Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System

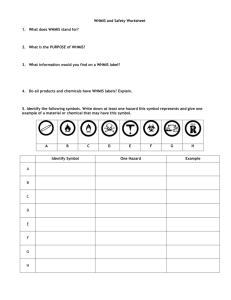
WHMIS
Purpose of WHMIS
• Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System
• Provides Information on Hazardous Materials used in
Workplace
• Facilitates the Process of Hazard Identification
• Ensures Consistency of Information in all Canadian
Workplaces
Federal Legislation:
Bill C 70
Hazardous
Products Act
Hazardous
Materials Information
Review Act
Regulations
Canada
Labour Code
Regulations Controlled
Products
Legislation
Ingredient
Disclosure
List
Ontario Legislation:
Hazardous
Physical
Agents Regulation
Bill 79
WHMIS
Regulation
Inventory
Regulation
Responsibilities Under WHMIS
• Duties of the Supplier
– Classify Product
– Apply Supplier Label
– Provide Material Safety Data Sheet
Responsibilities Under WHMIS
• Duties of the Employer
– Conduct Workplace Inventory
– Ensure Proper Labeling is Used
– Label Piping Systems/Vessels/Reactors
– Maintain and Make Available MSDS’s
– Train Workers
Responsibilities Under WHMIS
• Duties of a Worker
– Participate in Training
– Apply Knowledge and Training
Exclusions Under WHMIS
• The Explosives Act
• The Food and Drug Act
• The Pest Control Product’s Act
• The Atomic Energy Control Act
• Hazardous Wastes
• Consumer Products/Tobacco/Manufactured Articles
“Right to Know”
• Worker’s have Access to Information through their Employer
• Public has Access to Information through
Local Medical Officer of Health
Trade Secret Protection
• Hazardous Materials Information Review
Commission
• Tripartite
Trade Secret Protection
• Criteria
– Information Known Outside Business
– Information Known Inside Business
– Measures Taken to Guard Secrecy
– Value of Information to Firm or Competition
– Financial Expenditures
Information Delivery
• Labels
– Supplier Label
– Workplace Label
• Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)
• Worker Education
WHMIS Hazard Classifications
Class A
• Compressed Gas
– Any Hazardous Material that is contained under pressure including compressed gas, dissolved gas, or liquefied gas
Compressed Gas Cylinders
• store and transport with safety cap
• comply with storage restrictions
• DO NOT store fuel gas with oxygen
• secure in an upright position
• use in a well ventilated area
• use the proper type of regulator and know its history
Class B
• Flammable and Combustible Material
– Flammable Gases
– Flammable and Combustible Liquids
– Flammable Solids
– Flammable Aerosols
– Reactive Flammable Material
Flammable Materials
• Methanol, Toluene, Butane, Ethanol
• Store liquids in Flammable Storage Cabinet
• Store minimum quantities in lab
• Explosion-proof fixtures required
• Decant in large quantities in fume hood
• NEVER store with oxidizers
• Keep away from heat, ignition sources, and direct sunlight
• Use static lines when transferring
• Refrigerator must meet NFPA Standard 56C ( Flammable Material
Storage Units)
Class C
• Oxidizing Material
– Any Hazardous Material which causes or contributes to the combustion of another material by giving oxygen or some other oxidizing substance, whether or not it is combustible.
