Reading Assessment: A Natural Fit for SLPs
advertisement

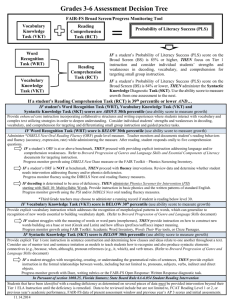
Reading Assessment: A Natural Fit for SLPs Pat Howard, Ph.D. Director of Assessment Programs phoward@fcrr.org www.fcrr.org/assessment Purposes of Assessment To Make Decisions About Students – Eligibility for Services Special Education ESOL – Instructional Planning and Support Needs Screening for Early Identification of Needs Diagnostics to Identify Strengths and Weaknesses Development of Academic Improvement Plans/Individual Educational Plans – Determine Effectiveness of Services Progress Monitoring to Produce Growth Charts Outcome Measures to Provide End-of-Year Evaluation To Make Decisions About the System – Program Evaluation – Determine Needs, Continuation and/or Revisions for Future Implementation What Questions Do You Have That Can Be Answered With Data From Reading Assessments? Are we meeting our Standards and Benchmarks for all students? Are we able to identify students at risk of reading failure Do we have a method for determining the effectiveness of our Dr. Marilyn Jackson-Rahming reading programs? Principal, Pineview El. 5 Key Areas of Knowledge and Skill in Reading Phonemic Awareness Phonics Fluency Vocabulary Comprehension Strategies Identifying words accurately and fluently Constructing meaning once words are identified The 4 Critical Assessments Screening: “First Alert” Progress Monitoring: “Growth Charts” Diagnostics: “In-depth View” Outcome Measures: “Reaching Our Goals” Screening and Progress Monitoring Grade Kindergarten First Second Third – Fifth Reading Component Assessed Reading Skill Measure DIBELS and FORF Phonemic Awareness Initial Sound, Phoneme Segmentation Phonics Letter Naming, Nonsense Words Phonemic Awareness Phoneme Segmentation Phonics Letter Naming, Nonsense Words Reading Fluency Oral Reading Phonics Nonsense Words Reading Fluency Oral Reading Reading Fluency Oral Reading Sixth - Eighth Reading Fluency Comprehension Florida Oral Reading Mazes Overview of DIBELS Measures Letter Naming Fluency Intended for students in kindergarten through the fall of first grade Provides a measure of a student’s proficiency in naming upper and lower case letters Primarily an indicator of risk Students identified at risk should be instructed in phonological awareness and alphabetic principle Probe 1 c c N u Q M u h S i n b e N F f o a K k g p k p a H C e G D b w F i h O x j I K x t Y q L d f T g v T V Q o w P J t B X Z v U P R l V C l W R J m O z D G y Z y A m X z H S M E q n j s W r d s B r A E L c N u Q M c U Y I Total: ____/110 Overview of DIBELS Measures Initial Sounds Fluency This measure assesses a student’s ability to recognize and produce the beginning sound(s) in an orally presented word Administered through the late winter of kindergarten Students performing below expectations in this measure will benefit from instruction in phonological awareness Overview of DIBELS Measures Phoneme Segmentation Fluency Measures ability to segment three- and fourphoneme words into their individual phonemes The student must produce verbally the individual sounds in words presented by the examiner It is administered in kindergarten and first grades It is a good predictor of later reading achievement and strengthened by phonological awareness activities Overview of DIBELS Measures Nonsense Word Fluency It taps the student’s knowledge of letter-sound correspondence and ability to blend letters into words (test of the alphabetic principle) This measure is provided in kindergarten, first and second grades Students performing below expectations will benefit from activities focusing on decoding kik kaj lan yuf bub wuv nif suv yaj tig woj fek nul pos dij nij vec yig zof mak sig av zem vok sij pik al dit um sog faj zin og viv vus nok boj tum vim wot yis zez nom feg tos mot nen joj vel sav Overview of DIBELS Measures and FORF Oral Reading Fluency measure of fluency in oral reading of connected text. Students in grades one, two and three will be administered three passages from grade-level text Students who are weak in reading fluency will often experience difficulty in comprehending what they read There was a robin’s nest outside our kitchen window. The nest was in a tall bush. The mother robin sat in the nest all day long. One day when I was watching, the mother bird flew away. I saw the eggs she was sitting on. There were four blue eggs. I watched and watched. The eggs moved. I watched some more. The eggs started to crack. Finally, the eggs hatched. I saw four baby birds. The baby birds opened their beaks