allow us to understand behaviour The mind is split into 3 – the preconscious, unconscious and conscious. Dreams are the royal road to the consciousness and it is the conflicts in the unconscious that manifest into phobias and mental illness. Strengths The approach allows us to recognise that childhood is a critical period and that unconscious influences can effect behaviour Adopts the idiographic, using one participant, you gain lots of rich data. Data is qualitative – meaning a greater degree of understanding and elaboration of human behaviour Weaknesses No actual empirical evidence, no experiments Based largely on non-generalisable samples – rich upper middle class, European. Deterministic – predicts behaviour, assumes all will react and act in the same way. No way of testing whether the assumptions are true.