– Organic Peroxides
Oxidizers
• Chlorates, Nitric Acid, Peroxides, Permanganates,
Perchlorates, Nitrites, Nitrates
• Easily oxidize metal powders, organic materials
• Keep minimum quantities in lab
• Segregate from other materials, such as organic solvents
• Use a glass-heating mantle or sand bath to heat material
• PPE and/or Explosion barriers may be require
Perchloric Acid
• Perchlorate salts are explosive
• Use a perchloric acid fume hood
• Wash down fume hood after use
• Never store with organic chemicals especially alcohols and glycerol
• Store in a ceramic tray
Organic Peroxides
• Some are very unstable
• Sensitive to heat, friction, impact, sparks, light
• Use minimum quantities in lab
• NEVER replace unused peroxides into original container
• NEVER use a metal spatula to handle peroxides
• Refrigerate to minimize decomposition
Peroxide Formers
• Have caused several severe laboratory explosions
• Contributing Factors: Oxygen, Light,
Storage Time
• Visual Identifiers: Crystals, Floating wisplike structures
• Date and Dispose of within 1 year
Common Chemicals forming
Peroxides
• Diethyl ether
• Tetrahydrofuran
• Dioxane
• Methyl isobutyl ketone
Class D1
• Poisonous & Infectious Materials
– Material causing immediate and serious toxic effects
– Materials which are potentially fatal or may cause permanent damage if inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed through the skin, or may burn the skin or eyes upon contact
Class D2
• Poisonous & Infectious Materials
– Material causing other chronic or long term effects
– Material which may cause dealth or permanent damage as a result of repeated exposure over an extended period of time; may be an irritant to the skin, eyes, or respiratory system; may cause cancer, birth defects, or sterility.
Class D3
• Poisonous & Infectious Materials
– Biohazardous and Infectious Materials
– Materials which may cause disease in humans and animals, such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi; may also include cultures and diagnostic specimens such as blood, urine, and body tissue.
Class E
• Corrosive Material
– Material which may corrode aluminum and steel or human flesh
– Material which are anhydrous corrosive gases
Inorganic Acids
• Sulfuric Acid, Nitric Acid, Perchloric Acid,
Hydrochloric Acid
• Segregate from bases and organic compounds
• Store in a ventilated acid cabinet
• Know the location of eye washes and safety showers
• Use a safety carriers
• Store on lower shelves
Bases
• Sodium hydroxide, Ammonium hydroxide
• Segregate from acids and organic compounds
• Store in a ventilated cabinet
• Know the location of eye washes and safety showers
• Use a safety carrier
• Store on lower shelves
Hydrogen fluoride
• Is extremely corrosive
• Dissolves glass
• Absence of immediate pain, penetration can be extensive, leading to serious injury or death
• Causes severe eye irritation and skin burns
Class F
• Dangerously Reactive Material
– Materials which undergo vigorous polymerization, decomposition, or condensation
– Materials which become self-reactive under conditions of shock, or increased temperature or pressure
– Materials which react vigorously with water to produce a very toxic gas
Ethylene Oxide
• Used as a Sterilant at hospital
• Extremely flammable
• Supplies its own oxygen/Chemically decomposes
• Highly Reactive
• Very Corrosive
• Human Carcinogen
Water Reactive Materials
•Sodium metal, acid and metal anhydrides, calcium, phosphorous pentachloride, aluminum chlorideanhydrous
•Special storage requirements
Pyrophoric Materials
•Air reactive
•White phosphorus, diborane, diethyl aluminum chloride, lithium
•Store under an inert atmosphere such as nitrogen
Cryogenic Materials
•Liquid Nitrogen
•Never use to cool substances which are combustible in air - explosion risk from condensation of oxygen from air
•Use insulated gloves and face shield
•Keep cryogenic substances in containers which are not tightly closed to prevent explosive pressure buildup
•Use only equipment designed for cryogenic materials
General Dry Chemicals
•Relatively innocuous or unreactive
•No special storage requirements
Chemical Compatibility
• Never store incompatible materials together
• Vapours will react
• Chemical Compatibility Chart
WHMIS Labels
Supplier Label
• Product Identifier
• Hazard Symbols
• Border
• Bilingual
• Risk Phrases and Precautions
• First Aid, Supplier Information
• Precautions
• Safe Handling Precautions
• Reference to MSDS
Laboratory Labels
• No Supplier Label Required:
– If Controlled Product
• originates from lab supply house
• intended solely for lab use
• package quantity is less than 10 kgs
– If Package Label contains
• product identifier
• statement indicating MSDS available
• risk phrases/precautionary measures
• first aid measures
Laboratory Samples
• No Supplier Label Required:
– If the Controlled Product
• container is less than 10 kgs
• intended for lab analysis
– If supplier provides a label containing
• product and/or chemical identifier
• supplier identifier
• statement “Hazardous Laboratory Sample for hazard information or in an emergency call” plus emergency phone number
Workplace Label
• Product Identifier
• Safe Handling
Precautions
• Reference to MSDS
Workplace Label Uses
• Transfer of material from a Supplier Labelled container to another container
• Replacement of a damaged Supplier Label
NFPA Hazard Classifications
Laboratory Samples
• No Supplier or Workplace Label Required
– If controlled product is:
• produced in workplace
• originates from lab supply house
• intended solely for lab use
• product and/or chemical identifier
• “Hazardous Laboratory Sample” statement which includes an emergency phone number
MSDS Contents
• Hazardous Ingredients
• Preparation Information
• Fire & Explosion Hazard
• Toxicological Properties
• First Aid Measures
• Product Information
• Physical Data
• Reactivity Data
• Preventative Measures
Hazardous Ingredients
• Chemical Identity
• CAS Number
• LD
50
Route
Species and
• LC
50
Species and
Route
• Concentration
• PIN Number
Product Information
• Product Identifier
• Manufacturer’s/Supplier’s Name and
Address
• Emergency Telephone Number
• Product Use
Preparation Information
• Prepared by (Group, Department, etc.)
• Phone Number
• Date of Preparation
Physical Data
• Odor Threshold
• Vapor Pressure
• Coefficient of Water/Oil
Distribution
• Boiling Point ( o C) and
Freezing Point ( o C)
• Evaporation Rate
(Butyl Acetate=1)
• Physical State
• Odor & Appearance
• Specific Gravity
(Water=1)
• Vapor Density (Air=1)
• pH
• Percent Volatile (by volume)
Fire & Explosion Hazard
• Conditions of Flammability
• Means of Extinction
• Sensitivity to Mechanical Impact
• Sensitivity to Static Discharge
• Flashpoint ( o C) and Method
• Upper and Lower Flammable Limits (%)
• Auto ignition Temperature ( o C)
• Hazardous Combustion Products
Class A Fires
• Are fires fueled by materials that, when they burn, leave a residue in the form of ash
• Paper, wood, cloth, rubber, and certain plastics
• Extinguisher type: Water, Dry Chemical
Class B Fires
• Fires which involve flammable liquids and gases
• Gasoline, paint thinner, grease, propane, acetylene
• Extinguisher type: Carbon Dioxide, Dry
Chemical
Class C Fires
• Fires that involve energized electrical wiring or equipment (motors, computers, electrical panels). Note once the power has been cut, a Class CF fire becomes one of the other classes
• Extinguisher type: Carbon Dioxide, Dry
Chemical
Class D Fires
• Class D fires involve exotic metals, such as magnesium, sodium, titanium, and certain organometallic compounds such as alkyllithium and Grignard reagents
Reactivity Data
• Stability
• Incompatible Materials
• Conditions of Reactivity
• Hazardous Decomposition Products
Toxicological Properties
• Irritancy to Product
• Effects of Acute
Exposure
• Evidence of
Carcinogenicity,
Reproductive Toxicity,
Teratogenicity or
Mutagenicity
• Routes of Entry
• Exposure Limits
• Synergistic Products
• Sensitivity to Product
• Effects of Chronic
Exposure
Preventative Measures
• Personal Protective Equipment
• Engineering Controls
• Spill and Leak Procedures
• Waste Disposal
• Handling Procedures and Equipment
• Storage Requirements
• Special Shipping Information
When a Spill Strikes
• 1) Assess the risk
– Minor Spill, handled by personnel within lab or department
– Major Spill, isolate area, Declare a Code Brown, HAZMAT
Team required
– Provide HAZMAT Team with MSDS for spilled material, quantity spilled
When a Spill Strikes
• 2) Select personal protective equipment
– consult MSDS and other literature sources
• 3) Confine the spill
– Speed Counts
– Limit the spill area by blocking, diverting, or confining spill
– Use absorbents, tiger tails, drain plugs, dikes
When a Spill Strikes
• 4) Stop the Source
• 5) Evaluate the Incident & Implement
Clean-up
– Used absorbents should be considered hazardous waste
When a Spill Strikes
• 6) Decontaminate
– Decontaminate site, personnel, & equipment by removing or neutralizing the hazardous materials
• 7) Complete Incident Report
First Aid Measures
• Inhalation
• Eye Contact
• Ingestion
• Skin Contact
Additional Information
• MSDS’s Must be Readily Available
• 3 Year Expiry Date
• New Information becomes Available
MSDS Standardization
• International Organization for
Standardization (ISO)
• American National Standards Institute
(ANSI)
• International Labor Organization (ILO)
• European Union (EU)
Canadian Acceptance
Conditions
• Meets CPR Information Requirements
• Includes Statement: “ This product has been classified according to the hazard criteria of the CPR and the MSDS contains all the information required by the CPR”.