wide. I heard them peeping. Soon the mother bird came back. Then the mother robin put worms in their mouths. Every day I watched the baby birds and their mother. Pretty soon the babies were so fat there was no room for the mother. Then one morning the nest was gone from the bush. Overview of Mazes Reading Comprehension Measure of fluency in selecting appropriate word to complete text For students in grades 6-8 Score also influenced by reading rate Group administered Predicts performance on FCAT equally as well as ORF Reading is the most critical academic skill students will learn and one of the best predictors of overall success in school and society. Therefore, reading continues to be a (cabbage / leading / thruway) topic at the national level and (at / is / my) the school level. There is no (snowshoe / question / practical) that teaching all of our students (or / me / to) read by the end of third (grade / spoon / below), as mandated under NCLB is a (following / challenge / paperclip). To accomplish this task, assessments are (belief / throws / needed) to help educators efficiently… Assessment Schedule Kindergarten Grade Interval 1 2 3 4 First 1 2 3 Third -Eighth Second 4 1 2 3 Initial Sounds Fluency Letter Naming Fluency Phoneme Segmentation Fluency Nonsense Word Fluency Oral Reading Fluency / Mazes Assessments @ 45 day intervals beginning with instructional days 20 - 29 4 1 2 -3 E 4 Screening and Progress Monitoring Data Interpretation Indicators of Effectiveness – Effectiveness of core and interventions Identification of schools that are “beating the odds” Identification of greatest needs – Individual, classroom, grade, school Growth profiles – – Individual, classroom, grade, school levels Risk Status Colors provide a quick indication of the student’s progress and the risk that a student has of not achieving the expected level of proficiency. Low Risk “Good to Go” Moderate Risk Caution High Risk DANGER! Are We Meeting Our Reading Goals to… 1. Maintain students on grade level through effective core program, and 2. Decrease students in need of additional support through strong and effective supplemental strategies and intensive interventions? Beginning Middle End The Results of Effective Core, Supplemental, and Intensive Instruction Assessment 1 2 3 4 Overall Level of Effectiveness Indicator of Effectiveness Paul Maria 100% Janet Marcel Gria 66% Joseph Carmen Tabitha Lilly Johana John 60% The Progress Monitoring and Reporting Network (PMRN) Reports Targeted to Principals – School Reports Assessment Calendar Recommended Level of Instruction School Status Report Student Instructional Level Report How to Use the Calendar • Avoid overlap of activities during testing windows • Plan for any training associated with assessment • Make sure all test materials are on hand Teacher A Teacher B Teacher C Teacher D Teacher E How to Use Recommended Level of Instruction Report • Identify instructional support needs of students by grade and teacher • Determine additional resources needed for grade levels or teachers • Prioritize coaching services How to Use the School Status Report • Determine, by grade level, by measure, student instructional needs • Make decisions about areas on which to focus professional development • Determine probability of FCAT performance by third graders Student 1 Student 2 Student 3 Student 4 Student 5 Student 6 Student 7 Student 8 Student 9 Student 10 Student 11 Student 12 Student 13 Student 14 Student 15 Student 16 Student 17 Student 18 Student 19 Student 20 Student 21 Student 22 Student 23 Student 24 Grade Status Report PMRN Examples Reports Targeted to Coaches, Teachers and SLP’s – Class Reports Class Status Report Progress Tracking Tool Class Progress Monitoring Report – Student Reports Student Progress Monitoring Report Class Status Report The Class Status Report is the first report a teacher sees. It provides a “snapshot” or quick indication of the class progress and a quick indication of each child’s success. It also has links to other reports. The Class Status Report helps answer the question of who is at risk. Recommended Instructional Level • Combination of scores from each of the individual measures Individual Measures • Target, next target, student score, risk level indicated in color and notation Progress Tracking Tool The Progress Tracking Tool allows the teacher to view the progress of all of the students at one time. From the graph, it is easily determined which students are at risk and which of them are not making significant gains. The list can be sorted in a variety of ways