Webinar Presentation Slides
advertisement

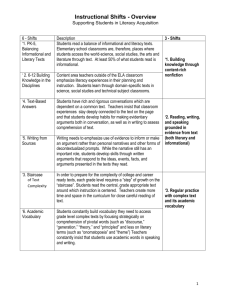
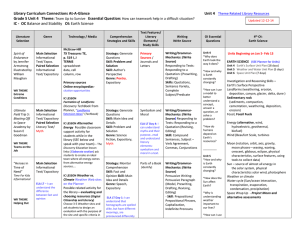
Building Literacy in Elementary Social Studies Focusing on the The Shifts Introductions Summary This module focuses on the development, purpose, and structure of shifts in ELA and Social Studies and how they relate to the Core. As a result of this session, participants will be able to: ●Identify the key shifts in ELA related to Social Studies. ●Identify shift connections between the curricular areas. ●Reflect on critical components of ELA Shifts and where/how they fit into Social Studies. ELA Shifts Continuum Arrow I am very familiar with the ELA Core Literacy shifts. 5 I am not very familiar with the ELA Core Literacy shifts. 4 2 3 1 Connections to C3 Shifts: C3 Dimensions: *Balancing Literature & Expository *Buildinging Knowledge in the Disciplines *Staircase of Complexity *Academic Vocabulary *Text-Based Answers Writing From Sources D1: Developing Questions Texts & Planning Inquiries D2: Applying Disciplinary Concepts and Tools D3: Evaluating Sources and Using Evidence D4: Communicating Conclusions and Taking Informed Action Multiple Choice What percentage of text should you be using in your classroom for literary and non fiction? A 30% informational & 70% literary B 50% informational & 50% literary C 70% informational & 30% literary D 40% informational & 60% literary Shift 1: Balancing Literature & Expository Distribution of Literacy and Informational Passages by Grade Level Bands on the 2009 NAEP Reading Framework Grade Literacy Informational K-5 50% 50% 6-8 45% 55% 9-12 30% 70% Common Core Standards for English Language Arts and Literacy in History/Social Studies, Science, and Technical Subjects. Retrieved from http://www.corestandards.org/assets/CCSSI_ELA%20Standards.pdf Informational text IS ● ● ● ● biographies and autobiographies books about history, social studies, and the arts technical texts: -including directions -forms -information in graphs, charts, or maps, and digital sources on a range of topics images and artifacts IS NOT ● a synonym for non-fiction Shift 2: Building Knowledge in the Disciplines Primary sources Secondary Sources Primary sources provide first-hand testimony or direct evidence concerning a topic under investigation. They are created by witnesses who experienced the events or conditions being documented. Materials that interpret, assign value to, conjecture upon, and draw conclusions about the events reported in primary sources. Connect Primary vs. Secondary Sources Sort Image Analysis United States Date: 1830 Artist unknown Library of Congress photo collection Graphic Organizers: ● Comparing Images SOCC Analysis Guide Jackson, Mississippi Date: 1937 Photographer: Dorothea Lange Library of Congress photo collection What does that look like in the classroom? Image Analysis while Sourcing, Observing, Contextualizing, and Corroborating Shift 3: Staircase of Complexity What does text complexity mean? What does that look like in the elementary setting? What is text complexity? Explore What impact will this have on your teaching and your students’ learning? Annotating Texts Interacting with the text: ? = question or unsure of meaning * = important [ ] = quotable # = info or statistic ___ = new vocabulary Tech tools for annotating Diigo (www.diigo.com) Google docs Question Stems for Text Dependent Questions Did you use evidence from the text to support your answers? Where is your proof? What passage number supports your thinking? Did you quote the text? What specific word or phrase can you use form the text to support your opinion? Where did the author give you a clue for your inference? How do you know that what part of the text helped you? What text features helped you understand the text? What do you think the word ------- means? Shift 5:Academic Vocabulary Why is vocabulary important? How does knowing the true meaning of a word affect you as a learner? Number of Terms Per Grade Level in Social Studies Subject Level 1 (K-2) Level 2 (3-5) Level 3 (6-8) Level 4 (9-12) Total % of Total History 162 959 743 715 2579 32.6% Geography 89 212 258 300 859 10.8% Civics 45 145 210 213 613 7.7% Economics 29 68 89 155 341 4.3% What does that Look Like in the Classroom? 3 Rs: Revolution, Reaction, and Reform Shift 6: Writing From Sources Is this an expository, opinion or persuasive piece of writing? A B C expository opinion persuasive Expository, Opinion, or Persuasive? Planner for writing piece Balance of Student Writing Expository/Informational Writing Opinion/Persuasive Writing Implications for Social Studies EXAMPLES: NY Toolkit: Open sourced RESOURCES: Article: Literacy As the Link Article: Using Primary Sources At the Heart of State Core Standards Site: Docs Teach Site: Teaching Like A Historian Site: C3 Teachers (NY Toolkit Resources) Site:Teaching History STRATEGIES/Short Video Clips: Third Grade Photo Analysis Using Source, Observe, Contextualize, Corroborate Analyzing Segregation Images Close Reading Strategy with Non-Fiction Text (Whole Class) Close Reading While Determining the Main Idea (Partners) Determining Where an Image Should Placed on the Classroom Timeline Connections What connections do you see with the ELA and Social Studies in moving your practice forward? ELA SOCIAL STUDIES Questions?