WHMIS II
• Proposed Modifications and/or Changes to
Current WHMIS laws
• Exempt categories may be required to follow labeling and MSDS requirements, such as Consumer Products, Explosives, and
Pest Control Products
• No official changes to WHMIS laws have occurred
Worker Education
• Generic
• Site Specific
• Annual Review
Occupational Hygiene
Routes of Entry
• Inhalation
• Skin Absorption
• Injection
• Ingestion
Physical Forms
• Dust
• Mist
• Fume
• Vapor
• Gas
Action of Toxins
• Acute Effects
• Chronic Effects
• Latency Period of Disease
• Sensitizers
Dose-Response Relationship
• Effect is Directly Related to Dose
• No Effect Level
Basis for Exposure Standards
• Chemical Analogy
• Animal Experimentation
• Human Epidemiological Data
Occupational Exposure
Standards
• Guidelines
• ACGIH, Occupational Health and Safety Act
• Threshold Limit Value (TLV)
• Short-term Exposure Limit (STEL)
• Ceiling
Methods of Control
• Engineering Controls
• Administrative Controls
• Personal Protective Equipment
Engineering Controls
• Elimination
• Substitution
• Local Exhaust Ventilation
• General Ventilation
• Isolation
• Preventative Maintenance
Personal Protective
Equipment
• Respirators, Gloves, Eye Protection, etc.
• The Human Factor
• Training Essential
Emergency Planning
• Moral Reasons - Good Corporate Citizen
• Legal Reasons - Legislation/Court Action
• Economic Reasons - $$$$$$$$
Objectives
• Prevent Death & Injury
• Reduce Damage to Plant and Equipment
• Get Back to Business ASAP
Emergency Planning
• Analysis
• Procedures
• Evacuation Plan
• First Aid Treatment
• Exercises and Drills
Inventory
• Annual Update and Review Required
• Feb 1st Compliance Date
Duties and Responsibilities
• Departmental Supervisor and/or Manager
– Responsible for WHMIS System within
Department
– Provide Departmental WHMIS Trainer
– Facilitate Training
– Ensure Departmental Trainer fulfils their duties
Duties and Responsibilities
• Departmental WHMIS Trainer
– Departmental Inventory
– Departmental WHMIS Training
– Training Records
– Ensure proper labeling is used
– Maintain Departmental WHMIS Manual
Duties and Responsibilities
• Campus Safety Officer
– Riverside/Civic Campuses:
• Murray Hyatt, 798-5555 x3336
– General Campus:
• Paul A. Cyr, 737-8415
– WHMIS Train-the-Trainer
– WHMIS Manual
Duties and Responsibilities
• WHMIS Clerk, Civic Campus
– Jeff Watkin, ext. 3955
– Material Safety Data Sheets
– Hospital WHMIS Inventory
Duties and Responsibilities
• JHSC
– Annual Review of WHMIS System