and can exclude students who have not been in the class for the entire year. This tool quickly identifies whether other students are exhibiting similar profiles. Class Progress Monitoring Test Report The school’s Reading Coach will assist teachers in reading and interpreting the Box and Whiskers graph. This example shows the class improved in nonsense word fluency, but is not improving at a rate to guarantee success. This report indicates whether the students are making adequate progress. Student PMT Report Compares student performance to the classroom. Using the PMRN for OPM The 4 Critical Assessments Progress Monitoring: “Growth Charts” Screening: “First Alert” Diagnostics: “In-depth View” Outcome Measures: “Reaching Our Goals” Diagnostic Tests Purpose – Provide additional, necessary diagnostic information to plan effective instruction An Integral Part of the Reading First Assessment Plan – Administered infrequently – Used to supplement information from screening, progress monitoring, and outcome Diagnostic Tests Instructional Utility – Tests used to determine a reading learning disability do not help to plan more effective instruction – ATI research – Developing fluency in all aspects of the basic skills and monitoring progress towards automaticity will alert teachers to support needs of students – Diagnostics should measure skills that can be directly taught and that affect important reading outcomes: PA, Phonics, Fluency, Vocabulary, and Comprehension Strategies – Other factors influencing reading outcomes: Motivation, parental support – not assessed with diagnostics; knowledge base, language ability, general intelligence – not a specific part of reading instruction Diagnostic Assessments of Reading: 2nd Ed. (DAR) Ages 5 – adult 9 individually administered tests of the components of reading and language No special qualifications to administer Untimed – approx. 40 min. per student Criterion referenced – mastery levels Materials: Teacher’s manual, response record, student book DAR – Information Provided Word Meaning: oral vocabulary test as an estimate of language and cognitive abilities; usually underestimates student ability if they have a reading problem Word Recognition, Word Analysis, Oral Reading, Spelling: basic word reading skills Print Awareness: basic concept in using printed word Phonological Awareness: ability to hear sounds that make up words Letters and Sounds, Word Analysis, Spelling: knowledge of letter-sound correspondences Oral Reading: basic word reading skills, fluency, word meanings, language, comprehension Silent Reading Comprehension: basic word recognition and analysis, background knowledge, language and cognitive development DAR and DIBELS Area DAR Measures DIBELS Measures Letter Identification Naming Capital Letters; Naming Lower Case Letters; Matching Letters; Matching Words Letter Naming Fluency Phonological Awareness Rhyming words; Segmenting into syllables; Initial and Final Consonant Sounds; Auditory Blending of phonemes Initial Sound Fluency Phoneme Segmentation Fluency Word Identification Word Recognition Decoding Word Analysis Consonant sounds and blends; short vowel; silent E; digraphs; diphthongs; etc. Nonsense Word Fluency Oral Reading Oral Reading – accuracy & fluency Oral Reading Fluency Reading Comprehension Silent Reading Comprehension - retell Spelling Spelling Words Vocabulary Word Meaning Fox in a Box (FIB) Grades K - 3 4 Strands: Phonemic Awareness, Phonics, Reading and Oral Expression, Listening and Writing Fall and spring administrations with same form Teacher administration Untimed – 35 minutes per child; 80 minutes per class Criterion referenced – benchmarked Materials: Teacher’s guide, puppet, word lists, books, student recording booklets FIB Strands and Subtests Phonemic Awareness – K – Rhyme Recognition, Rhyme Generation, Syllable Clapping, Initial Consonants, Final Consonants, Blending, Segmenting Phonics – K – 2 – Alphabet Recognition (Uppercase, Lowercase, Vowels), Alphabet Writing, Spelling, Decoding (Real and Non-words) Reading and Oral Expression – K – 2 – Sight Words, Reading (Concepts of Print, Emergent Reading, Accuracy, Comprehension, Oral Expression), Reading Fluency (Rate, Expression) Listening and Writing – Listening Comprehension, Writing Development, Writing Expression Technically Adequate Diagnostic Components* K-1 K-2 1-1 1-2 2-1 2-2 Phonological Awareness Yes Yes Phonics Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Word Recognition - Sight Words Reading Comprehension Yes Text Reading Fluency *As determined by reliability of .8 and above Yes Yes FIB and DIBELS Area FIB Measures DIBELS Measures Phonemic Awareness Phonemic Awareness (K) Rhyme Recognition, Rhyme Generation, Syllable Clapping, Initial Consonants, Final Consonants, Blending, Segmenting Initial Sound Fluency Phoneme Segmentation Fluency Phonics Phonics (K – 2) Alphabet Recognition, Alphabet Writing, Spelling, Decoding Letter Naming Fluency Nonsense Word Fluency Reading Fluency Reading and Oral Expression: (K – 2) Sight Words (K – 2) Text Reading Fluency (2) Oral Reading Fluency Reading Comprehension Reading and Oral Expression: (K – 2) Reading Comprehension (2) Early Reading Diagnostic Assessment: 2nd Ed. (ERDA) Grades K - 3 5 Skill Clusters: Phonological Awareness, Phonics, Fluency, Vocabulary, Comprehension Norm-referenced – Emerging or Below Basic; Basic; Proficient Teacher administration: 15 – 110 minutes Timed and untimed sections Materials: Administration manual, technical manual, stimulus book, record form, stopwatch, parent report forms ERDA Clusters and Subtests Phonological Awareness – Phonological Composite: Rhyming, Rimes, Phonemes, Syllables Phonics – Letter Recognition, Pseudoword Decoding Fluency – Word Reading, Target Words in Context, RAN – Automaticity Composite, Passage Fluency Composite: Narrative Composite, Informational Composite Vocabulary – Vocabulary Composite: Receptive and Expressive, Word Opposites, Synonyms, Word Definitions, Multiple Meanings Comprehension – Story Retell, Reading Comprehension, Listening Comprehension ERDA and DIBELS Area ERDA Measures DIBELS Measures Phonological Awareness Phonemic Awareness Composite: Rhyming, Phonemes, Rimes, Syllables Initial Sound Fluency Phoneme Segmentation Fluency Phonics Phonics Letter Recognition, Pseudo-word Decoding Letter Naming Fluency Nonsense Word Fluency Fluency Word Reading, Target Words in Context RAN – Automaticity Composite Passage Fluency Composite: Narrative Composite, Informational Composite Oral Reading Fluency Vocabulary Vocabulary Composite: Receptive and Expressive, Word Opposites, Synonyms, Word Definitions, Multiple Meanings Reading Comprehension Comprehension Story Retell, Reading Comprehension, Listening Comprehension Group Reading Assessment and Diagnostic Evaluation (GRADE) Grades PK – Adult: 11 Levels, on grade and out-of level testing 5 Components: Pre-Reading, Reading Readiness, Vocabulary, Comprehension, Oral Language Norm-referenced – Standard Scores and Percentiles available; Growth scale values Group or individual administration; two alternate forms Untimed – 45 – 90 minutes Materials: Administration manual for each level, teacher’s scoring and interpretive manuals, technical manual, answer sheets, handscoring templates Components and Subtests Pre-Reading – Picture Matching, Picture Differences, Verbal Concepts, Picture Categories Reading Readiness – Sound Matching, Rhyming, Print Awareness, Letter Recognition, Same & Different Words, PhonemeGrapheme Correspondence Vocabulary – Word Reading, Word Meaning, Vocabulary Comprehension – Sentence Comprehension, Passage Comprehension Oral Language – Listening Comprehension GRADE and DIBELS Area GRADE Measures DIBELS Measures Phonological Awareness Sound Matching Rhyming Initial Sound Fluency Phoneme Segmentation Fluency Letter Identification Letter Recognition Letter Naming Fluency Phonics Phoneme-Grapheme Correspondence Word Reading Letter Naming Fluency Nonsense Word Fluency Fluency Oral Reading Fluency Vocabulary Word Meaning Vocabulary Reading Comprehension Sentence Comprehension Passage Comprehension Oral Language Listening Comprehension The 4 Critical Assessments Progress Monitoring: “Growth Charts” Screening: “First Alert” Diagnostics: “In-depth View” Outcome Measures: “Reaching Our Goals” Outcome Measures Vocabulary and Comprehension PPVT-III, Form B – receptive vocabulary Gates MacGinitie Reading Tests – reading vocabulary Stanford -10 – reading comprehension Peabody Picture Vocabulary Test (PPVT-III) Oral receptive language test Provide word and student selects the appropriate picture from 4 options Norm-referenced Individually administered: 15 – 20 min. Outcome measure for vocabulary along with GMRT for reading vocabulary Internet Resources Risk Level Charts – DIBELS and FORF – http://www.fcrr.org/assessment/pdffiles/k3_risk_levels.pdf – http://www.fcrr.org/assessment/PDFfiles/45_RISK_LEVELS.pdf – http://www.fcrr.org/assessment/PDFfiles/Risk-Levels6-8-FORF-FCRR.pdf University of Oregon – DIBELS – http://dibels.uoregon.edu Coaches Guide - FCRR – http://www.fcrr.org/assessment/pdf/coaches/coaches guide2005.pdf