Transformations in the work of M.C. Escher
advertisement

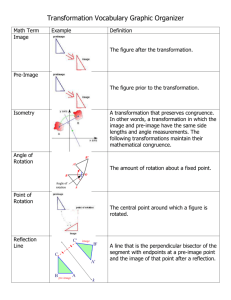
Transformations transformation •A change of position or size of a figure. 1.Translations 4 types: 2.Reflections 3.Rotations 4.Dilation translation • A transformation that moves points the same distance and in the same direction. * The figures are congruent! * The original image is slid! Example: reflections • The mirror image of the original figure * The figures are congruent! * The original image is flipped! Example: Line of Reflection The line of Reflection is also called the line of symmetry. It is also possible to have a reflection image with respect to a point. Point of Symmetry • The point must be the midpoint for all segments that pass through it and have endpoints on the figure. Example Does Rhombus MATH have point symmetry? Yes A M T H rotation • A transformation that turns a figure about a fixed point. Fixed point Example: Another Example: Dilation • Change in size of a figure –Enlarge or shrink –Similar figures (congruent angles, proportional side lengths) Original Figure isometry • Congruence Transformation –Maps every segment to a congruent segment • No change in size! –Congruent sides and congruent angles State whether each of the following have isometry. • Translation Yes • Reflection Yes • Rotation Yes • Dilation No Transformations are used to make tessellations tessellation • A repeating pattern of figures that completely covers a plane without gaps or overlaps. Transformations in the work of M.C. Escher Learn more about M.C. Escher • http://www.mcescher.com/