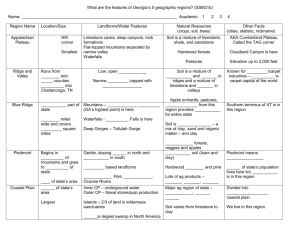
Consolidation
advertisement

Figure 1 Example: 1. 2. 3. 4. gsand = 96 pcf Soil sample was obtained from the clay layer Conduct consolidation test [9 load increments ] Plot e vs. log (p) (Figure 2) Determine Compression Index (Cc ) & Swelling Index (Cs) 0.9 Sand Void Ratio (e) 0.7 0.6 Soil Sample eo = 0.795 Cc = 0.72 Cs = 0.1 In the lab and before the consolidation test the stresses on the sample = 0. During testing, the geostatic stress is gradually recovered 0.4 0.3 100 Determine Po 16 ft wc = 0.3 In the ground, the sample was subjected to geostatic stresses. 0.5 5. Clay gclay = 110 pcf 4 ft Dp1 Dp 2 0.8 In the lab the stresses are added to the soil sample 3 ft W.T. 1 In the lab and after removing the soil sample from the ground, the stresses on the soil sample = 0 Dp1 Dp Stress Dp7 Increments Dp Dp9 G.S. Po = 3.(96) + 4.(96-62.4) + 8.(110-62.4) = 803.2 lb/ft2 Cc Cs Dp9 Po 1000 Log (p) 10000 Figure 2 Tangent to point 1 Example: 6. G.S. gsand = 96 pcf Using Casagrande’s Method to determine Pc 3 ft W.T. Sand gclay = 110 pcf Pc = 800 lb/ft2 4 ft Clay Po 16 ft wc = 0.3 Overconsolidation Ratio Pc Po 1 =1 The soil is Normally Consolidated N.C. soil 0.9 Dp1 2 6 0.8 Void Ratio (e) OCR = Point of maximum curvature X X 1 4 0.7 5 3 0.6 0.5 0.4 7 0.3 100 Po = Pc1000 Log (p) 10000 Casagrande’s Method to Determine Preconsolidation Pressure (Pc) 1 Normally Consolidated Soil Point of maximum curvature 1 0.9 2 Horizontal line Void Ratio (e) 0.8 X X 1 0.7 3 0.6 0.5 0.4 7 0.3 Po = Pc1000 100 Log (p) Overconsolidation Ratio OCR = Pc Po =1 The soil is Normally Consolidated (N.C.) soil 10000 2 Casagrande’s Method to Determine Pc Overconsolidated Soil Point of maximum curvature 2 Horizontal line X X Void Ratio (e) 1 3 7 Po Overconsolidation Ratio OCR = Pc Po The soil is oversonsolidated (O.C.) soil >1 Pc Log (p) Building qdesign Example: G.S. gsand = 96 pcf A 150’ x 100’ building will be constructed at the site. The vertical stress due to the addition of the building qdesign =1000 lb/ft2 W.T. Sand Clay 3 ft 4 ft DP1 Po Po 16 ft The weight of the building Qdesign will be transferred to the mid height of the clay layer eo = wc . Gs = 0.3 x 2.65 = 0.795 1 Qdesign = 15,000,000 lb The added stress at 15’ from the ground surface is 0.9 Dp1 Dp = 15,000,000 lb (150+15) x (100+15) DP = 790.51 lb/ft2 Void Ratio (e) 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 DP + Po = 790.51 + 803 = 1593.51 lb/ft2 0.4 0.3 100 Po1000 Log (p) 10000 Building Example: qdesign G.S. DP + Po = 790.51 + 803 = 1593.51 lb/ft2 gsand = 96 pcf Consolidation Settlement DH = DH = Cc H 1 + eO log ( W.T. Sand Po + DP ) Po 0.72 x 16 1593.51 log ( ) 1 + 0.795 803 DH = 1.9 ft Clay 3 ft 4 ft DP1 Po Po 16 ft eo = wc . Gs = 0.3 x 2.65 = 0.795 1 0.9 Dp1 Void Ratio (e) 0.8 DP1 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 100 Po1000 Po + DP Log (p) 10000 Demolished When the building was removed, the soil has become an overconsolidated clay. qdesign G.S. gsand = 96 pcf The rebound has taken place through swelling from pint 1 to point 2 W.T. Sand Clay 3 ft 4 ft Po Po 16 ft eo = wc . Gs = 0.3 x 2.65 = 0.795 1 0.9 Dp1 Void Ratio (e) 0.8 DP1 0.7 2 0.6 1 0.5 0.4 0.3 100 Po1000 Po + DP Log (p) 10000 Constructing a new building Scenario #1 The soil now is overconsolidated Soil: qdesign G.S. gsand = 96 pcf Sand The new building is heavier in weight CS H 1 + eO DH = W.T. Clay 3 ft 4 ft DP2 Po Po 16 ft P C CH P + DP log ( C ) + log ( o ) Po PC 1 + eO eo = wc . Gs = 0.3 x 2.65 = 0.795 1 eo = 0.61 0.9 DH = 0.1 x 16 1 + 0.61 log ( 1593.51 803 + 0.72 x 16 log ( 2100 1 + 0.61 1593.51 ) DP2 0.8 Void Ratio (e) Assume Po + Dp2 = 2100 psf Dp1 DP1 0.7 0.6 CS 0.5 CC ) 0.4 = 0.3 100 Po1000 Pc Log (p) Po + DP New Building 10000 Constructing a new building Scenario # 2 The soil now is overconsolidated Soil: qdesign G.S. gsand = 96 pcf W.T. Sand Clay The new building is lighter in weight 3 ft 4 ft DP2 Po Po 16 ft eo = wc . Gs = 0.3 x 2.65 = 0.795 CS H P + DP log ( o ) P0 1 + eO DH = 1 0.9 eo = 0.61 = log ( 1600 1593.51 ) Void Ratio (e) 0.1 x 16 1 + 0.61 DP2 0.8 Assume Po + Dp2 = 1600 psf DH = Dp1 DP1 0.7 0.6 CS 0.5 0.4 0.3 100 Po1000Po + DP Log (p) 10000 New Building Example of Semi-log Scale 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.1 1 10 100 1000